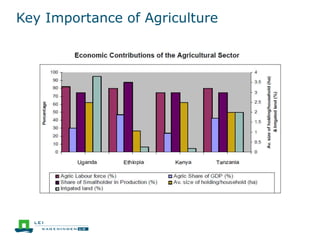
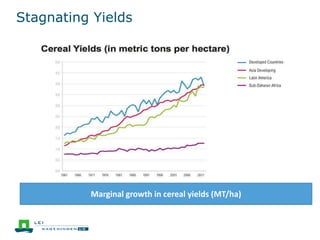
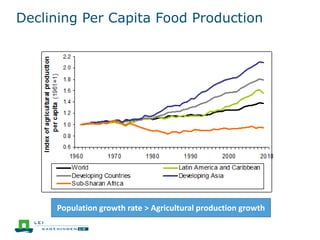
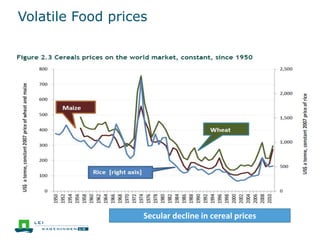
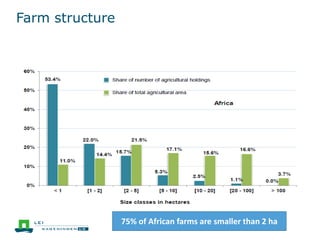
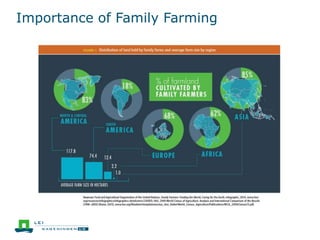
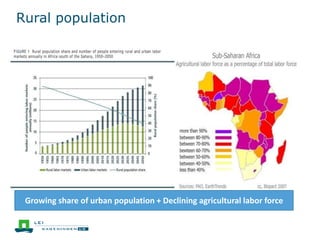
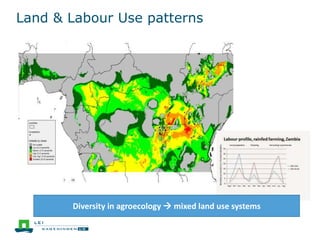
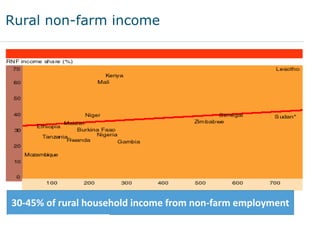
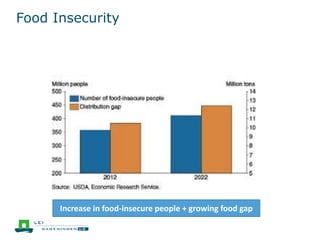
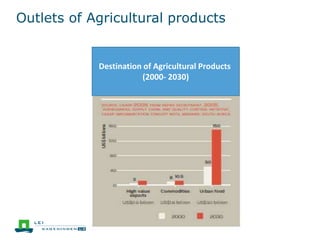
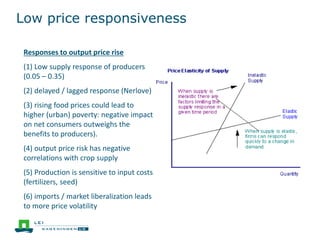
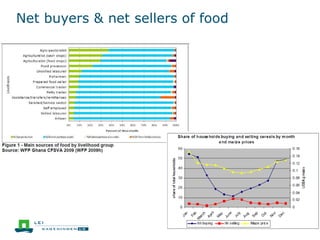
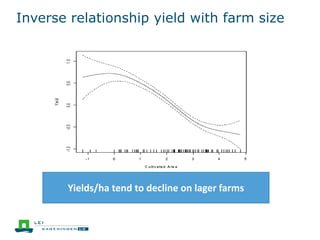
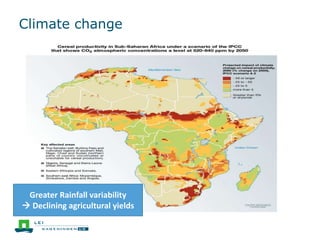
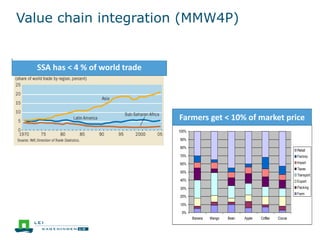
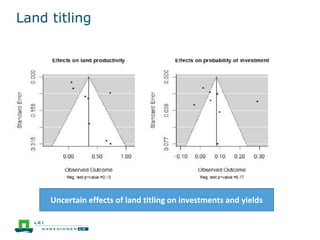
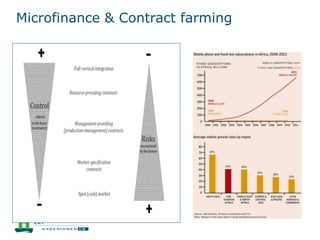
This document discusses the future prospects for smallholder agriculture and family farming in sub-Saharan Africa. It notes that while cereal production has tripled in the last 50 years, cereal output per capita has fallen. The majority of Africans remain undernourished and poverty stricken. Agriculture provides over half of employment but farm sizes are shrinking and yields are stagnant due to population growth, climate challenges, and lack of investment. The document examines policies around market access, land rights, social safety nets, and contract farming that could help boost smallholder productivity and food security going forward.