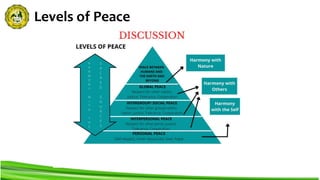
This document discusses concepts related to peace and violence. It defines peace as a relationship between parties, not a property of one alone. There are four levels of peace: personal, interpersonal, intergroup/social, and global. Violence is typified as physical, sexual, psychological, and neglect. Peace studies equips students with knowledge of conflict and peaceful alternatives, as well as skills like critical thinking and communication. Integral attitudes for peace education include respect, compassion, cooperation, justice, and social responsibility.