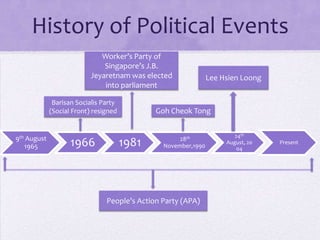
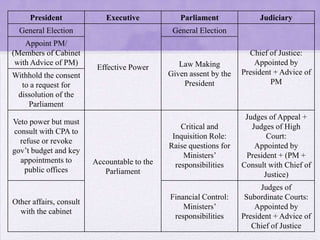
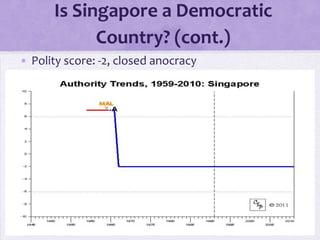
Singapore has a parliamentary system of government led by the People's Action Party, which has been the dominant political party since independence. While Singapore holds regular elections, its political culture emphasizes pragmatism, authority, and national security over full political pluralism and freedom of expression. As a result, most analysts consider Singapore to be a limited democracy or competitive authoritarian regime rather than a full liberal democracy.