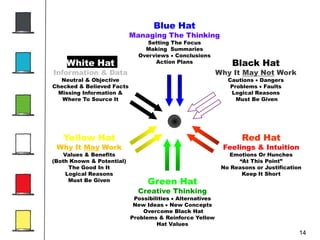
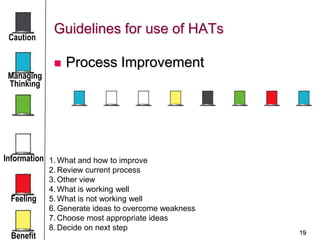
The document discusses the Six Thinking Hats method by Dr. Edward de Bono, aimed at improving group thinking and decision-making in organizations. Each 'hat' represents a different mode of thinking - creative, analytical, emotional, and more - allowing participants to explore ideas from multiple perspectives. This structured approach has been successfully applied in various organizations and sectors, enhancing collaboration and reducing decision-making time.