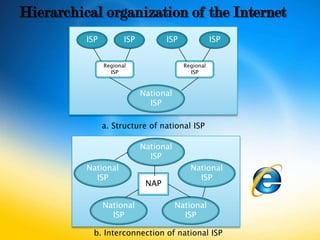
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that connects billions of devices worldwide. It is a network of networks comprised of private, public, academic and government networks linked together using various networking technologies. The Internet enables new forms of human interaction like social networking and allows people worldwide to access a vast amount of information and resources through services like the World Wide Web and email.