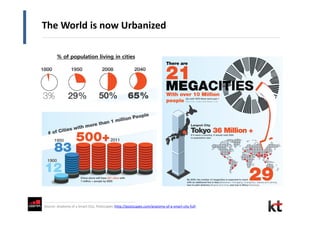
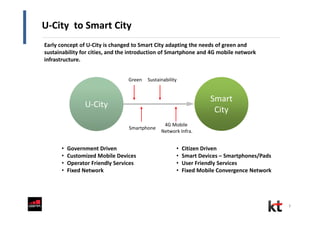
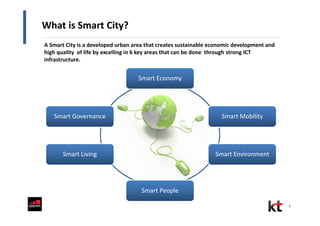
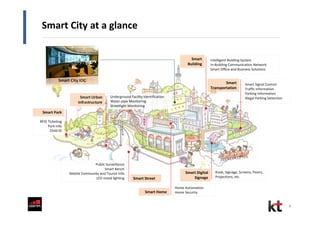
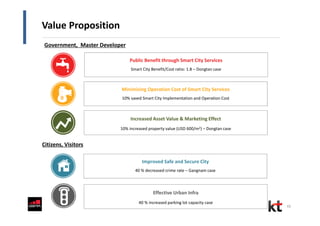
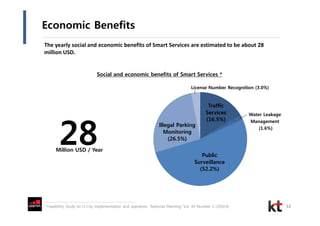
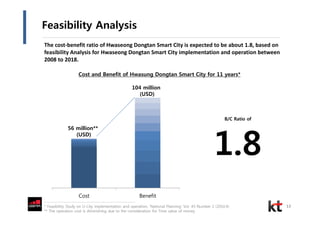
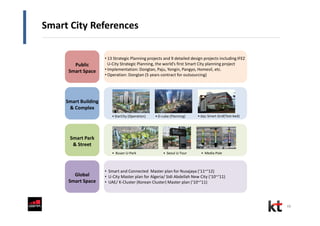
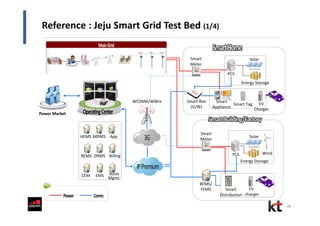
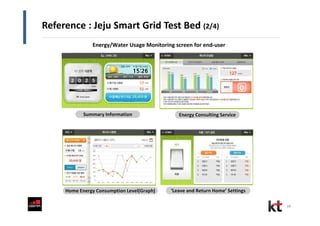
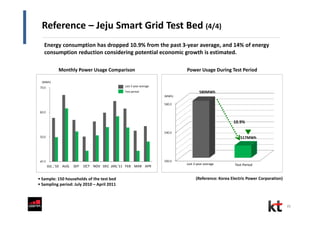
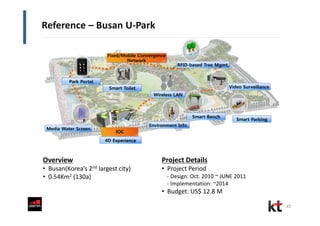
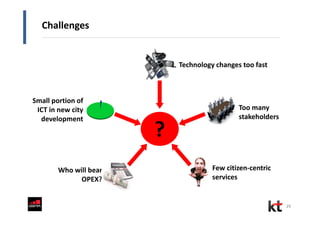
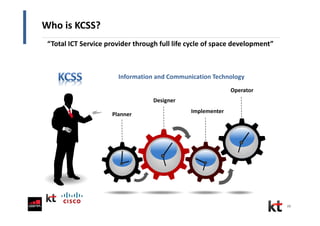
This document discusses smart cities and KT Corporation's smart city strategy. It begins with definitions of traditional urban ICT, U-City, and smart city concepts. It then outlines KT's vision for smart cities and its partnership with Cisco to provide total ICT services through all phases of smart space development. KT aims to export its smart city expertise and has established a public-private company called Incheon U-City to implement its first smart city project in South Korea.