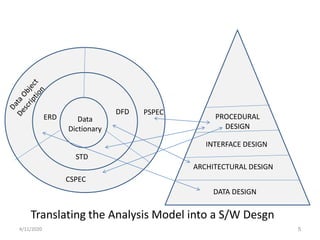
This document discusses key concepts and principles of software design. It defines design as the process of applying techniques and principles to define a system in sufficient detail to allow its implementation. The goal of design is to translate requirements specified in an SRS document into a design document. Design involves data design, architectural design, interface design, and procedural design. It serves as the foundation for software engineering and maintenance. The document outlines general design tasks, objectives, goals, constraints, and criteria for a good design, emphasizing that design fosters quality and allows accurate translation of requirements into a software product.