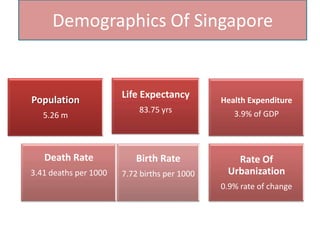
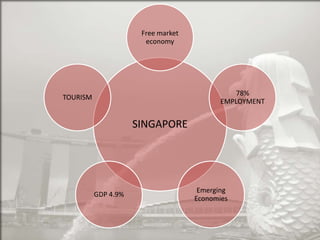
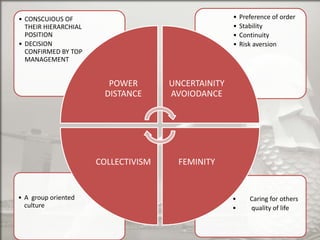
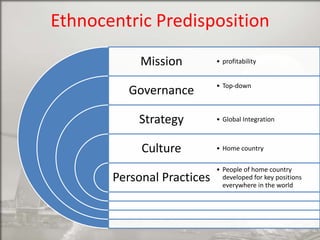
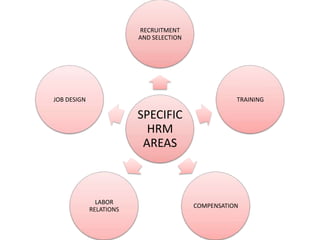
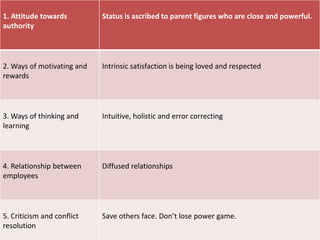
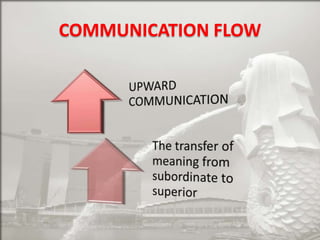
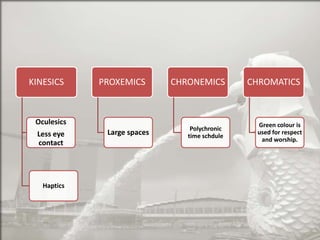
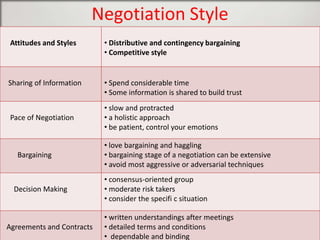
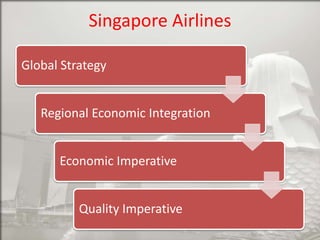
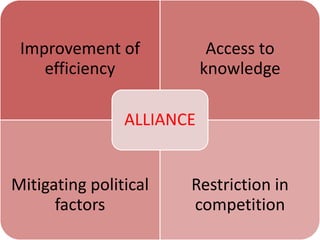
Singapore is an island country located in Southeast Asia with a population of 5.26 million people. It has a highly developed market economy and ranks highly in terms of economic competitiveness and human development. The flag features red, white, and crescent moon/stars which symbolize brotherhood, purity, and the nation's ideals. The document provides details on Singapore's demographics, geography, history, culture, government, economy, and some of its young entrepreneurs.