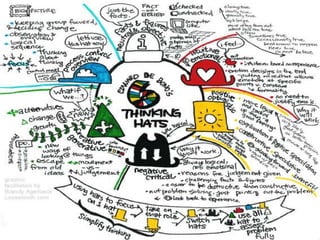
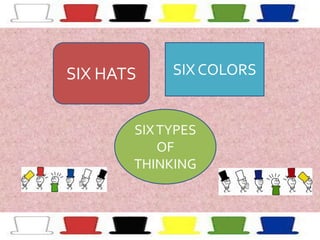
This document introduces the Six Thinking Hats method for structured thinking and discussion. It outlines six colored hats that each represent a different perspective or mode of thinking: white for objective facts; red for emotions and feelings; black for cautionary thoughts; yellow for optimism and benefits; green for creative ideas; and blue for process control. The method aims to improve thinking by considering perspectives sequentially rather than simultaneously, focusing discussion and allowing diverse viewpoints. Benefits include using more of our thinking abilities, reducing ego and confrontation, and creating more effective plans.