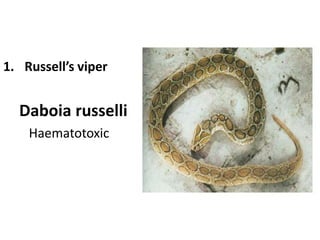
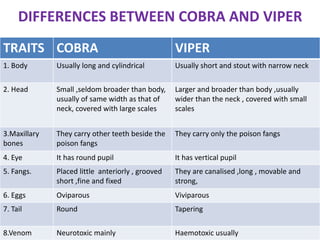
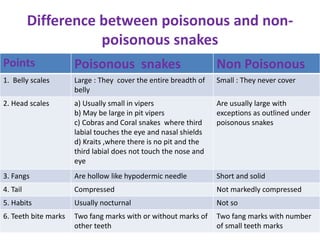
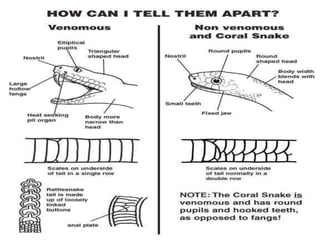
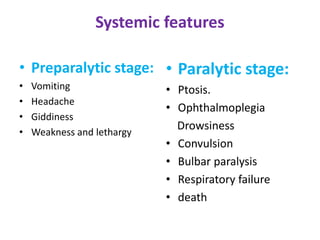
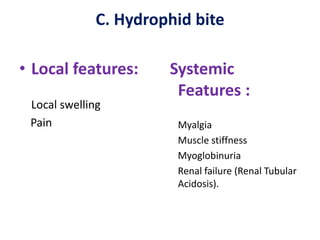
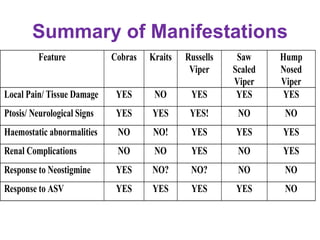
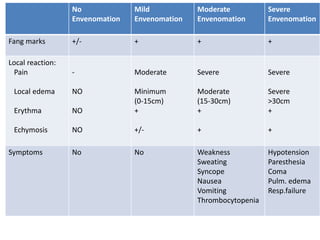
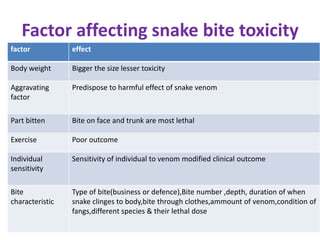
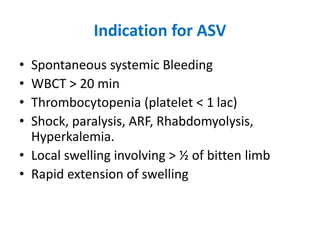
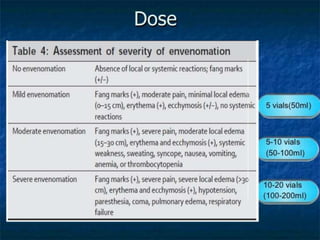
Snake bites can be classified based on the type of venom secreted by the snake's poison glands. Elapidae snakes secrete neurotoxic venom. Viperidae snakes secrete vasculotoxic venom which affects blood vessels. Hydrophidae snakes secrete myotoxic venom which damages muscle tissue. Common signs and symptoms of snake bites include localized swelling, pain, and discoloration at the bite site. Systemic effects vary depending on the snake family but can include neurologic impairment, coagulopathies, renal failure, and respiratory failure in severe cases. Treatment involves wound care, immobilization, antivenom administration, and supportive care depending on the clinical effects of the envenomation.