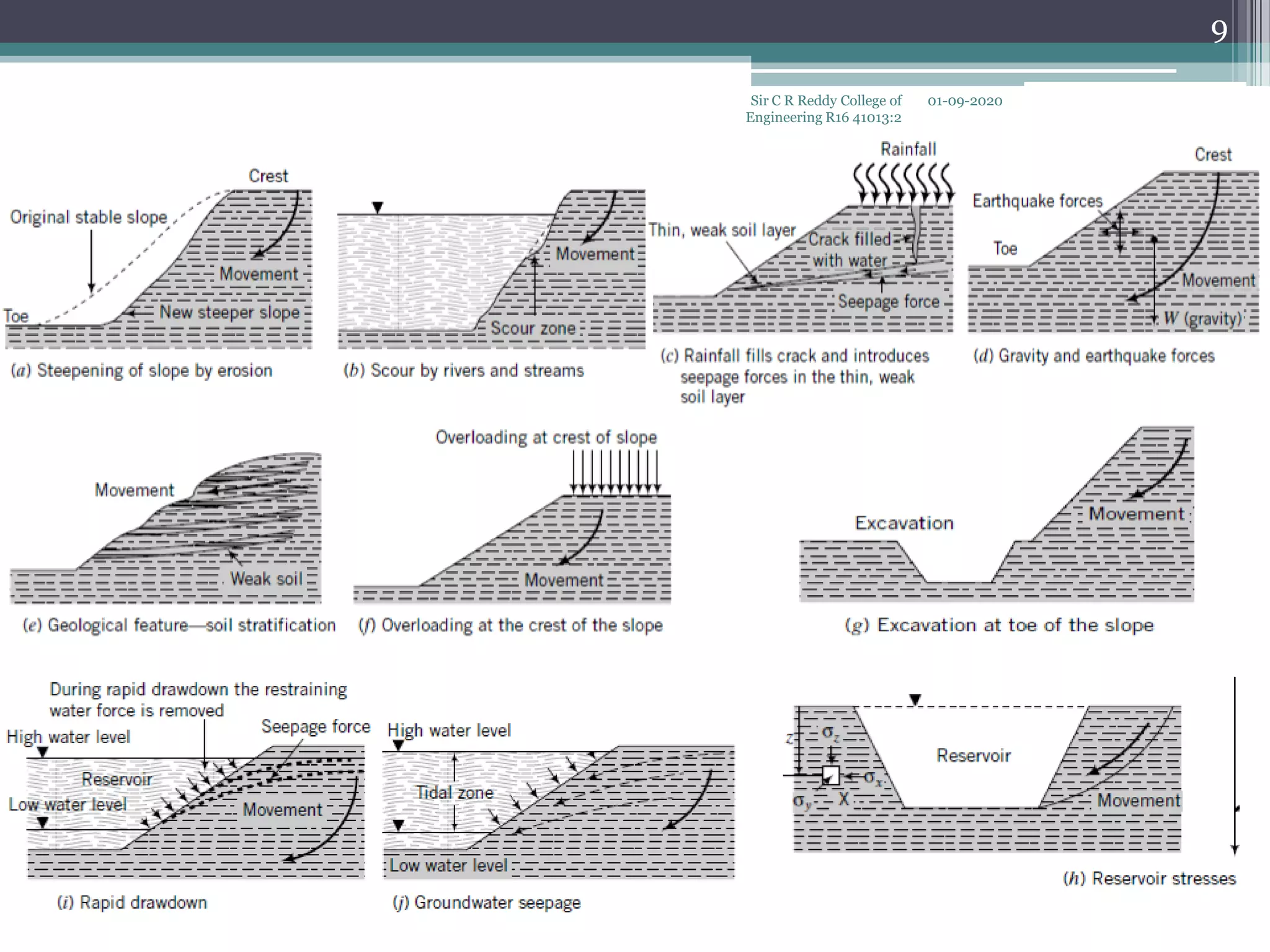
The document discusses slope stability analysis. It defines slopes and describes types of natural and man-made slopes. Slope stability is important for earth dams and natural slopes to prevent catastrophic failures. Factors that cause slope instability include gravitational forces, seepage water, surface erosion, lowering of adjacent water levels, and earthquakes. Common types of slope failures are rotational, translational, compound, and wedge failures. Rotational failures occur along a circular or non-circular slip surface. Translational failures occur along failure surfaces parallel to infinite slopes. Compound failures combine rotational and translational slips. Wedge failures involve separation of soil blocks along inclined planes of weakness.