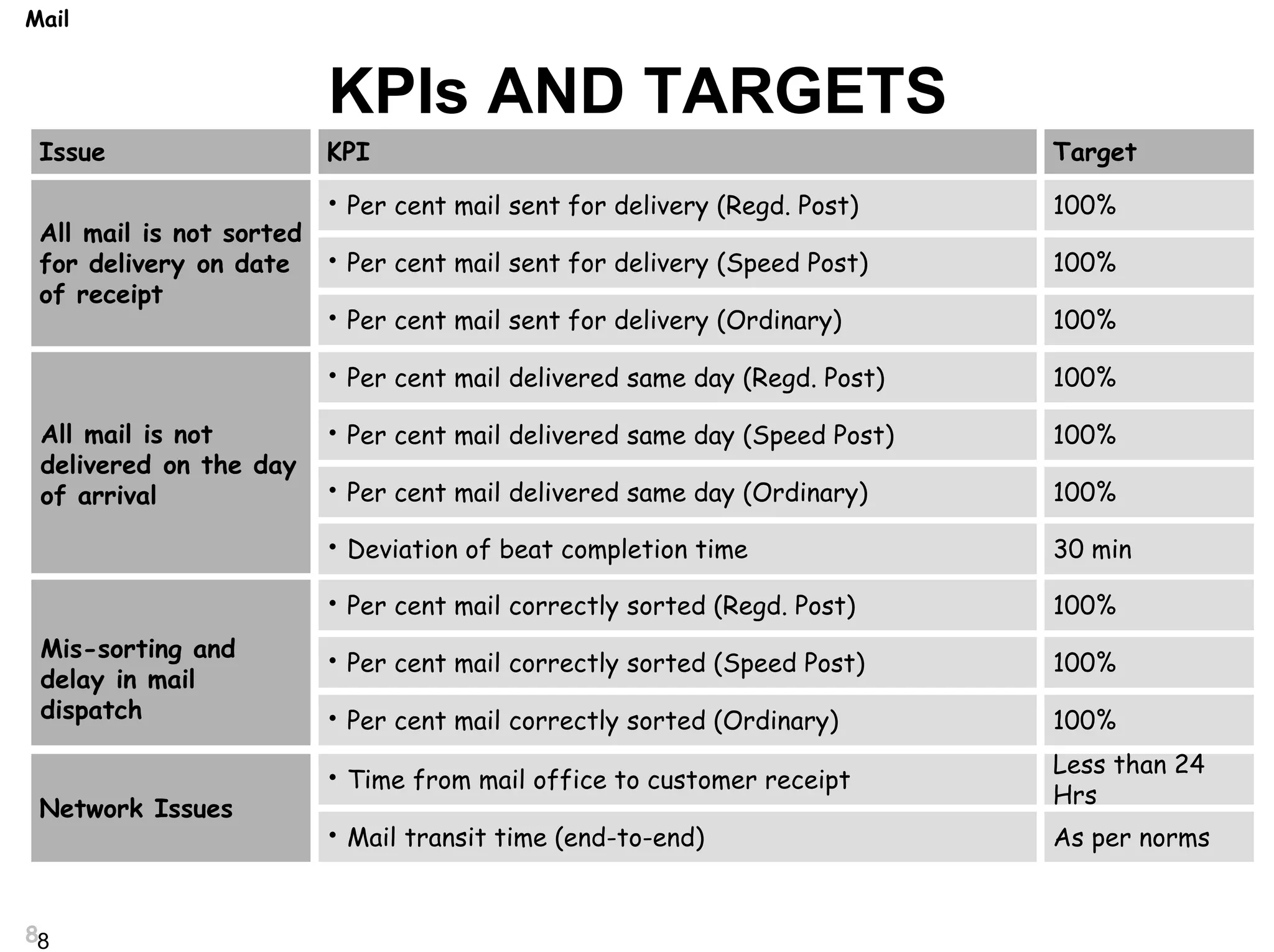
This document discusses KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), work flow, and evaluating performance. It defines KPIs as metrics that help organizations measure progress toward goals. KPIs should be limited to only the most essential factors for success. The document also discusses establishing work flow processes to improve efficiency and establish responsibilities. Performance management includes setting expectations, developing skills, continuously monitoring performance, and evaluating employees against standards to recognize outstanding work. Both ability and motivation impact performance, and low performance may be due to lack of either.