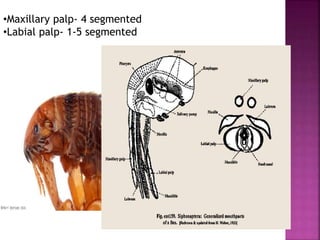
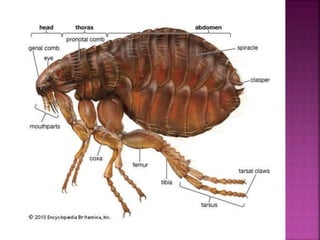
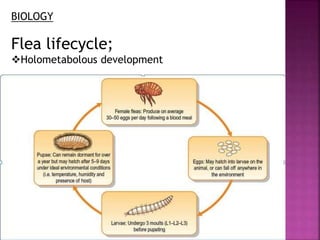
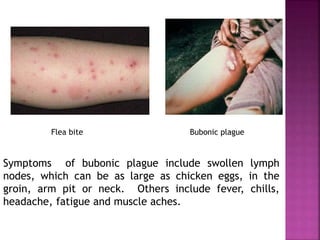
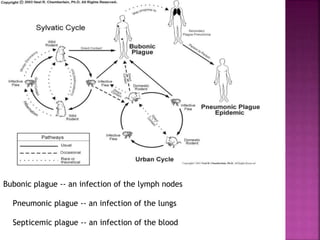
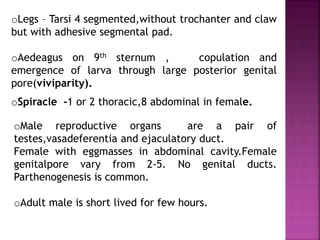
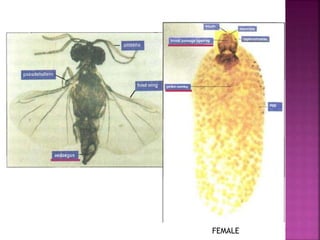
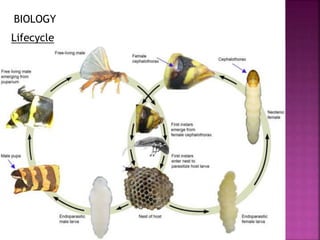
This document summarizes the order Siphonaptera (fleas) and Strepsiptera (stylopids or twisted-wing parasites). It describes their key physical characteristics, lifecycles, taxonomy, and economic importance. Fleas are small, wingless blood-sucking parasites of mammals and birds. Their lifecycle involves eggs, larvae, pupae, and wingless adults. They can transmit diseases like plague. Stylopids are endoparasites of insects that undergo hypermetamorphosis, with non-feeding larval females and winged adult males. Their lifecycle and parasitic behavior induces morphological changes in their hosts. Both orders contain medically and economically important species.