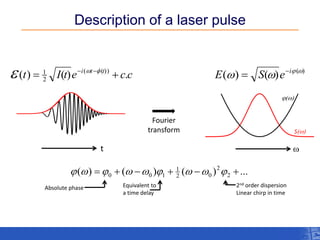
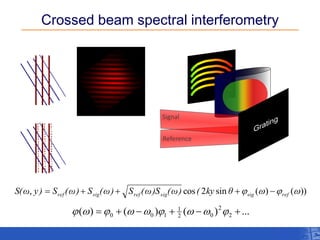
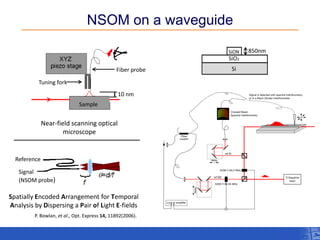
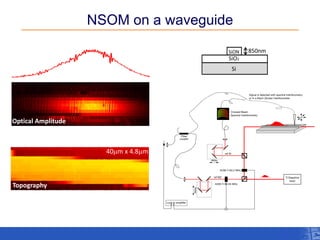
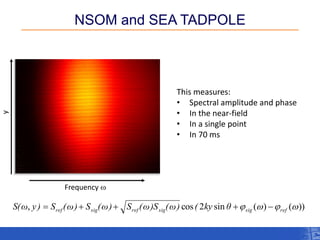
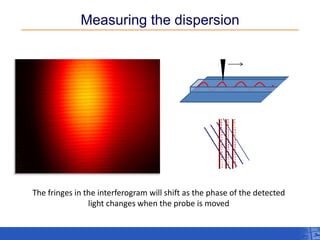
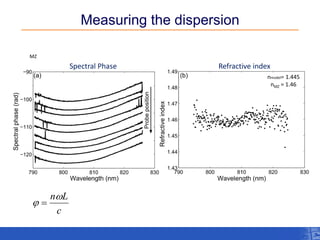
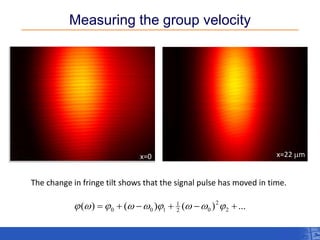
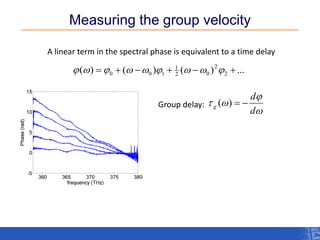
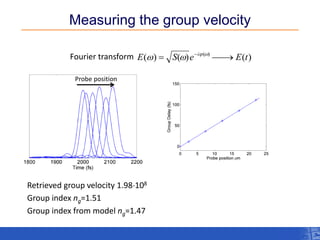
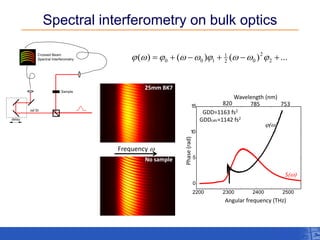
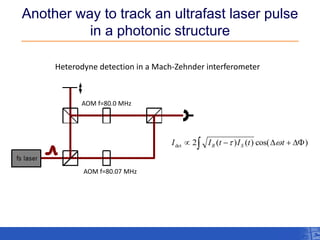
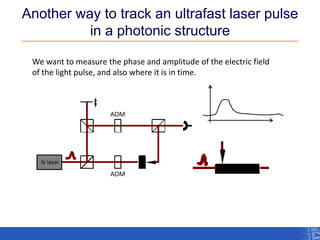
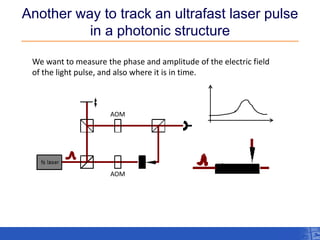
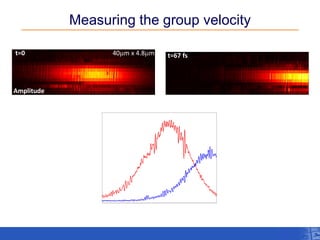
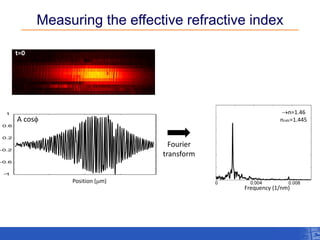
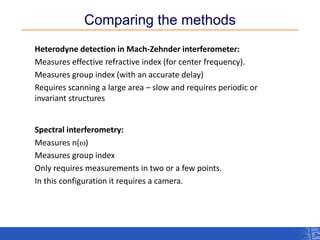
The document outlines a research project focusing on using near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) combined with spectral interferometry techniques to measure the electric field of light within photonic structures. It discusses the measurement of spectral amplitude, phase, and polarization, as well as the retrieval of group velocity and refractive index across various configurations. The findings highlight the advantages of NSOM for determining optical properties at a nanoscale level and for analyzing ultrafast laser pulses.