This document discusses social cognition and crime from a psychological perspective. It covers several key concepts:
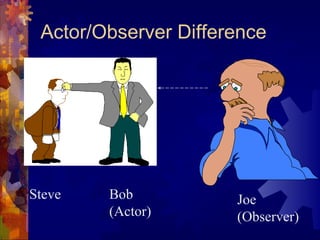
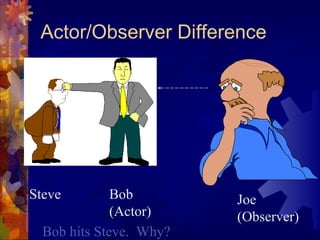
1. Attribution theory examines how people make internal or external attributions to explain behaviors. Offenders often attribute crimes externally rather than taking responsibility.
2. Locus of control refers to whether people see outcomes as based on their own actions or external forces. Studies find offenders often have an external locus of control.
3. Impulsivity is linked to a failure in self-control and can contribute to criminal acts. However, findings are mixed due to differing definitions and heterogeneity of offenders.
4. Learned helplessness and pessimistic explanatory styles may leave some feeling they cannot control outcomes, increasing criminal risk