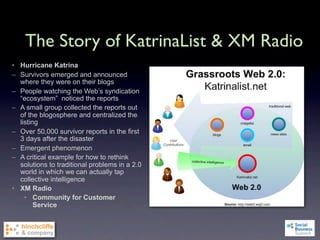
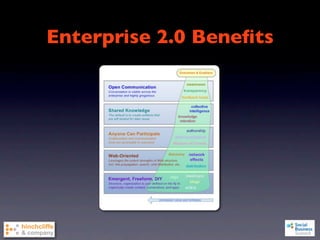
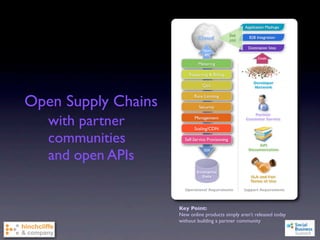
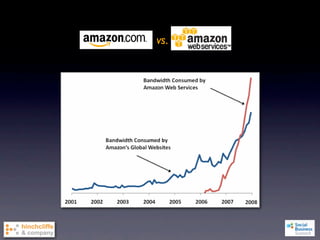
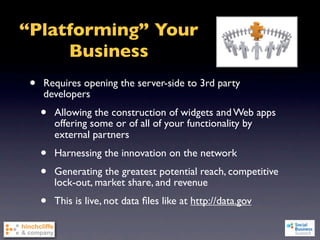
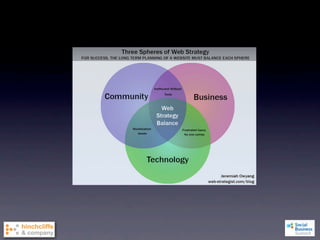
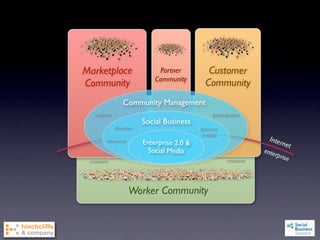
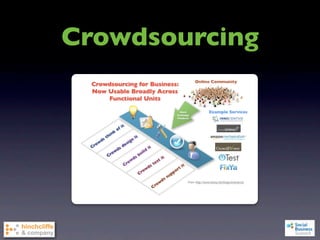
1) The document discusses emerging social business strategies in 2010 and what works and why.
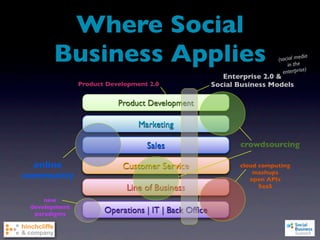
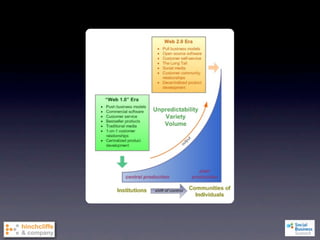
2) It examines major shifts like who creates value, how much control businesses have, and increased transparency, as well as forces like network effects and peer production.
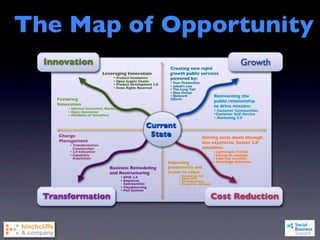
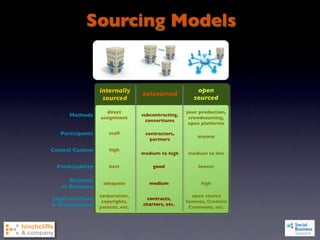
3) The document outlines challenges of social business like cultural challenges, disruption, cost and risk, and evaluates strategies in terms of challenges, repeatability, and strategic value.