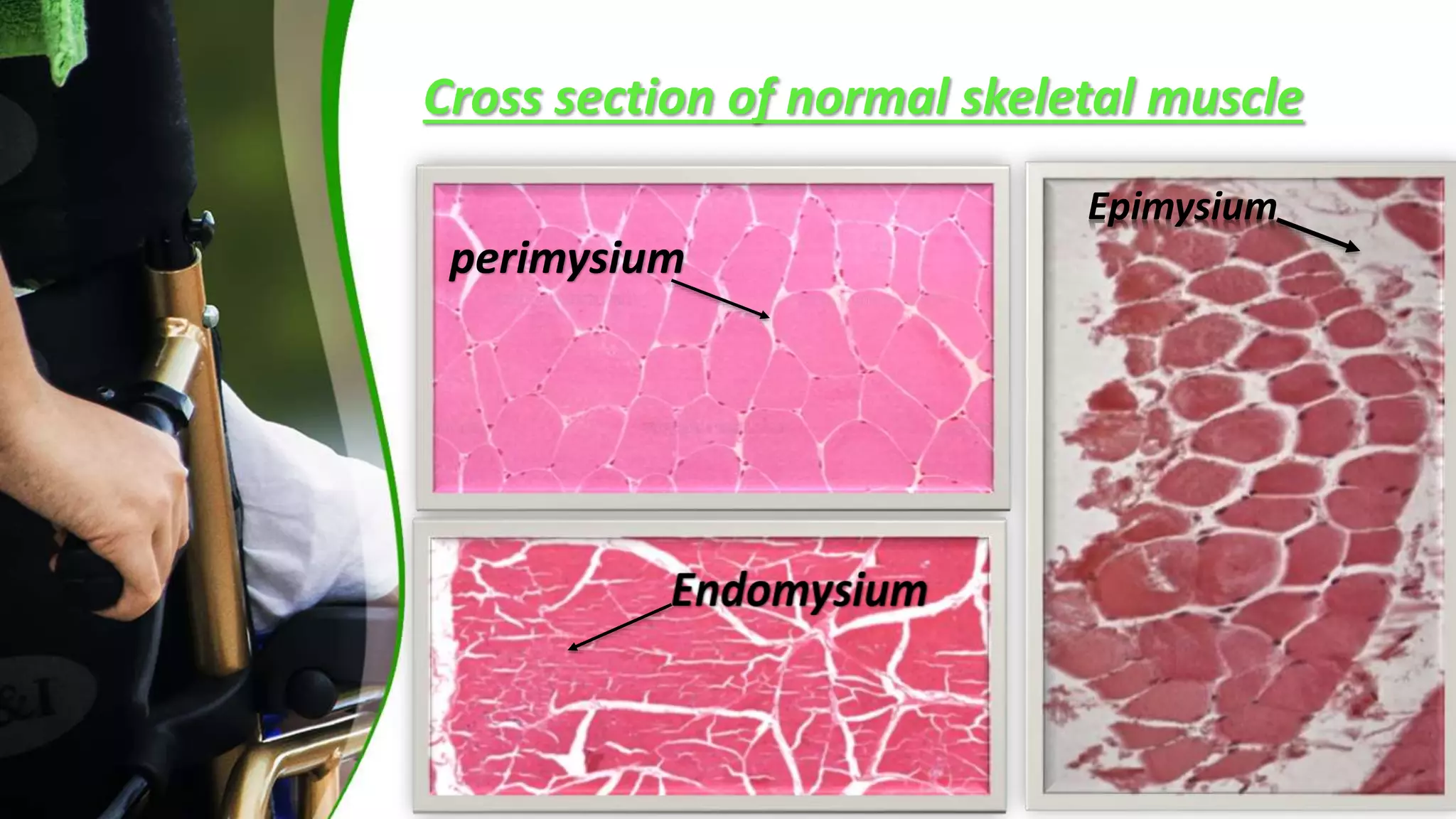
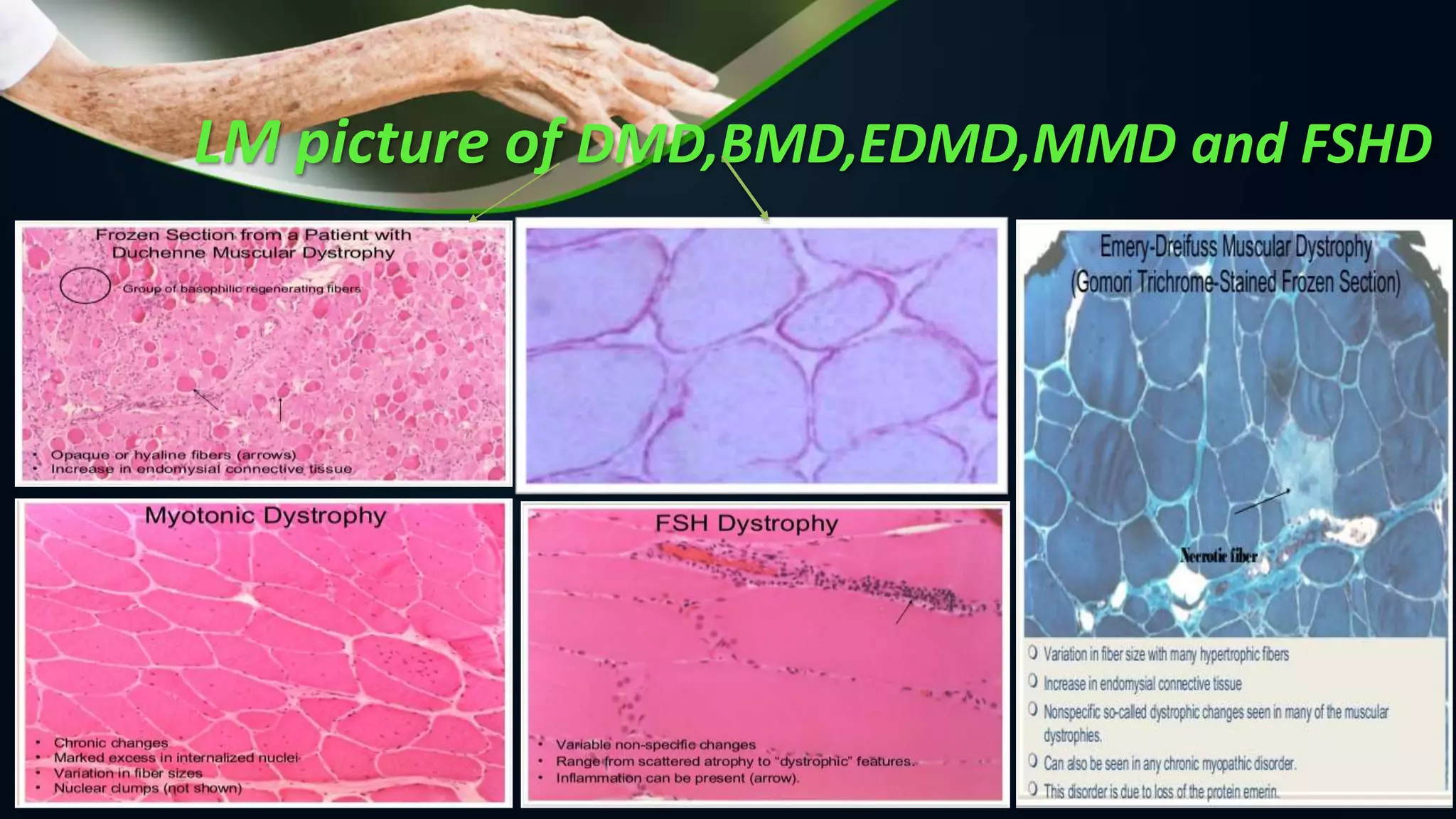
Skeletal muscle diseases, or myopathies, are disorders that cause structural or functional problems in muscles. They are classified as either acquired or hereditary. Acquired myopathies include inflammatory myopathies like polymyositis and dermatomyositis, endocrine myopathies, and toxic or drug-induced myopathies. Hereditary myopathies include muscular dystrophies, congenital myopathies, and metabolic myopathies. Muscular dystrophies are a group of inherited disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and wasting that can affect the heart and other organs. There are several major types of muscular dystrophies classified by inheritance pattern, age of onset, distribution, progression rate, and prognosis