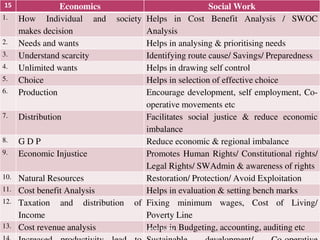
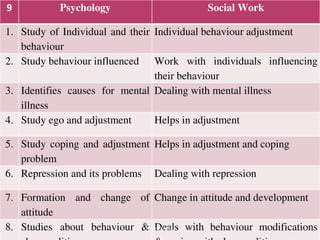
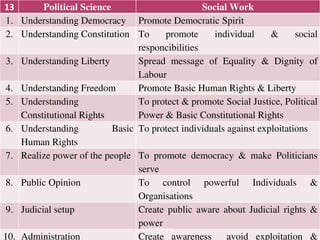
This document discusses social sciences perspectives relevant for social work. It covers how sociology, psychology, economics, history, and political science relate to social work. For each subject, it provides around 10 examples of how concepts from that field help inform social work practices. It also discusses society and community, the process of socialization, and the key agents involved in socializing individuals. Finally, it outlines factors that can contribute to the development of self.