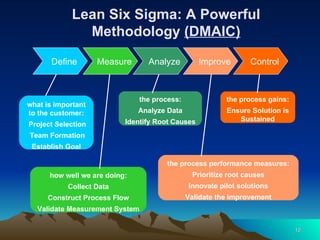
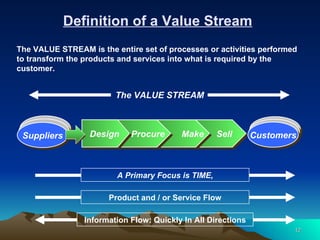
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines Lean and Six Sigma approaches to process improvement. It aims to reduce waste and variation and improve customer satisfaction by streamlining processes and eliminating defects. The methodology measures process performance, identifies sources of problems or waste, analyzes their causes, improves the process by addressing root causes, and controls future process performance. It requires organizational cultural change and leadership commitment to successfully deploy across all levels.