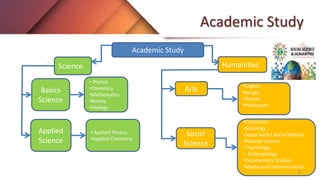
This document provides an introduction to social science. It defines social science as the branch of science devoted to studying societies and relationships between individuals within societies. Social science is described as applying scientific methods to study society in a way that is subdivided into subjects concerning specific aspects of individuals and society. Some key characteristics of social science mentioned are that it emphasizes facts, introduces new ideas, studies human relations and behavior which cannot be directly observed or controlled, and research conclusions may differ as phenomena are always changing.