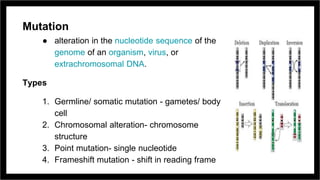
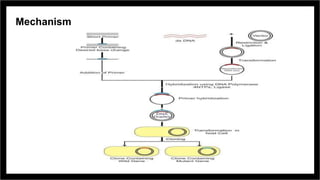
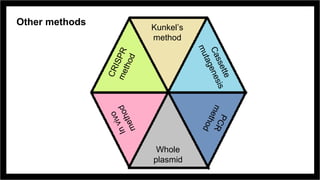
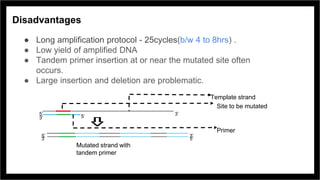
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology technique that introduces specific changes in DNA sequences to study the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, or proteins. It includes various methods for creating mutations, but can be limited by low yields and lengthy protocols. Historically, more random mutation methods were developed before advancements in targeted approaches began in the 1970s, leading to significant applications in research and commercial products.