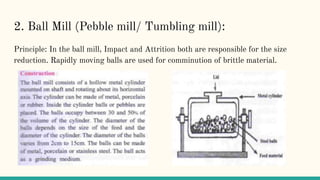
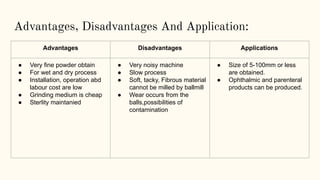
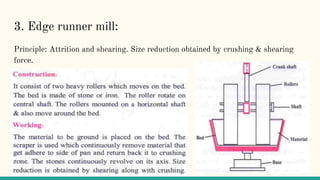
Size reduction is the process of reducing large substances into smaller particles through grinding, cutting, or emulsification. For pharmaceutical purposes, nano-sized particles are optimal. The objectives of size reduction include increasing surface area and absorption. Factors like hardness, toughness, and softening temperature affect the size reduction process. Common size reduction equipment includes fluid energy mills, ball mills, edge runner mills, end runner mills, and hammer mills. Each uses mechanisms like impact, attrition, shearing, or a combination to break down materials. Key considerations are achieving the desired particle size while avoiding contamination or decomposition from heat.