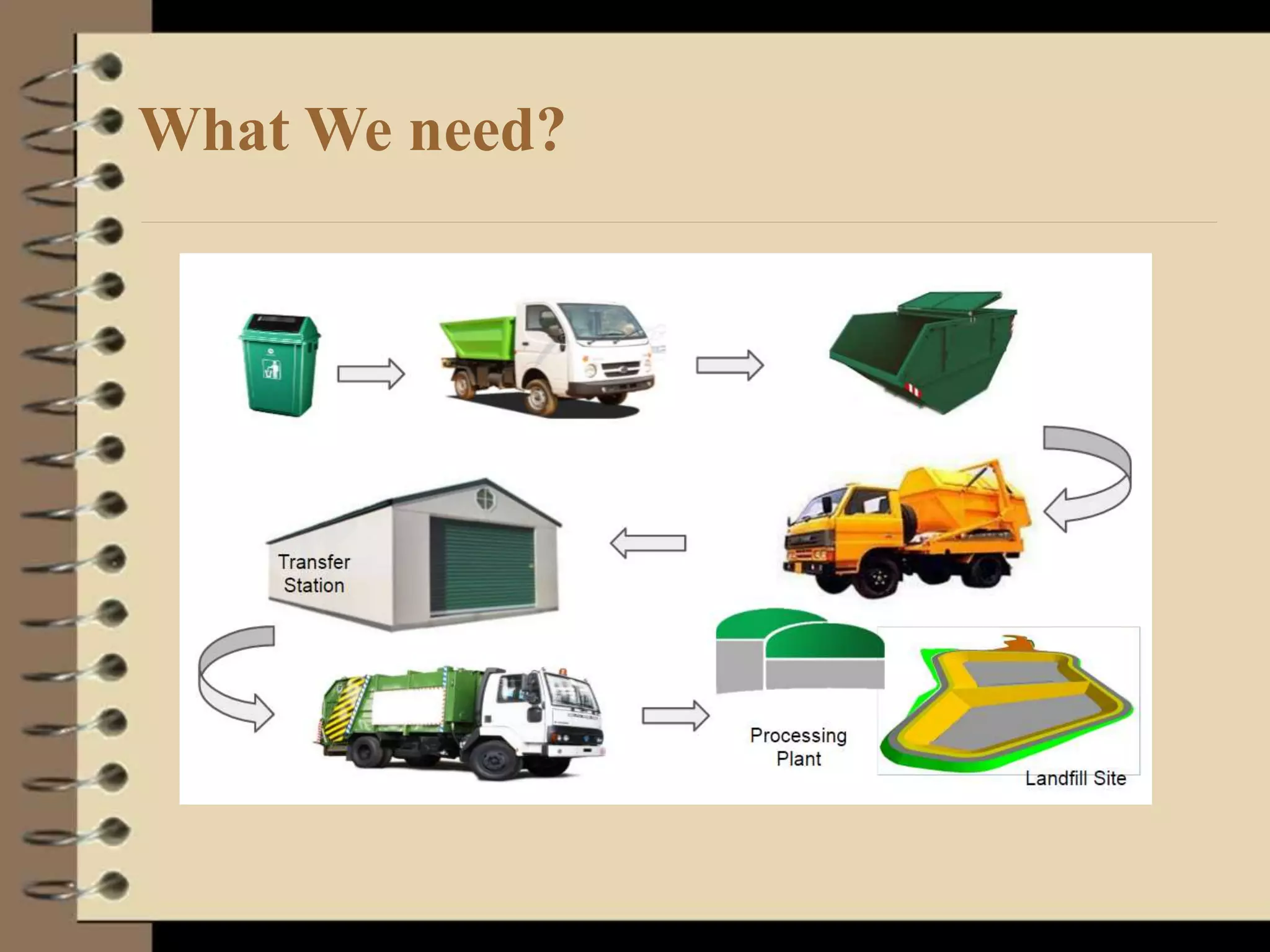
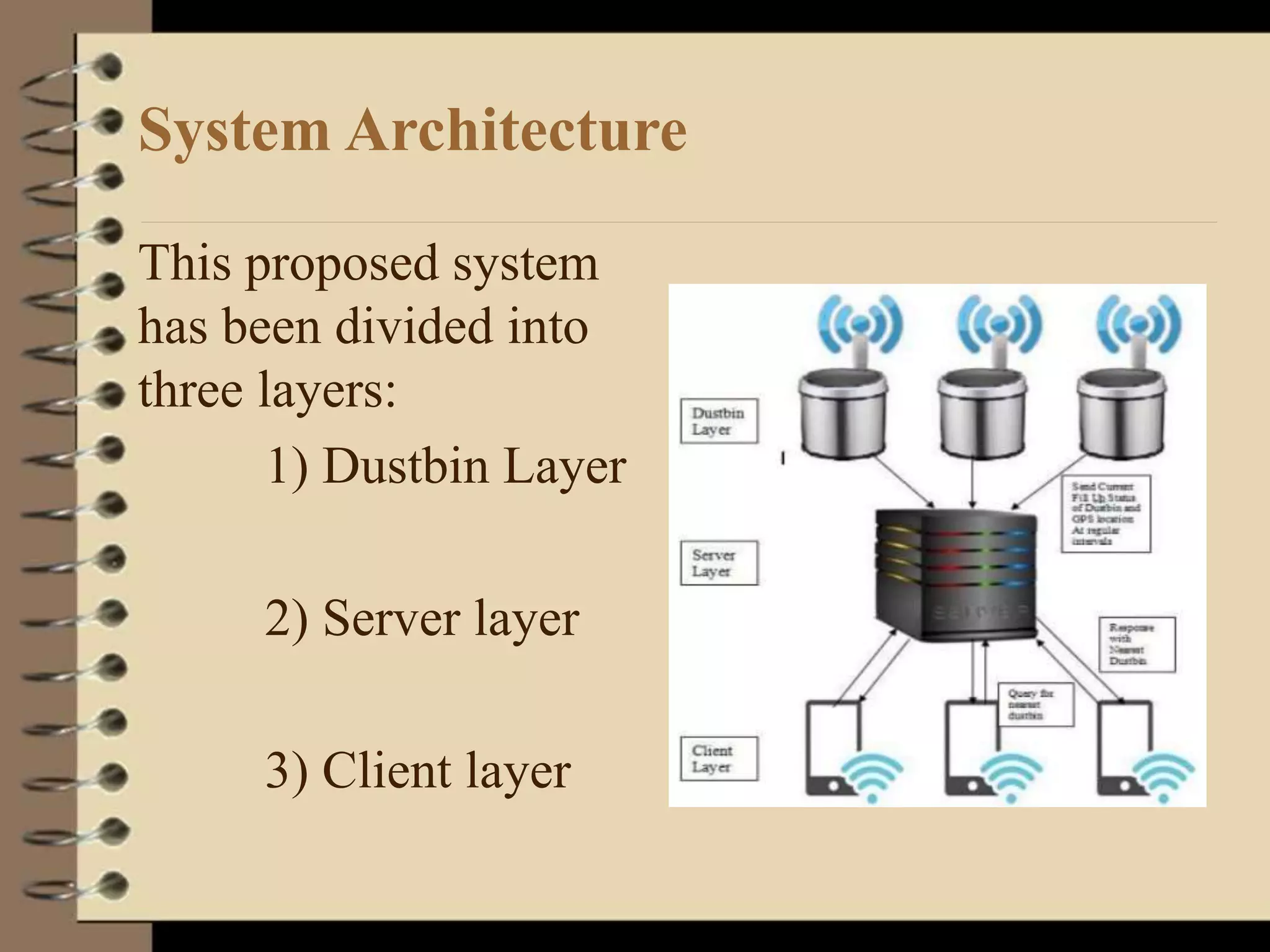
The document discusses a proposed smart dustbin system aimed at improving waste management in urban areas by integrating technology for better data collection and service efficiency. It outlines the need for effective garbage collection solutions due to increasing population and waste generation, detailing system architecture and various scheduling algorithms for optimal collection. The project also highlights real-life applications, advantages, technical challenges, and future development potential.