This document provides information about Singapore's history, government, and democratic system. It discusses:
- Singapore's founding by Stamford Raffles in 1819 and its history as part of Malaysia before becoming a republic in 1965.
- Its dominant People's Action Party (PAP) political system led by the PAP since 1959, which some see as a dominant party system with advantages of stability and prosperity but disadvantages of restrictions on individual rights.
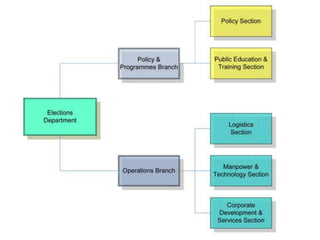
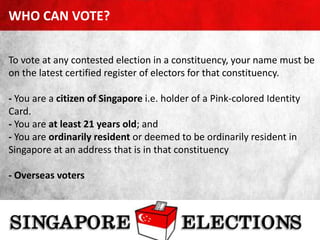
- Singapore's democratic institutions including regular parliamentary and presidential elections run by the Elections Department of Singapore, which are secret, compulsory, and held every 4-5 years.