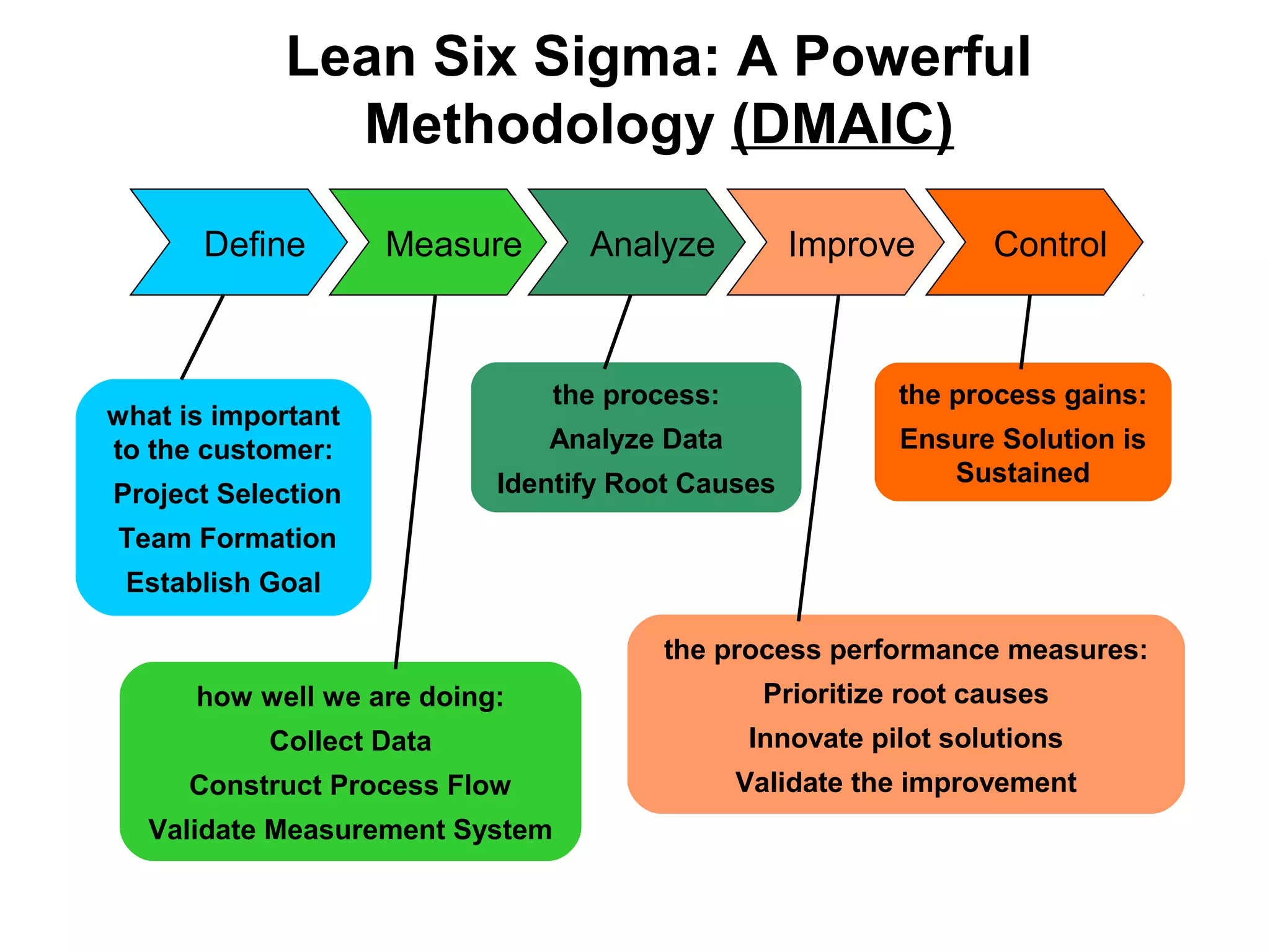
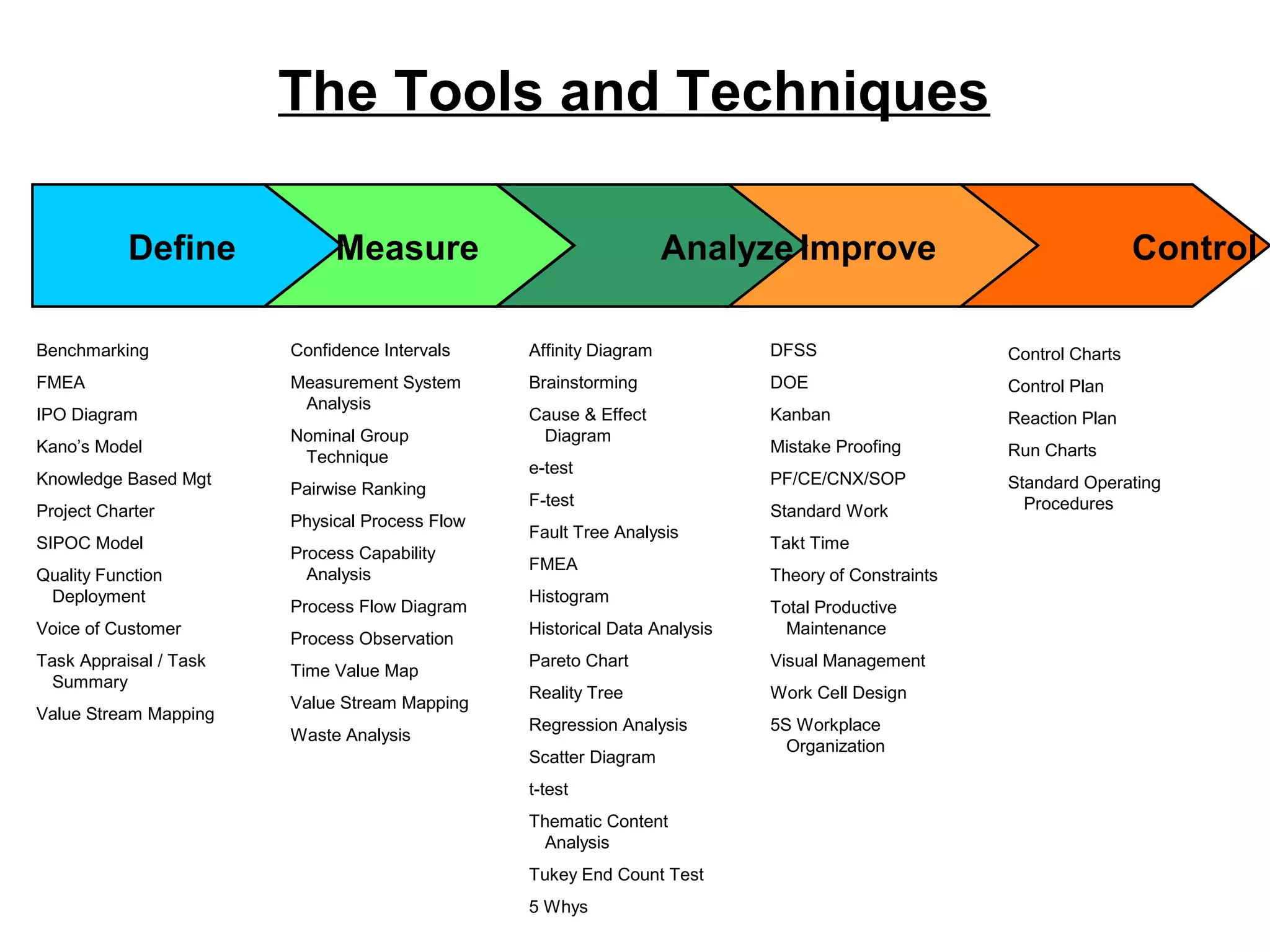
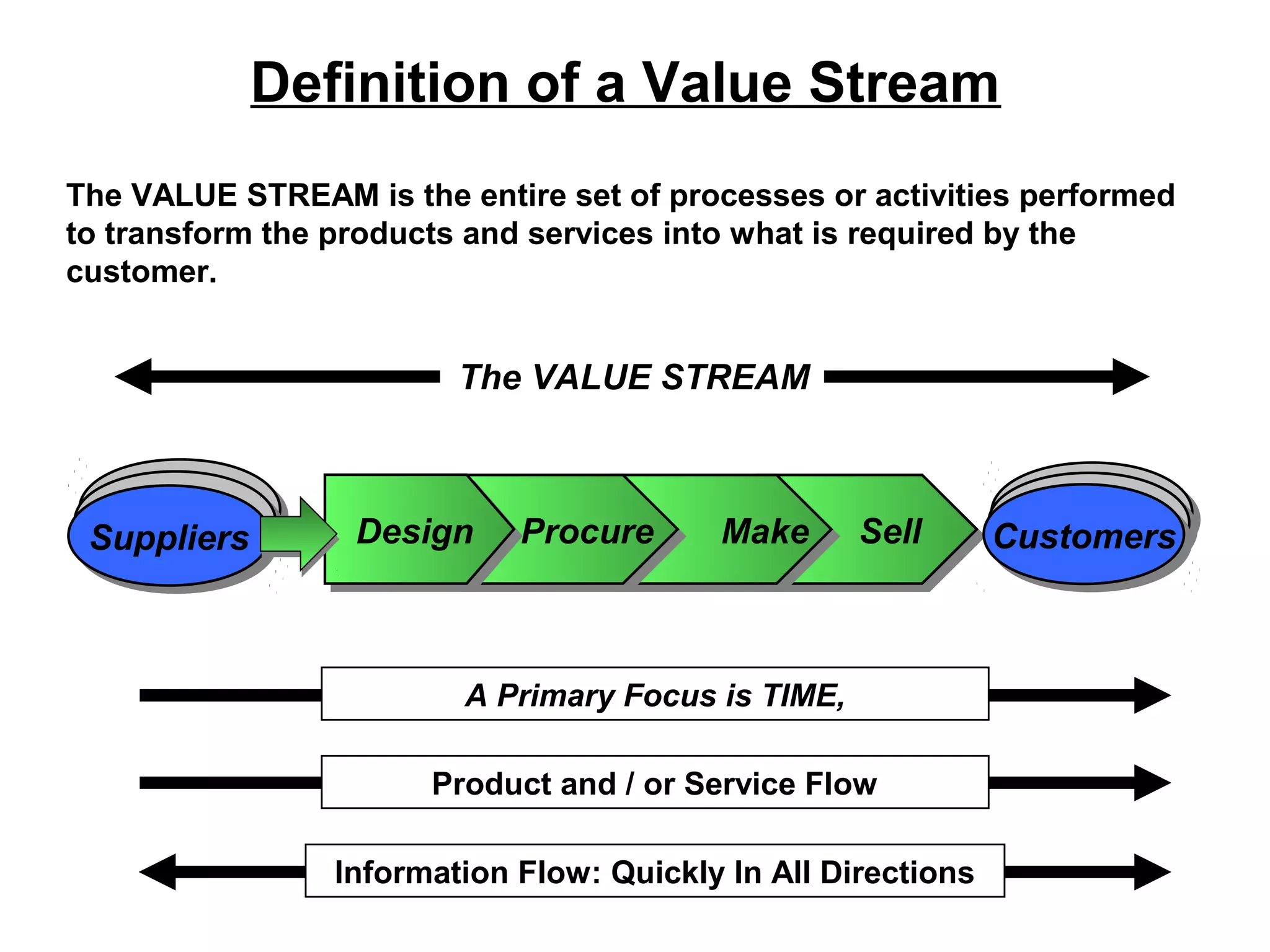
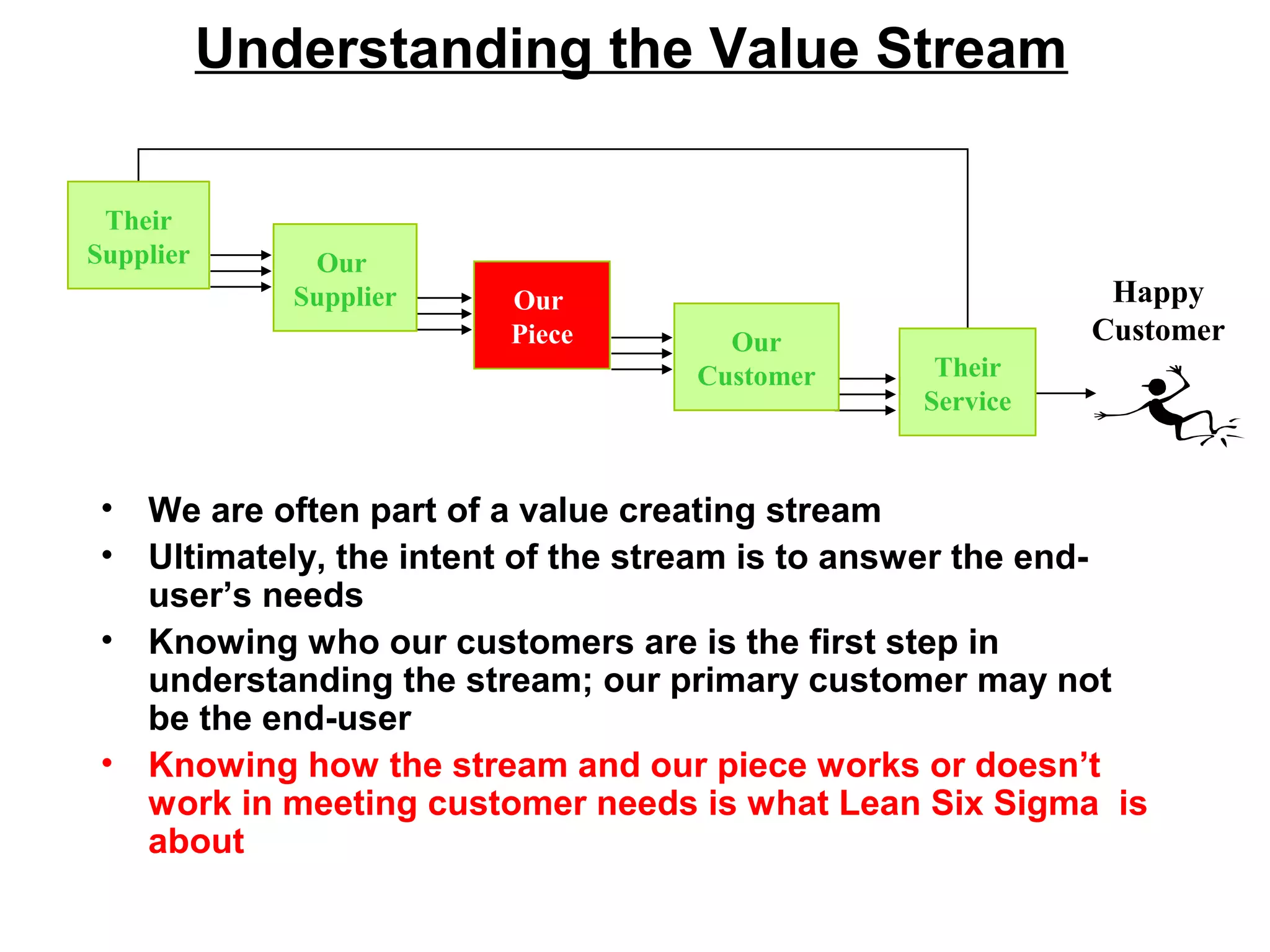
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines Lean and Six Sigma approaches to process improvement. It aims to eliminate waste and reduce process variation to improve quality, increase customer satisfaction, and reduce costs. Key aspects include defining customer value, mapping processes, using data-driven tools to analyze sources of waste and errors, testing solutions through pilots, and sustaining improvements through standardization and control. Successful deployment requires leadership commitment, cross-functional teamwork, and an organizational culture that embraces continuous improvement and challenges the status quo.