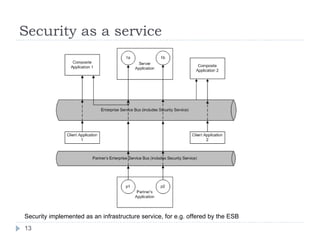
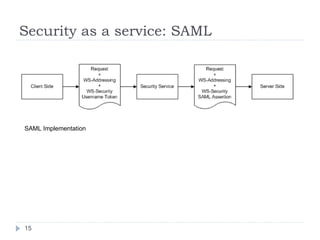
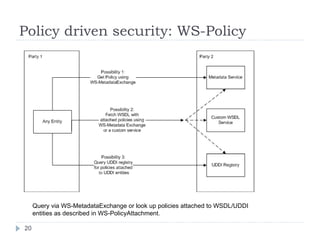
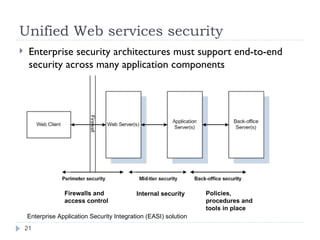
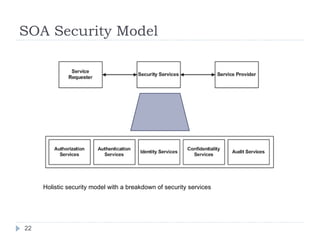
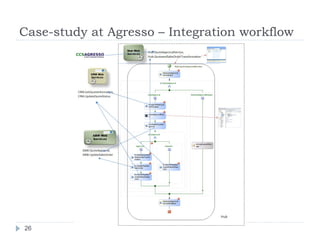
The document outlines a security model for Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) in enterprise systems, emphasizing the importance of various security requirements such as confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and authorization. It discusses approaches to ensuring security, including message-level security, security as a service, and policy-driven security, and presents a case study on the Agresso Integration Hub to illustrate these concepts. The conclusion highlights the need for a unified security framework to address the challenges of SOA security effectively.


![Introduction These three domains form together a so-called Service-based Business Environment [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soa-security-model-for-eai-1230633678246219-2/85/SOA-Security-Model-For-EAI-3-320.jpg)
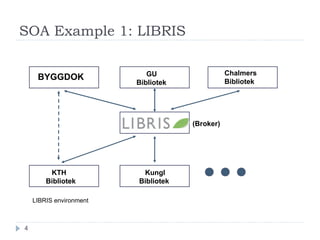
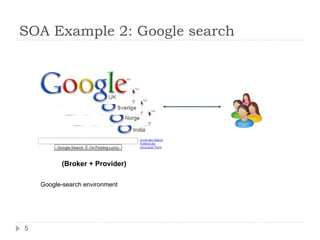
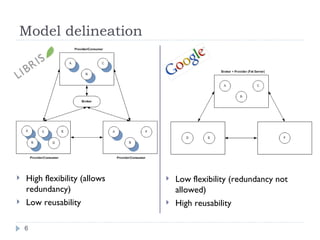
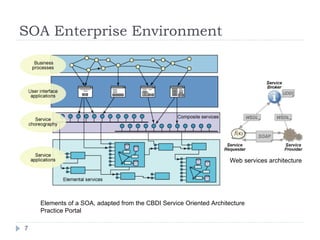


![Message level security Trust models depicting the point-to-point and end-to-end configurations [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soa-security-model-for-eai-1230633678246219-2/85/SOA-Security-Model-For-EAI-10-320.jpg)

![Message level security: WS-Security Security token service model [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soa-security-model-for-eai-1230633678246219-2/85/SOA-Security-Model-For-EAI-12-320.jpg)