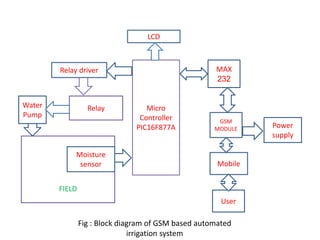
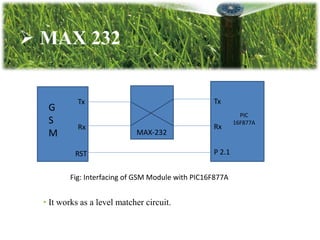
This document describes a GSM based automatic irrigation system. The system uses soil moisture sensors to detect the moisture level in soil. When the moisture level drops below a threshold, the sensor alerts a microcontroller which sends a signal to a GSM module to call a user's mobile phone. The user can then remotely turn on a water pump by answering the call. When the soil moisture increases, the sensor stops the pump. The system aims to automate irrigation and save water, labor, and time compared to traditional irrigation methods.














![ REFERENCES
RESEARCH PAPER
“Microcontroller Based Automated Irrigation System” The International Journal Of
Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 3,
Issue 06-9- 2014 ISSN (e):2319 –1813 ISSN (p):2319 –1805
“GSM based Automatic Irrigation Control System” IOSR-JMCE-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN:
2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. I (Jul-Aug. 2014), PP 49-55
H.T ingale and N.N. Kasat, “Automated Irrigation System”, Proceedings of the International
Journal of Engineering Research and Development, Volume 4, Issue 11 November 2012.
BOOKS:
Microcontrollers[ THEORY AND APPLICATIONS ]
By Ajay V Deshmukh
PIC Microcontroller and Embedded System using Assembly and C for PIC18
By Muhammad Ali Mazidi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irrigationsystemppt-180717165614/85/GSM-Based-Automatic-Irrigation-System-17-320.jpg)

