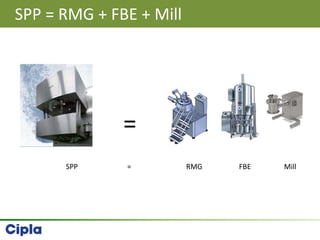
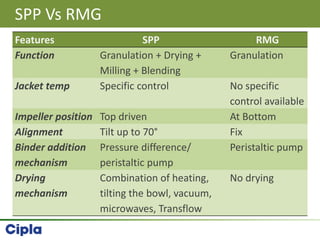
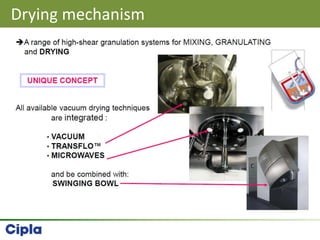
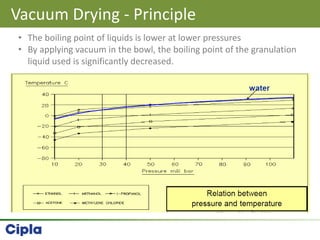
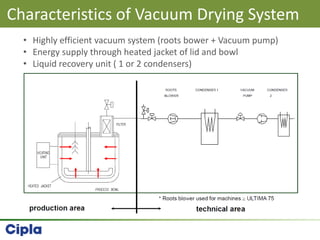
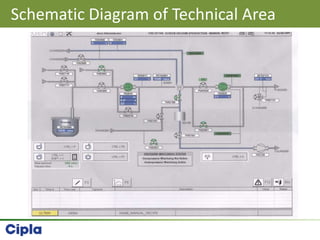
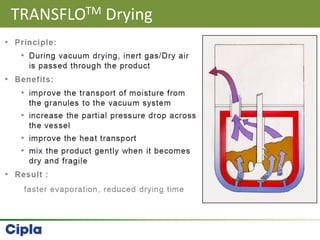
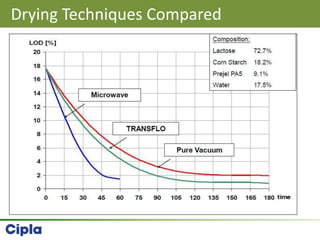
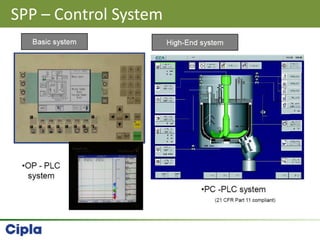
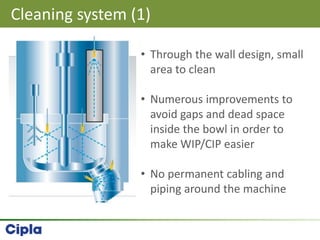
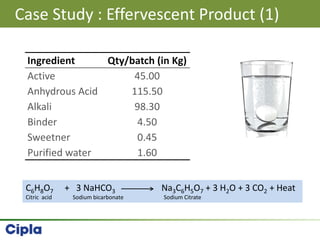
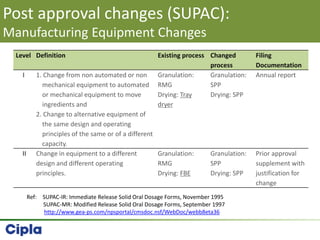
This document provides an overview of single pot processing (SPP) for pharmaceutical granulation. SPP combines mixing, granulation, and drying steps into a single machine. It has several benefits over traditional granulation methods like reduced processing time and material handling. The document outlines the key features of SPP systems including integrated heating, drying mechanisms like vacuum and microwaves, and enhanced process control. It also presents a case study of using SPP for an effervescent product and discusses regulatory considerations for post-approval changes involving new equipment.