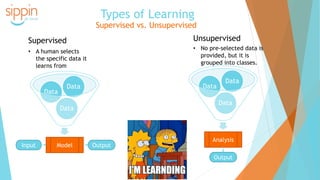
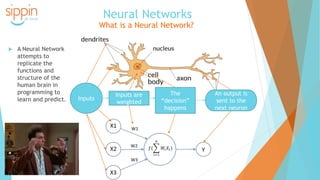
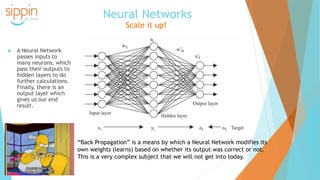
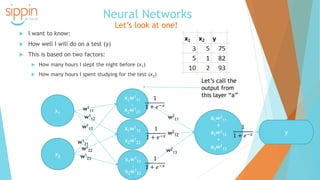
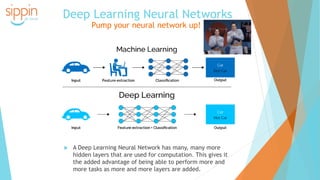
The document discusses the backgrounds of Pai Charasika and Ray Tri, co-founders of a company focused on mobile apps and artificial intelligence. It provides an overview of AI terminology, including distinctions between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and neural networks, and explains the differences between supervised and unsupervised learning along with their applications. Additionally, it touches on how neural networks function and the advantage of deep learning with increased hidden layers.