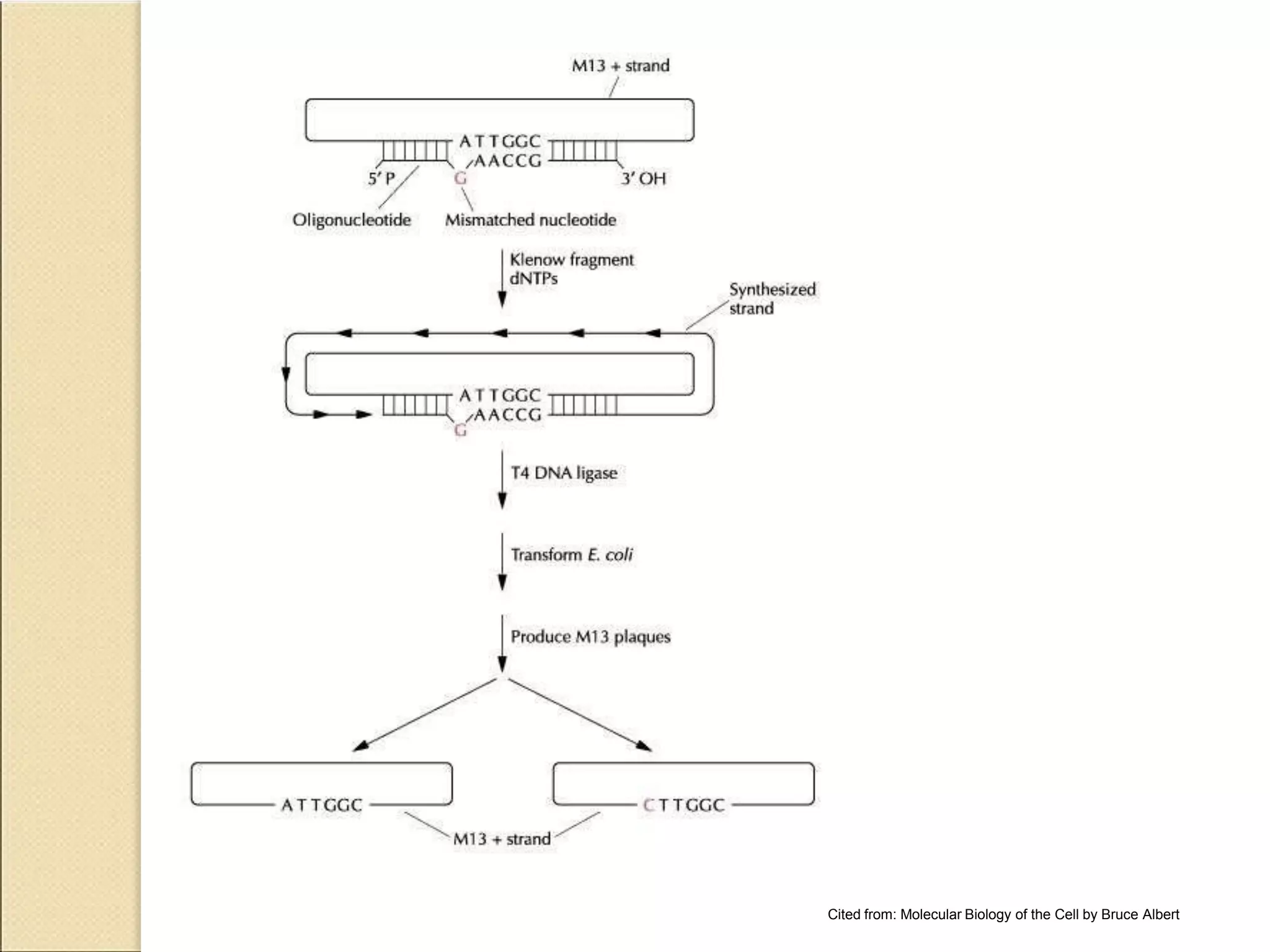
Directed mutagenesis allows scientists to make specific changes to the DNA code of a protein in order to improve it for a particular application. Common directed mutagenesis techniques include using M13 bacteriophage, plasmids, or PCR to introduce mutations and select for desired variants. These techniques enable modifying existing protein properties like temperature or pH stability to make proteins more suitable for industrial processes.