The document discusses snakehead fish (Channa spp.), highlighting their evolutionary history, ecological role, cultural significance, and importance in various economies. It details management strategies for addressing their impacts as invasive species and threats like emerging infectious diseases. Recent research findings on their adaptations and nutritional value are also summarized, emphasizing the need for balanced conservation efforts.



![INTRODUCTION:
The Bulli, or snakehead fish, is both a powerful predator and culturally
important.
Its sleek body and strong appetite make it a top predator in freshwater
ecosystems worldwide.
The Bulli's adaptability helps it thrive in different environments, playing a
vital role in ecological balance.
In Pakistan, it's a culinary staple and symbol of resilience.
Snakehead fish are celebrated globally in folklore, cuisine, and rituals,
highlighting their cultural significance. [8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-4-320.jpg)

![EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY:
Snakehead fish have a long evolutionary history, dating back over 100 million
years.
They belong to the family Channidae and the order Anabantiformes.
Originating in Asia, they diversified into various species adapted to different
environments.
Some species developed the ability to breathe air, aiding their survival in low-
oxygen environments. [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-6-320.jpg)
![TAXONOMY:
Snakehead fish belong to the following taxonomy:
Kingdom: Animalia (Animals)
Phylum: Chordata (Animals with a spinal cord)
Class: Actinopterygii (Ray-finned fishes)
Order: Perciformes (Perch-like fishes)
Family: Channidae (Snakehead fishes) [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-7-320.jpg)
![DISTRIBUTION:
Snakehead fish are found in freshwater ecosystems across Asia, Africa, and parts
of North America.
Common countries of distribution include India, Bangladesh, Thailand,
Malaysia, Indonesia, and various regions of Africa.
In Pakistan, they are prevalent in freshwater habitats like the Indus, Jhelum,
Chenab, and Ravi rivers, as well as irrigation canals and ponds. [10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-8-320.jpg)
![IMPORTANCE:
Ecological Role: Snakehead fish are vital apex predators in freshwater
ecosystems, regulating prey populations and maintaining balance.
Cultural Significance: In places like Pakistan, they are culturally
important, featured in local cuisines and traditions.
Economic Value: Snakehead fish support economies through commercial
and recreational fishing, providing livelihoods and trade opportunities.
[7,8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-9-320.jpg)
![INTERESTING FACTS:
Air-breathing Ability: Snakehead fish can breathe air using a specialized organ,
helping them survive in low-oxygen waters and even venture onto land.
Remarkable Parental Care: They fiercely guard their eggs and fry, exhibiting
exceptional parental care uncommon among fish species.
Rapid Growth: Snakehead fish grow quickly, reaching maturity faster than
other fish, aiding in their colonization of new habitats. [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-10-320.jpg)
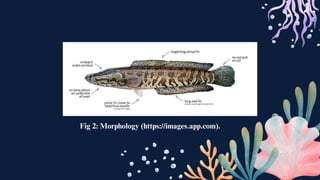
![MORPHOLOGY:
Scales: Smooth scales cover their cylindrical bodies.
Fins: Well-developed dorsal and anal fins.
Mouth: Large terminal mouth.
Body Shape: Elongated and cylindrical, resembling snakes.
Lateral Line System: Well-developed sensory organs along their body.
Labyrinth Organ: Unique organ above the gills. [8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-11-320.jpg)
![BEHAVIOR:
Migratory Behavior: Snakehead fish show migratory habits, moving
between habitats for breeding, food, or environmental conditions.
Parental Behavior: Snakehead fish display remarkable parental care, with
both male and female guarding and nurturing eggs and fry. [9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-13-320.jpg)
![MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES:
Habitat Restoration: Protecting and restoring natural habitats like
wetlands and rivers can support native fish populations and limit
snakehead fish spread.
Collaborative Efforts: Working with local communities, government
agencies, and conservation groups can implement effective management
plans and share resources to address challenges. [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-14-320.jpg)
![CULTURAL SIGNIFICANCE AND ECONOMIC VALUES:
Cultural Significance: In Pakistan, snakehead fish, known as Bulli, are not only a
food source but also culturally significant, celebrated in traditional dishes that
represent culinary heritage.
Economic Value: Bulli fisheries support livelihoods in rural areas, providing income
for fishermen and contributing to local economies through commercial fishing and
trade. [2,7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-15-320.jpg)
![THREATS AND CHALLENGES:
Predatory Behavior: Their aggressive feeding habits can lead to declines in native
fish populations and alter food webs.
Spread and Establishment: They can quickly establish populations in new areas
due to their adaptability and rapid reproduction, making control difficult once
introduced. [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-16-320.jpg)
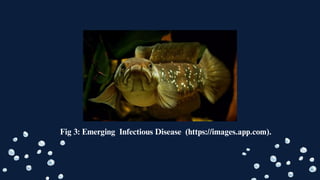
![EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE:
Snakehead rhabdovirus" (SHRV) affects snakehead fish, causing
significant mortality, particularly in aquaculture settings.Efforts to
manage SHRV and other diseases affecting snakehead fish are ongoing
due to their economic and ecological impacts. [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-17-320.jpg)
![RECENT RESEARCH:
Climate Change Indicators from Fossils: Fossils reveal past humid climates where
snakehead fish lived.
Nutritional Value Study: Guangdong variety has higher nutritional value than
Deqing, with more polyunsaturated fatty acids and essential amino acids.
Invasive Species in Florida: The invasive goldline snakehead fish in Florida poses
ecological threats due to its land-hunting ability and wide prey range.
Trophic Eggs and Snakehead Success: Some species, like the kampango catfish, feed
offspring with trophic eggs, aiding species diversity. [5,6,8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whata-4-240408093916-05a33cd2/85/Snakehead-Fish-Introduction-Morphology-it-s-Characteristics-19-320.jpg)



