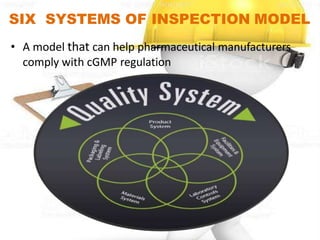
The six-system inspection model is used to help pharmaceutical manufacturers comply with cGMP regulations. The six systems are: quality, production, facilities and equipment, laboratory controls, materials, and packaging and labeling. Each system has specific requirements under cGMP. The quality system involves establishing a quality management system. The production system requires defining, approving, and controlling quality and manufacturing processes. The facilities and equipment system designates clean and dirty areas with proper separation, protection, and environmental controls. The laboratory controls system ensures adequate and calibrated equipment for intended testing. The materials system controls materials receipt and storage. The packaging and labeling system validates master copies and controls changes.