This document provides an overview of Six Sigma, including:
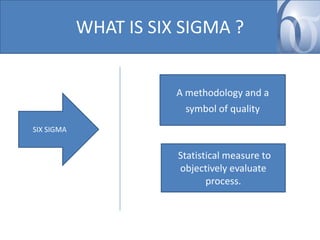
- Six Sigma aims to measure and reduce defects to 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It is a methodology and symbol of quality.
- Six Sigma is used to eliminate defects, meet customer specifications, and drive money savings, quality improvements, customer satisfaction, competitive advantage and growth.
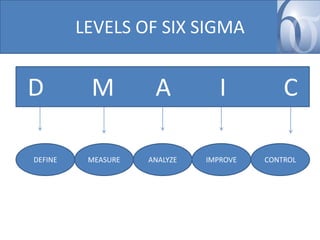
- The five phases of a Six Sigma project are Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC).
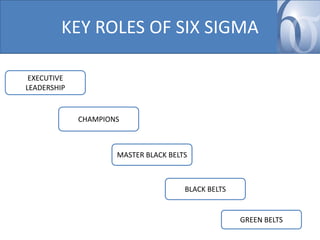
- Key Six Sigma roles include the Executive Leader, Champions, Master Black Belts, Black Belts and Green Belts.
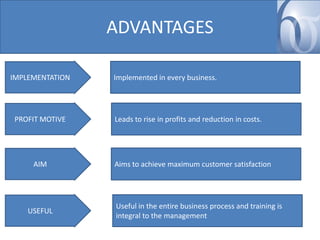
- Advantages include implementation across industries, profit motive, and customer satisfaction. Disadvantages include less process