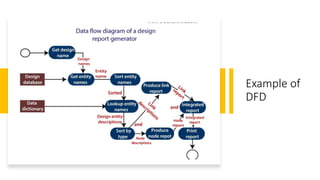
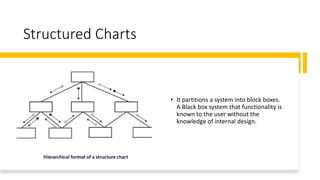
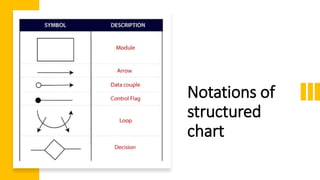
Function oriented design decomposes a software system into interacting units with clearly defined functions. It uses strategies like data flow diagrams, data dictionaries, structure charts, and pseudo code. Data flow diagrams show how data flows through a system. Data dictionaries define all data elements and structures. Structure charts partition a system into boxes and show module hierarchy and interaction. Pseudo code describes system characteristics using structured English phrases.