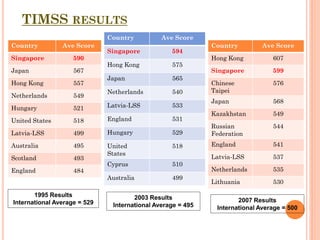
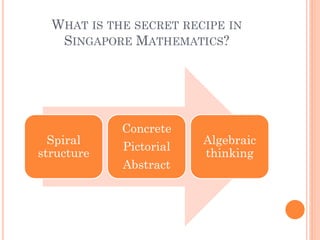
The document outlines the Singapore Math curriculum for Grade 1, focusing on addition and subtraction within 100, emphasizing a spiral structure for learning concepts progressively. It discusses the importance of number bonds as a foundational tool for understanding the relationships between numbers and operations, promoting both mental calculation and conceptual understanding. It also compares various methods for teaching addition and subtraction, highlighting their effectiveness in preparing students for more advanced mathematical concepts.