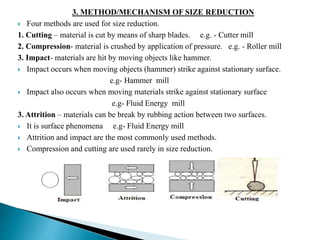
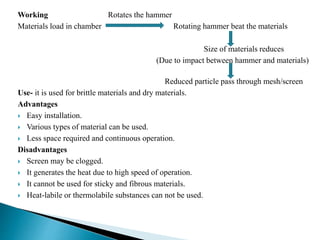
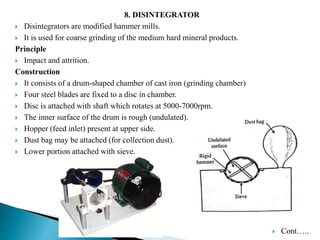
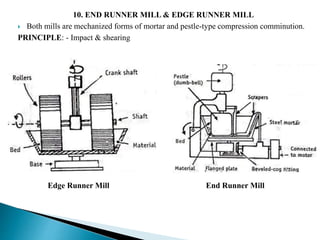
This document discusses size reduction, which is the process of reducing large solid masses into smaller particles or powder. It can be achieved through mechanical or chemical methods. The key factors that affect size reduction are the hardness, toughness, abrasiveness, stickiness, and moisture content of the material. Larger surface area and smaller particle size can increase properties like solubility, adsorption, and absorption. Common size reduction methods include cutting, compression, impact, and attrition. Ball mills and fluid energy mills are described as examples. Energy requirements depend on theories like Rittinger's, Bond's, and Kick's, relating to the work required based on new surface area, particle size, and material properties.