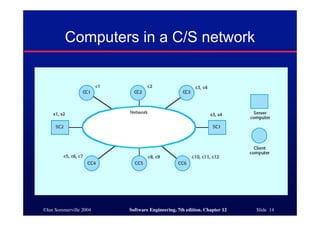
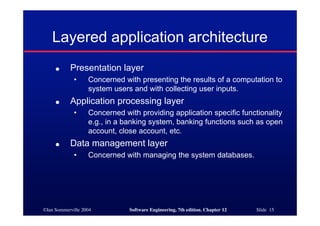
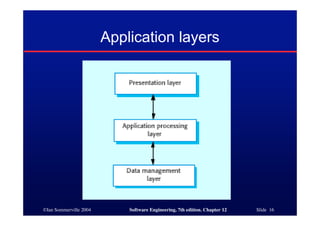
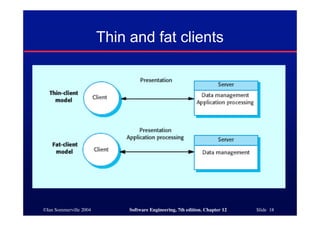
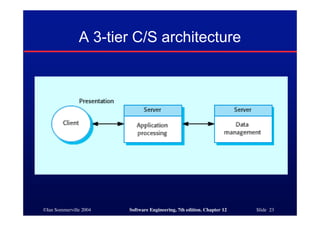
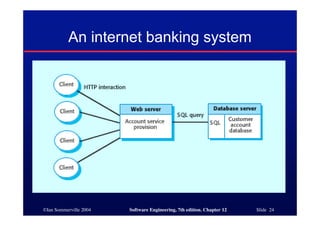
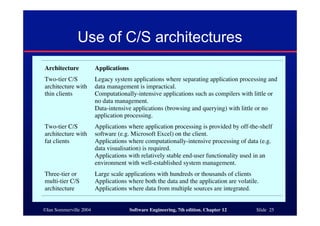
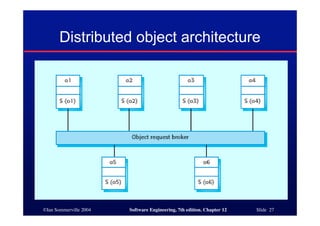
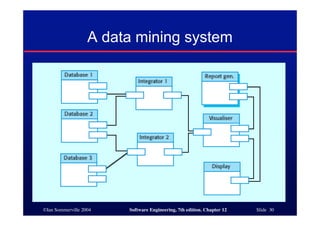
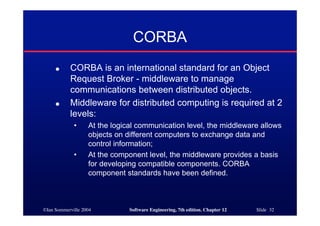
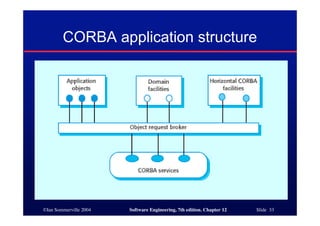
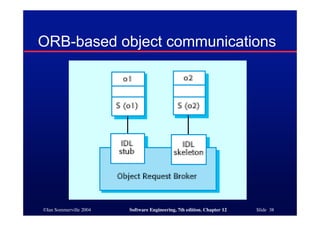
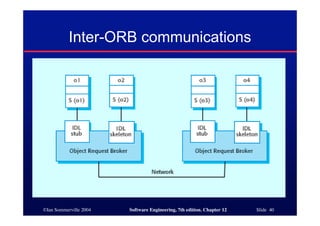
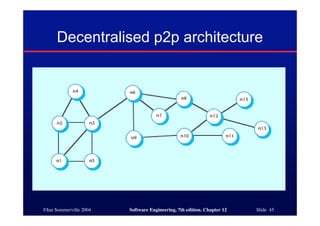
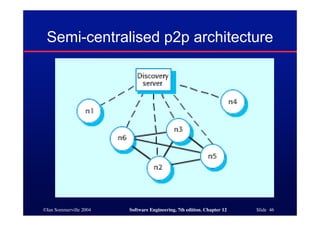
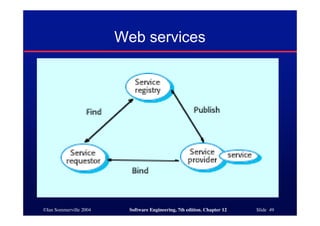
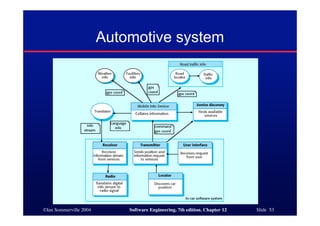
This document discusses different architectures for distributed systems, including client-server architectures, distributed object architectures, and middleware. It describes the characteristics and advantages of distributed systems as well as challenges like complexity, security, and unpredictability. Specific architectures covered include multiprocessor systems, thin and fat client models, and three-tier client-server approaches. Distributed object architectures are also introduced where any object can provide or use services.