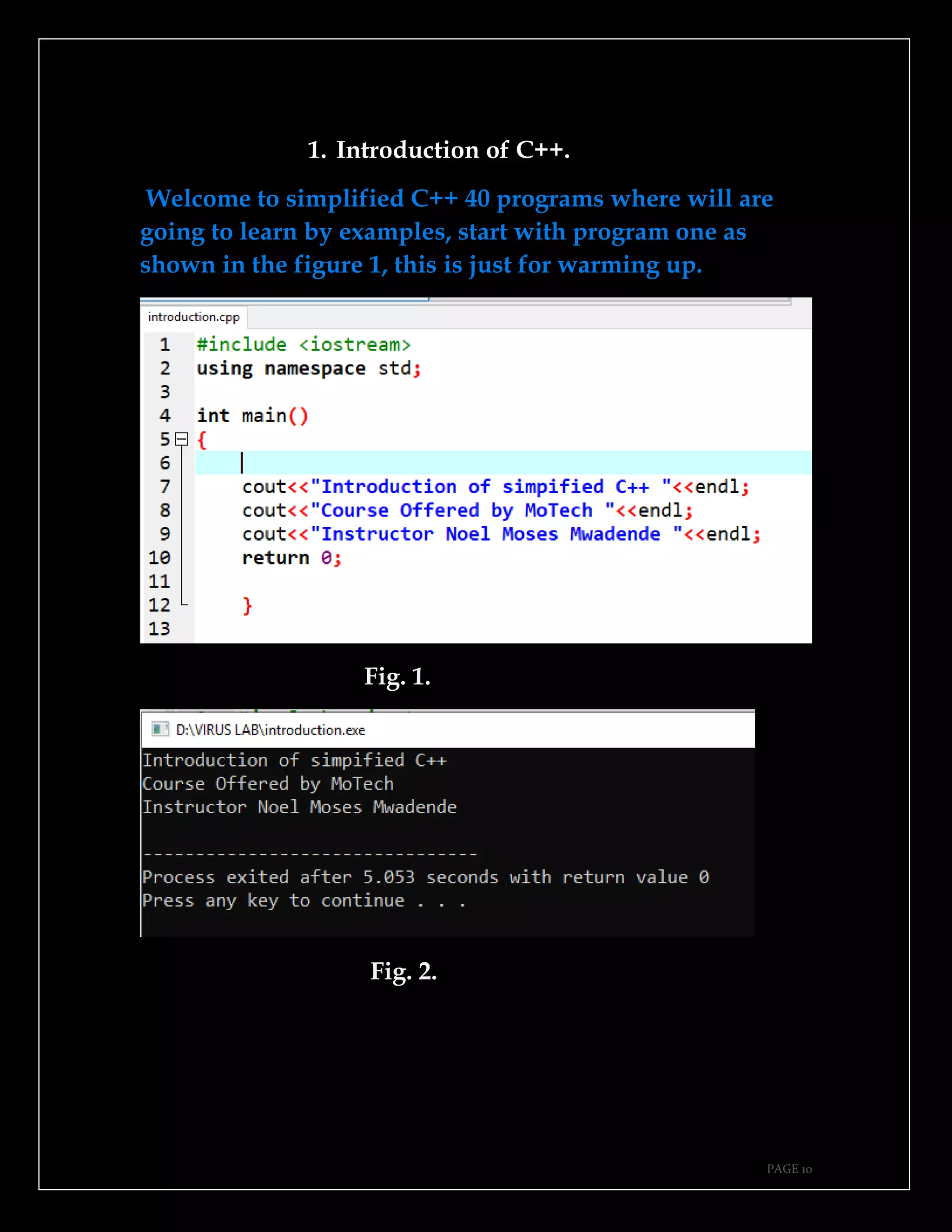
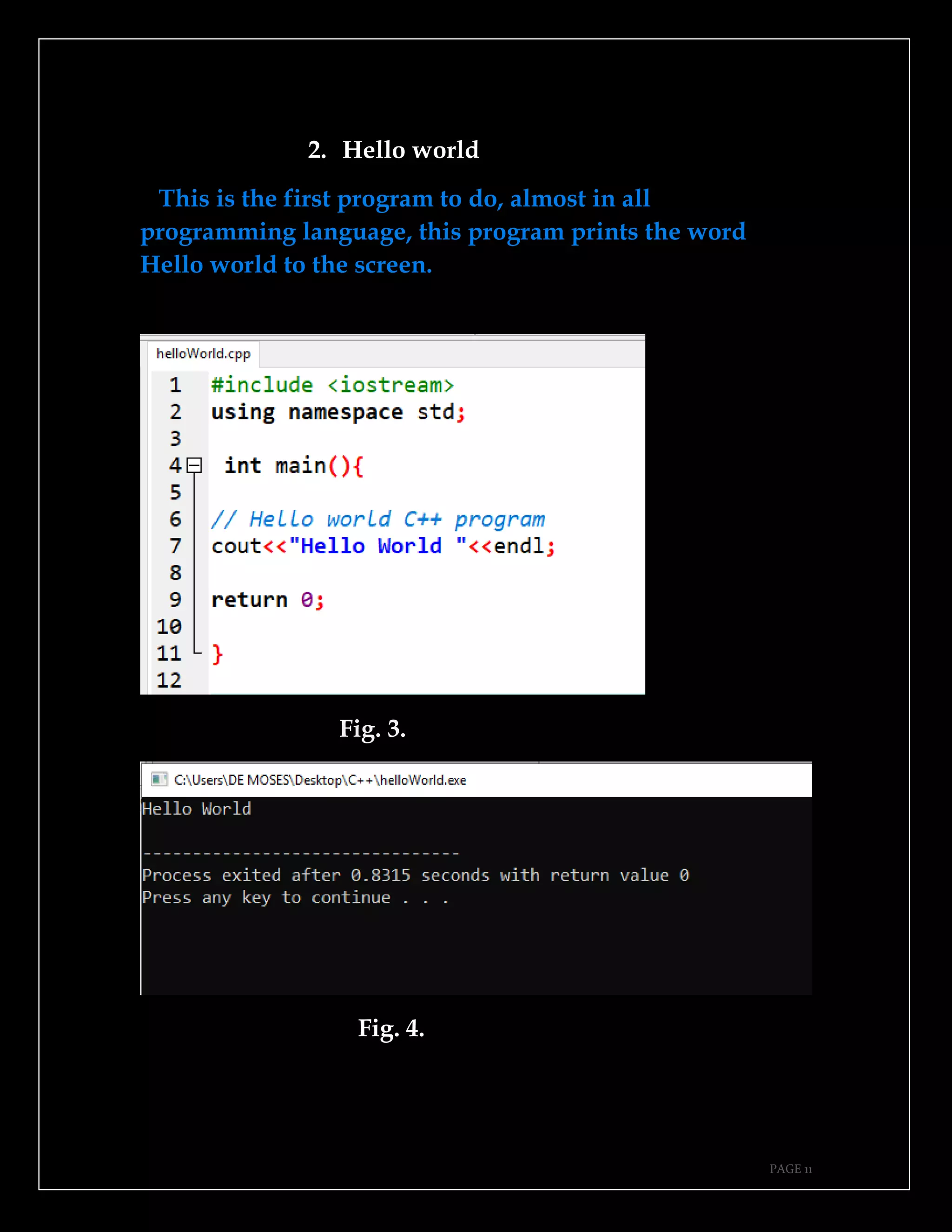
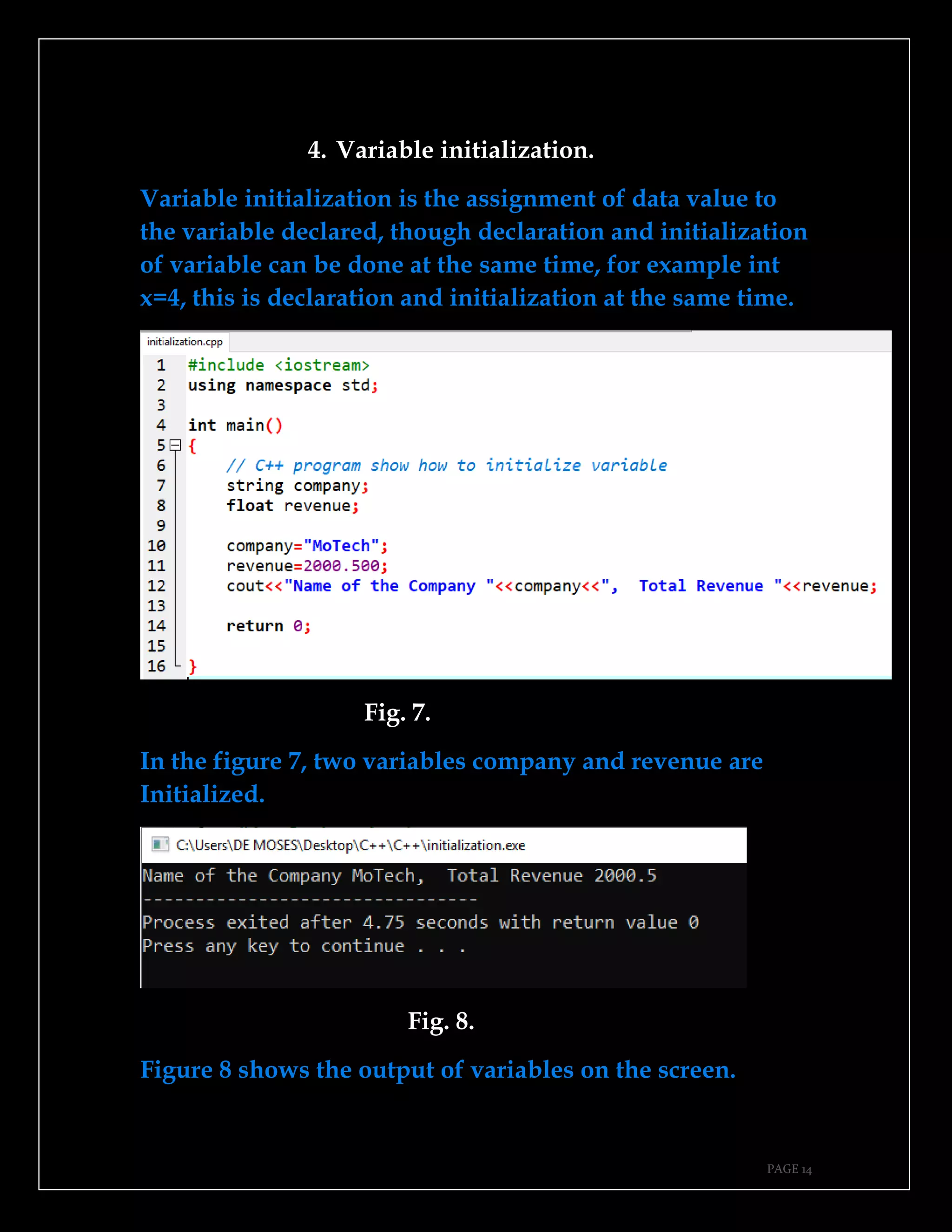
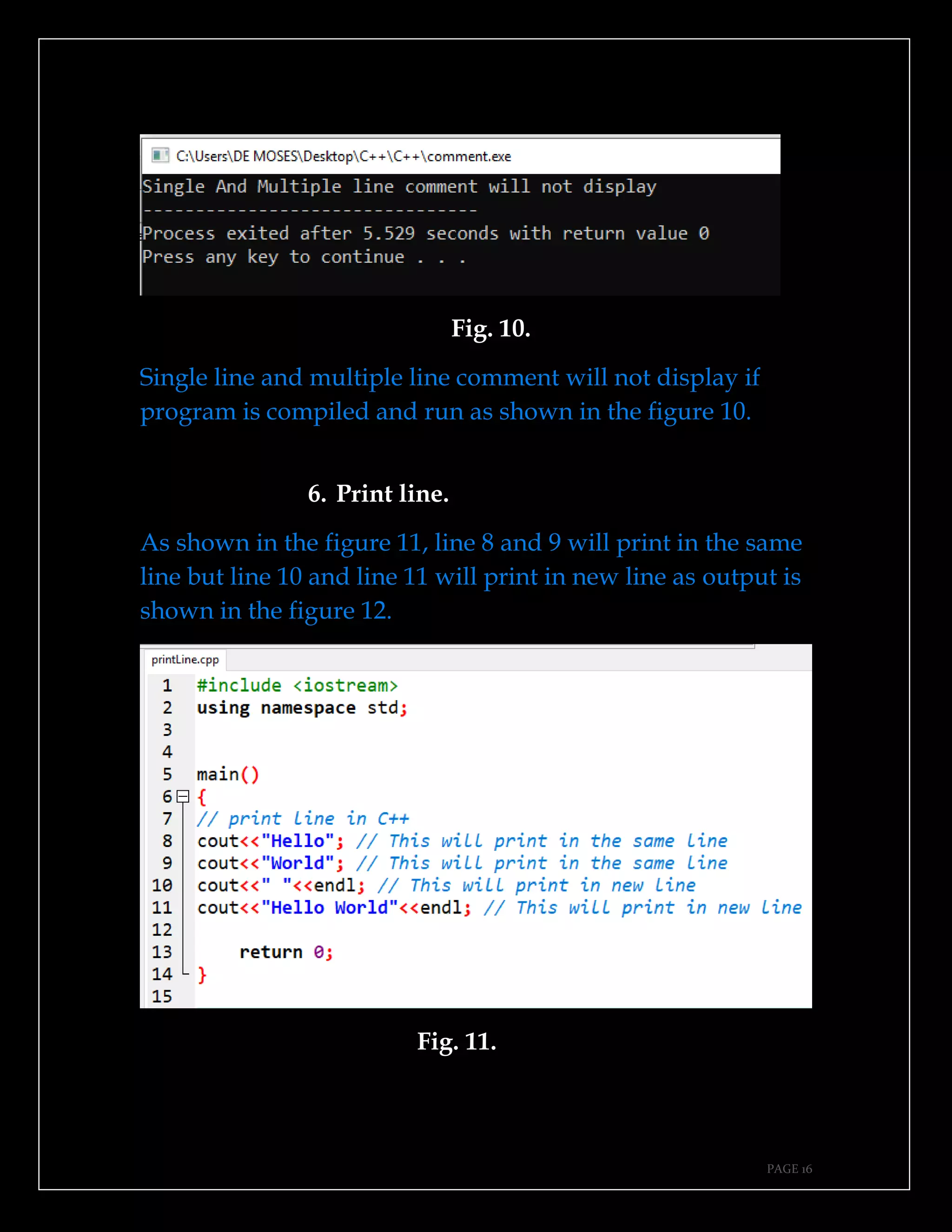
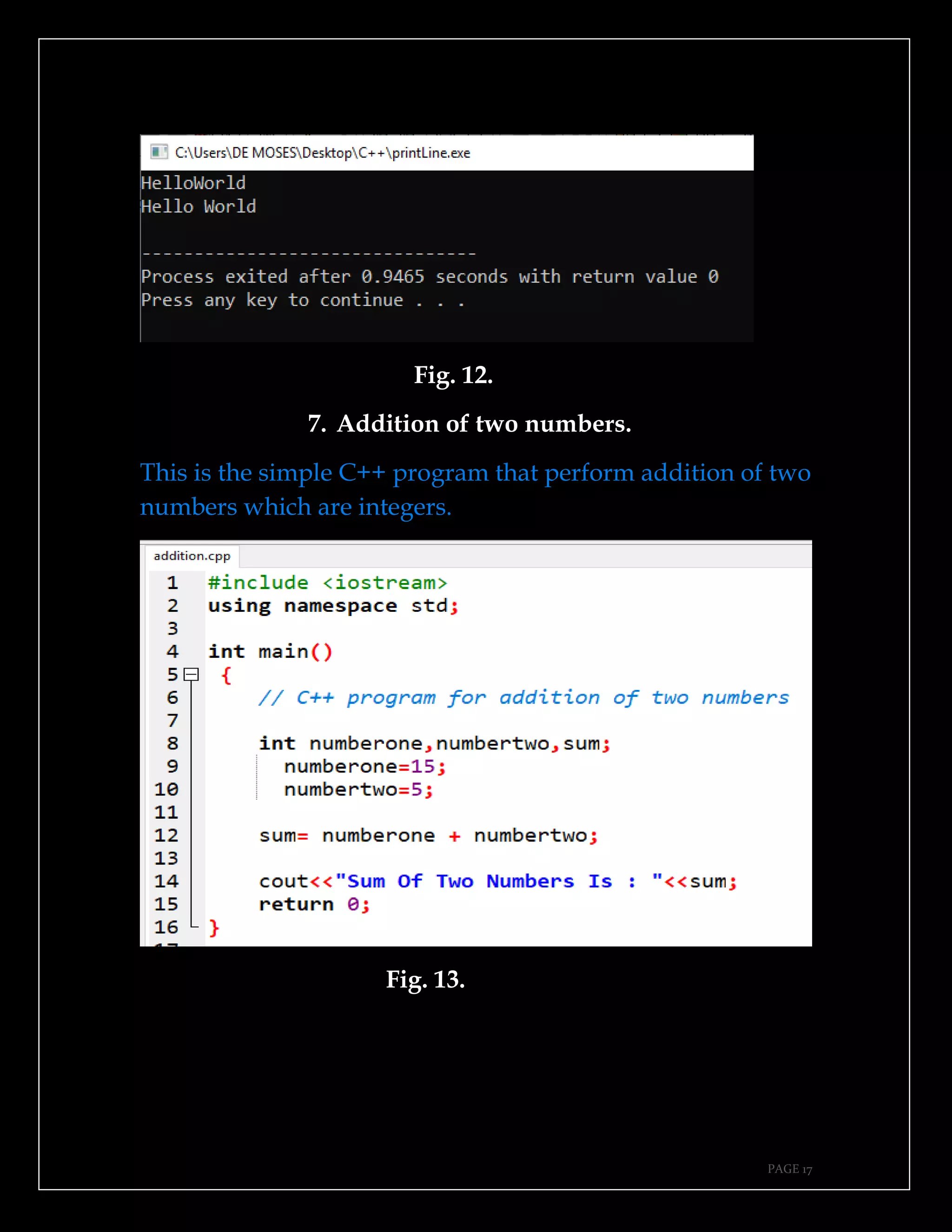
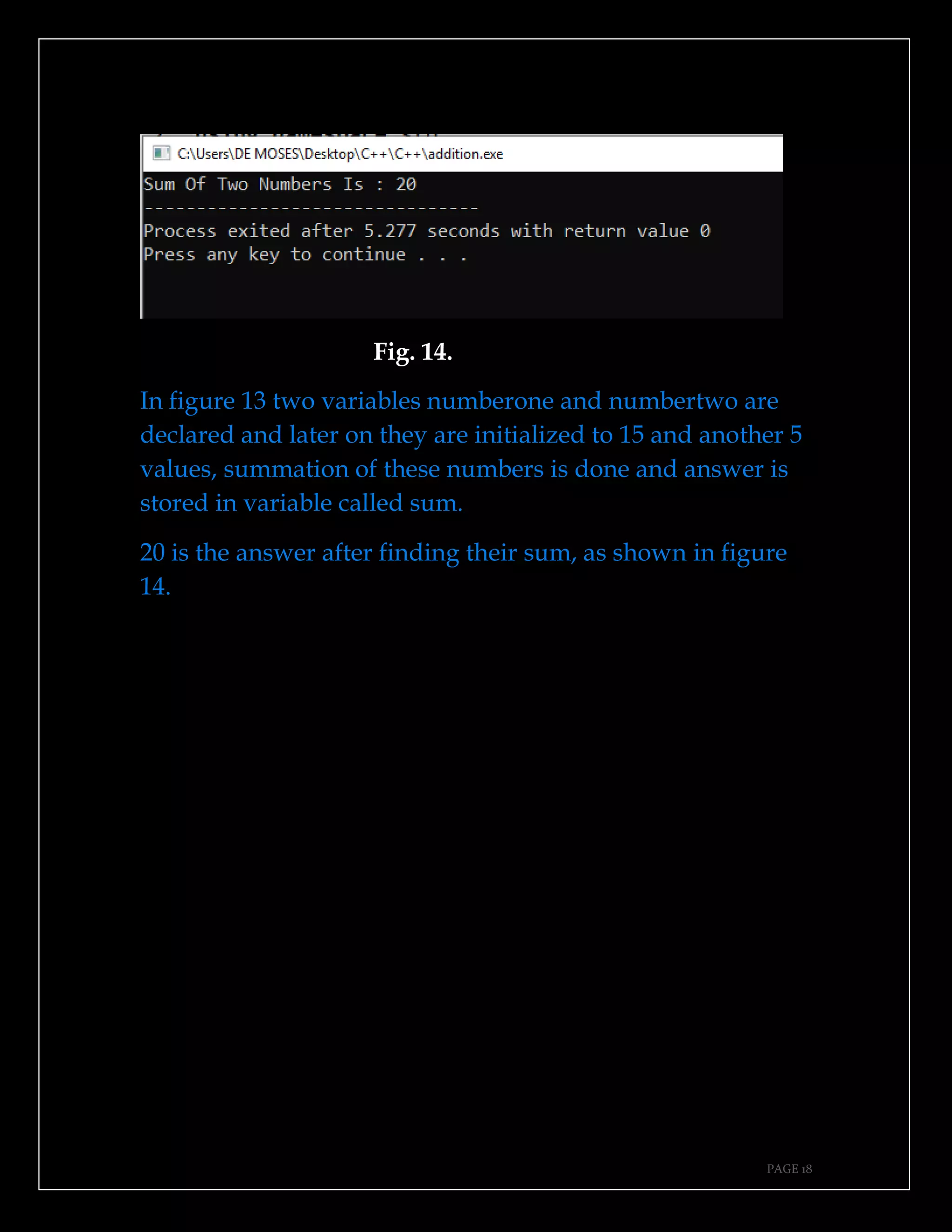
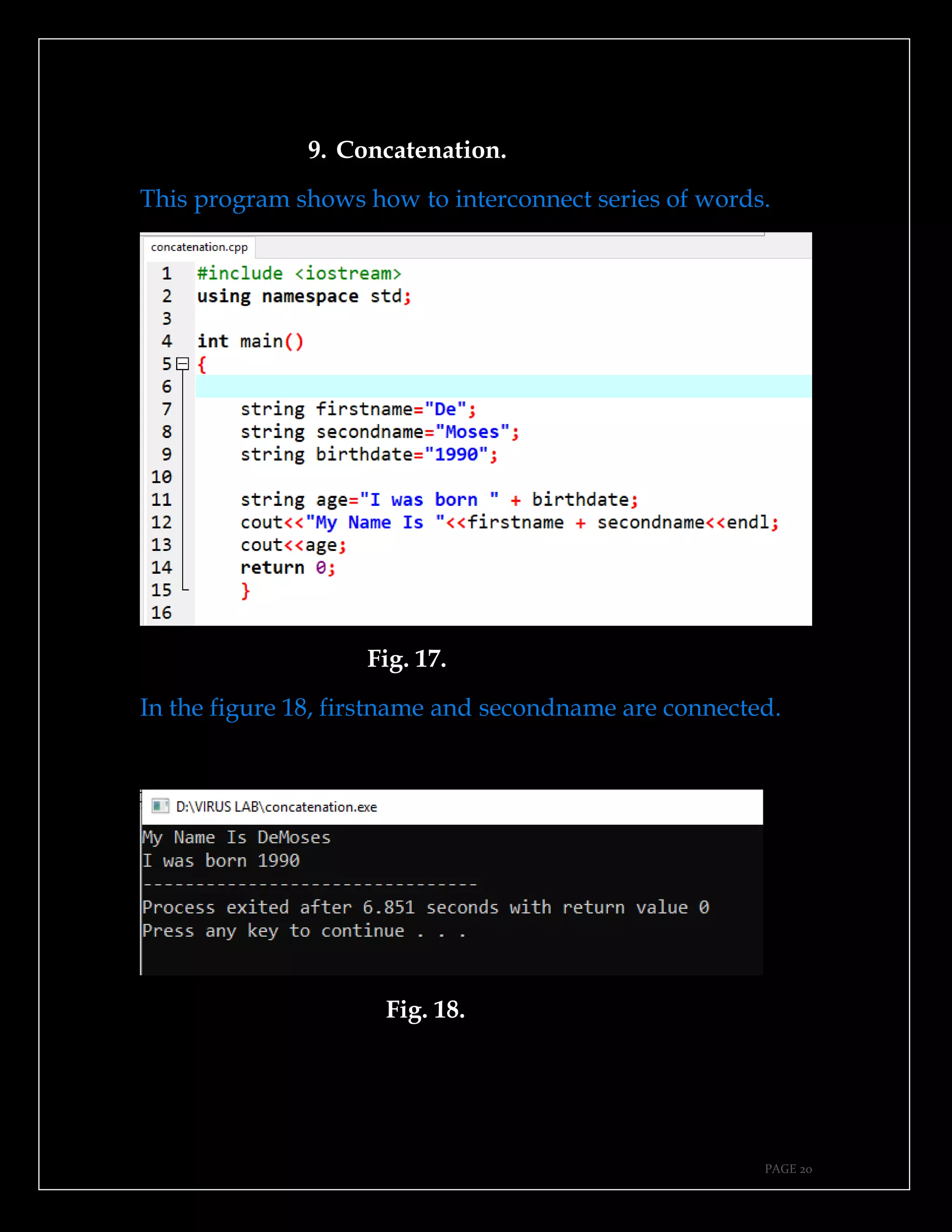
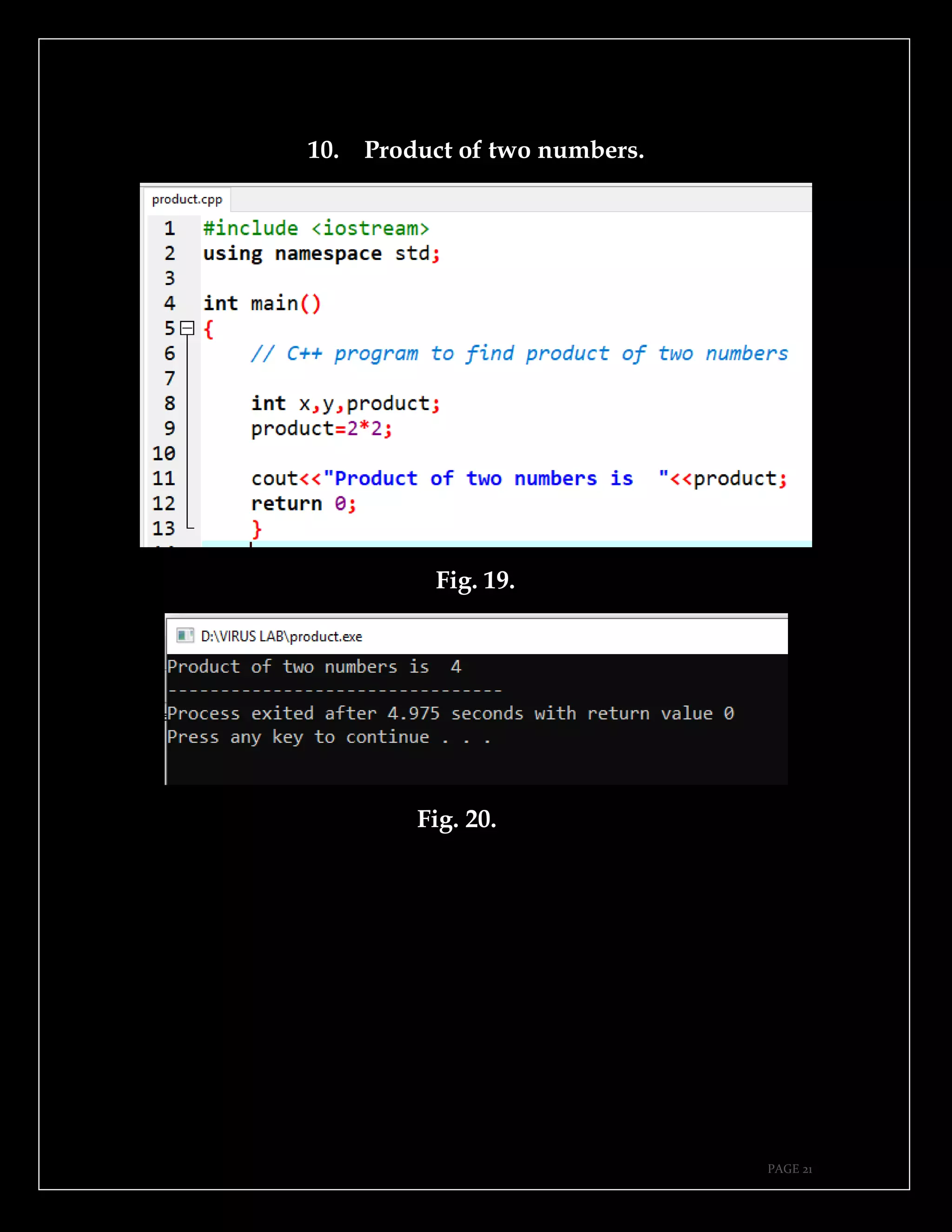
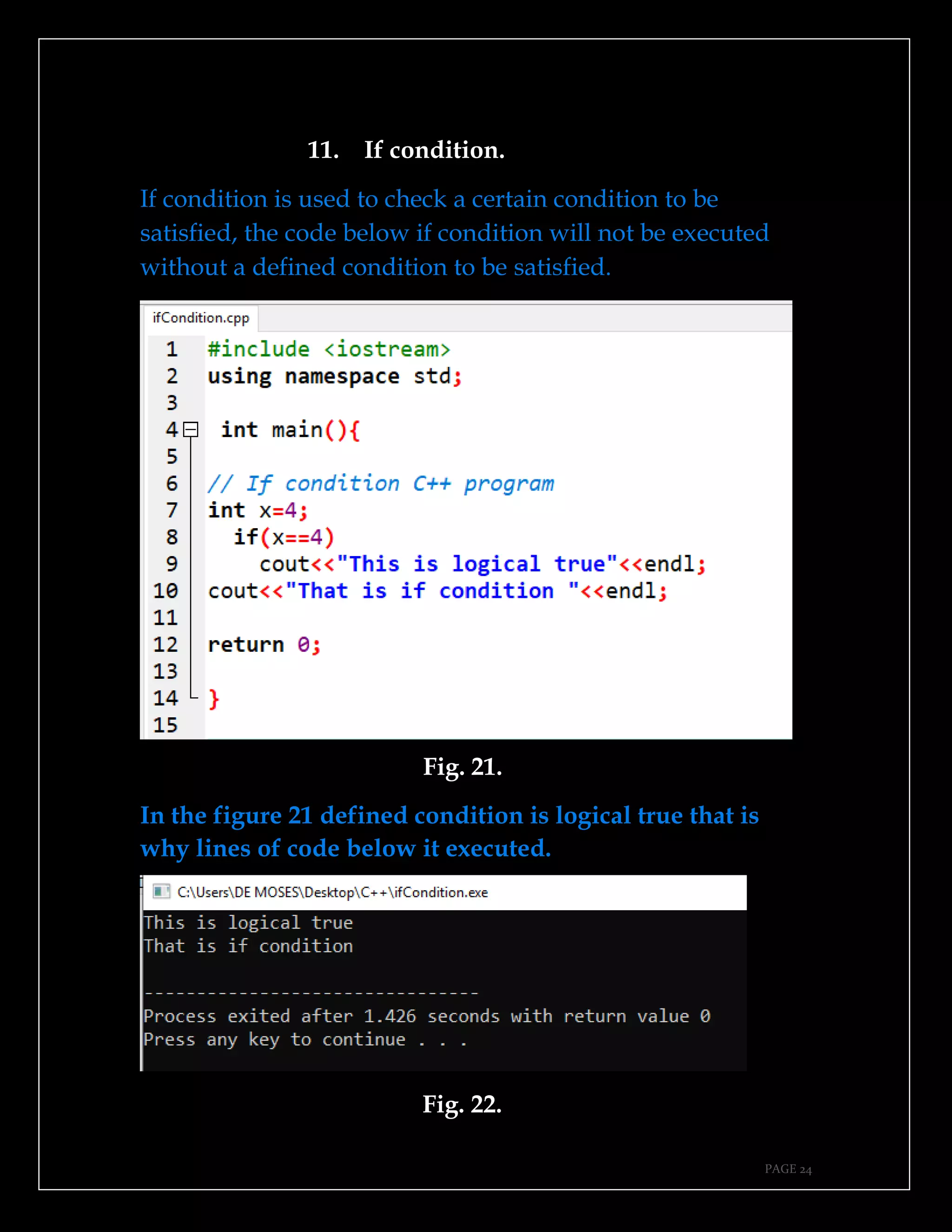
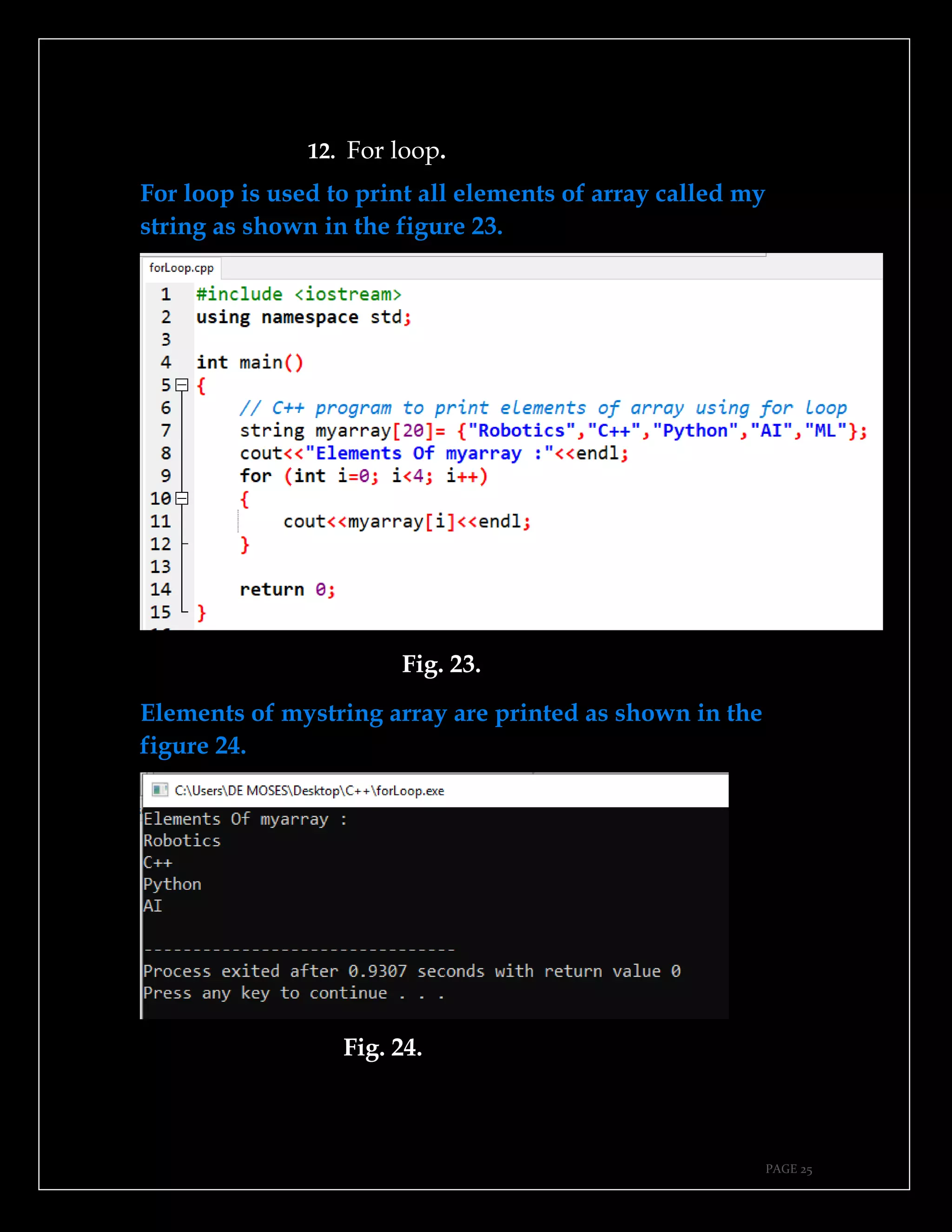
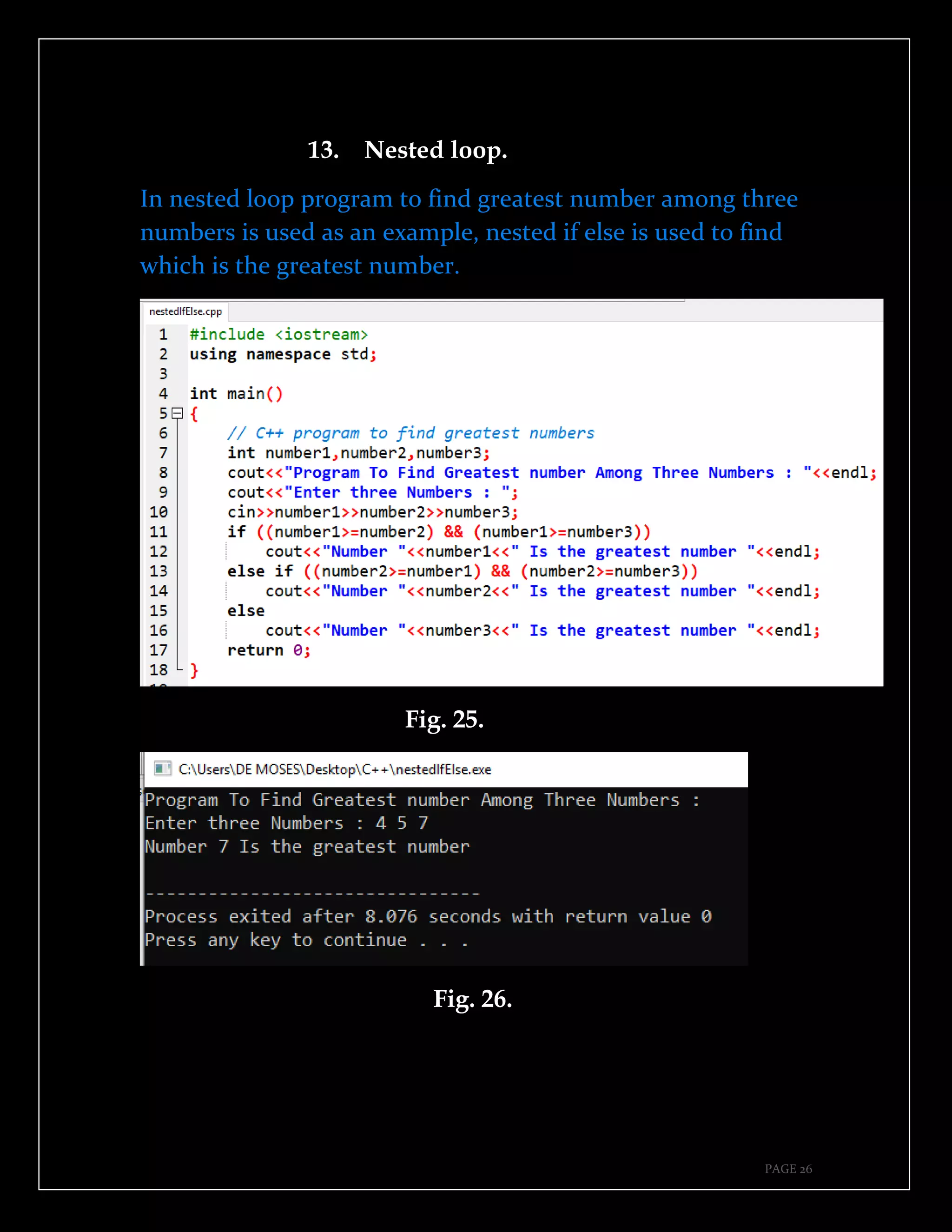
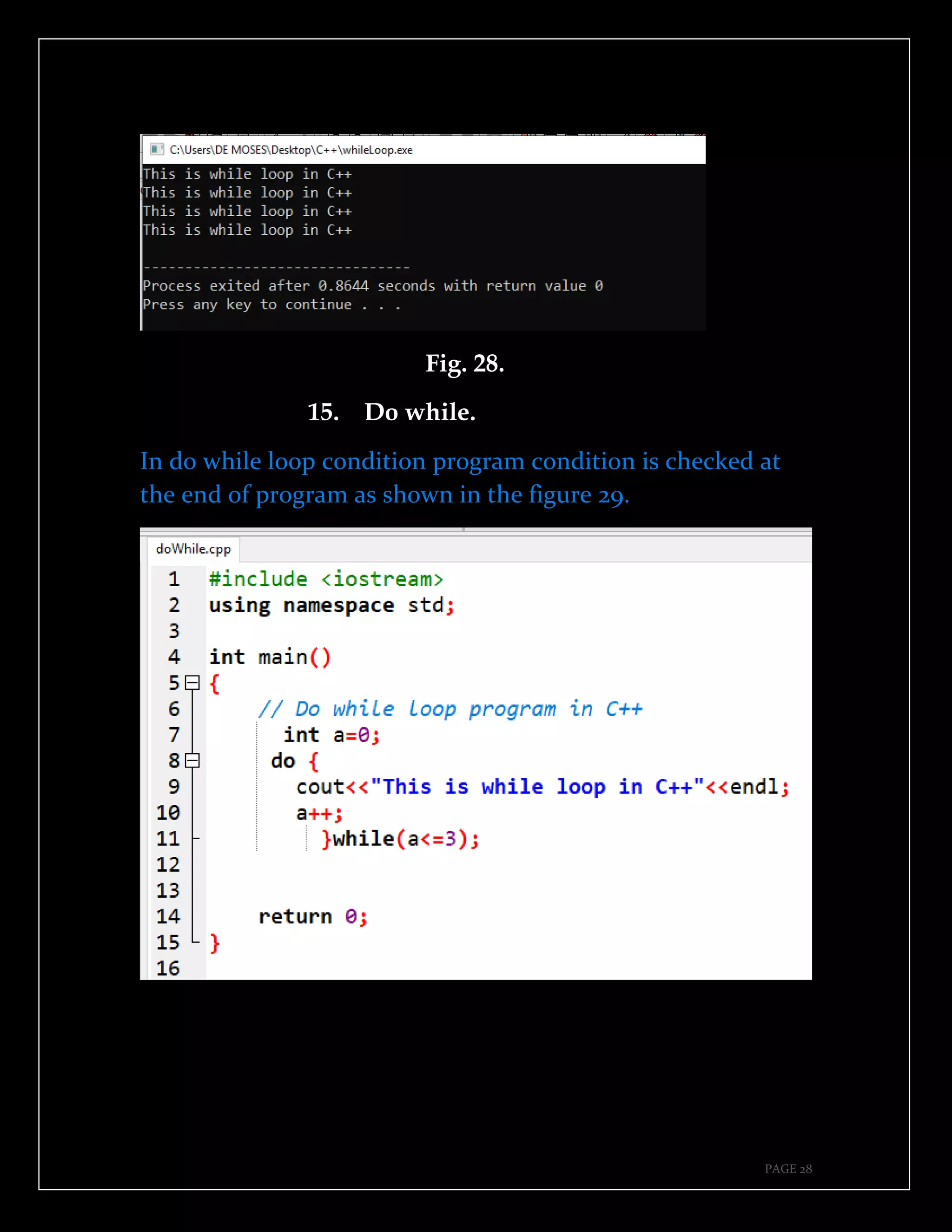
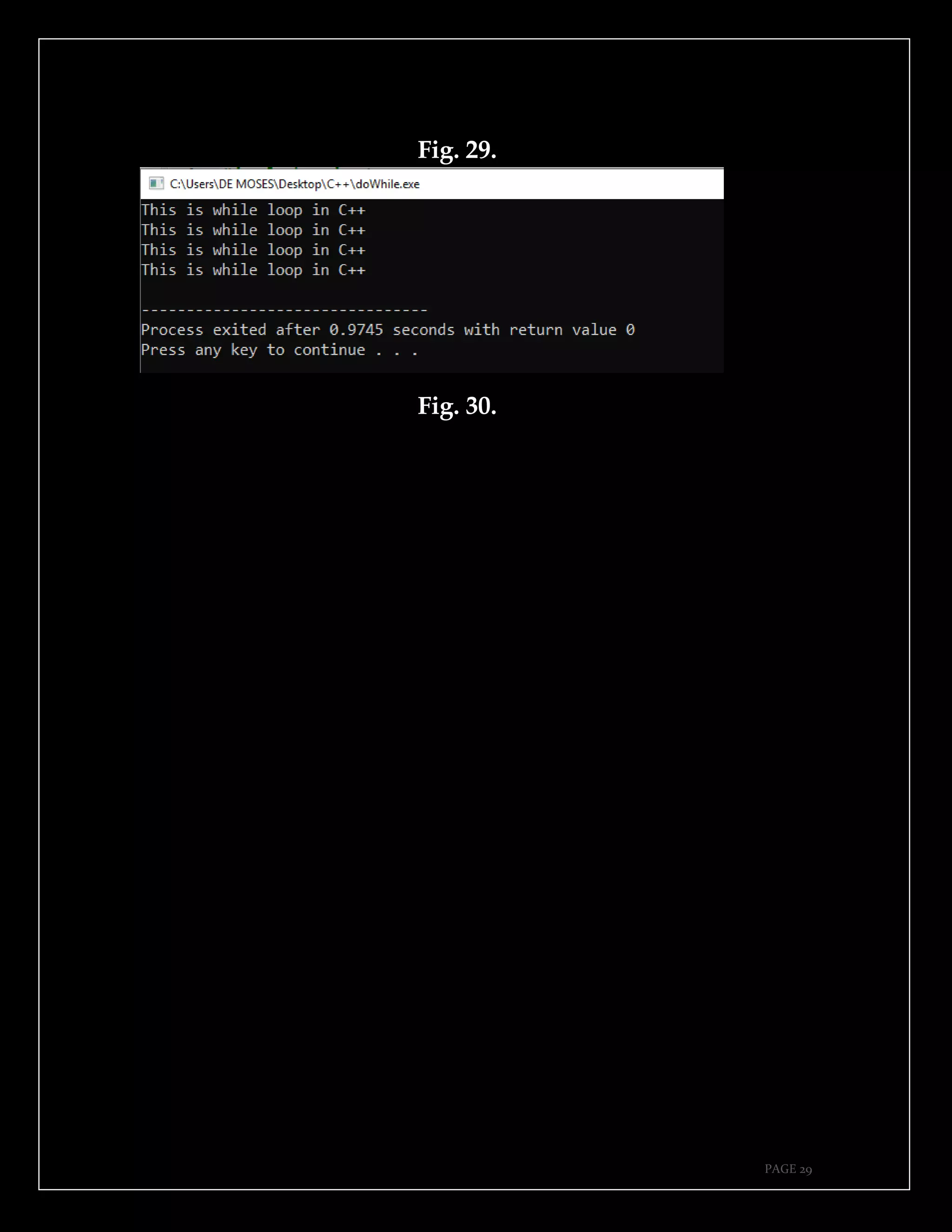
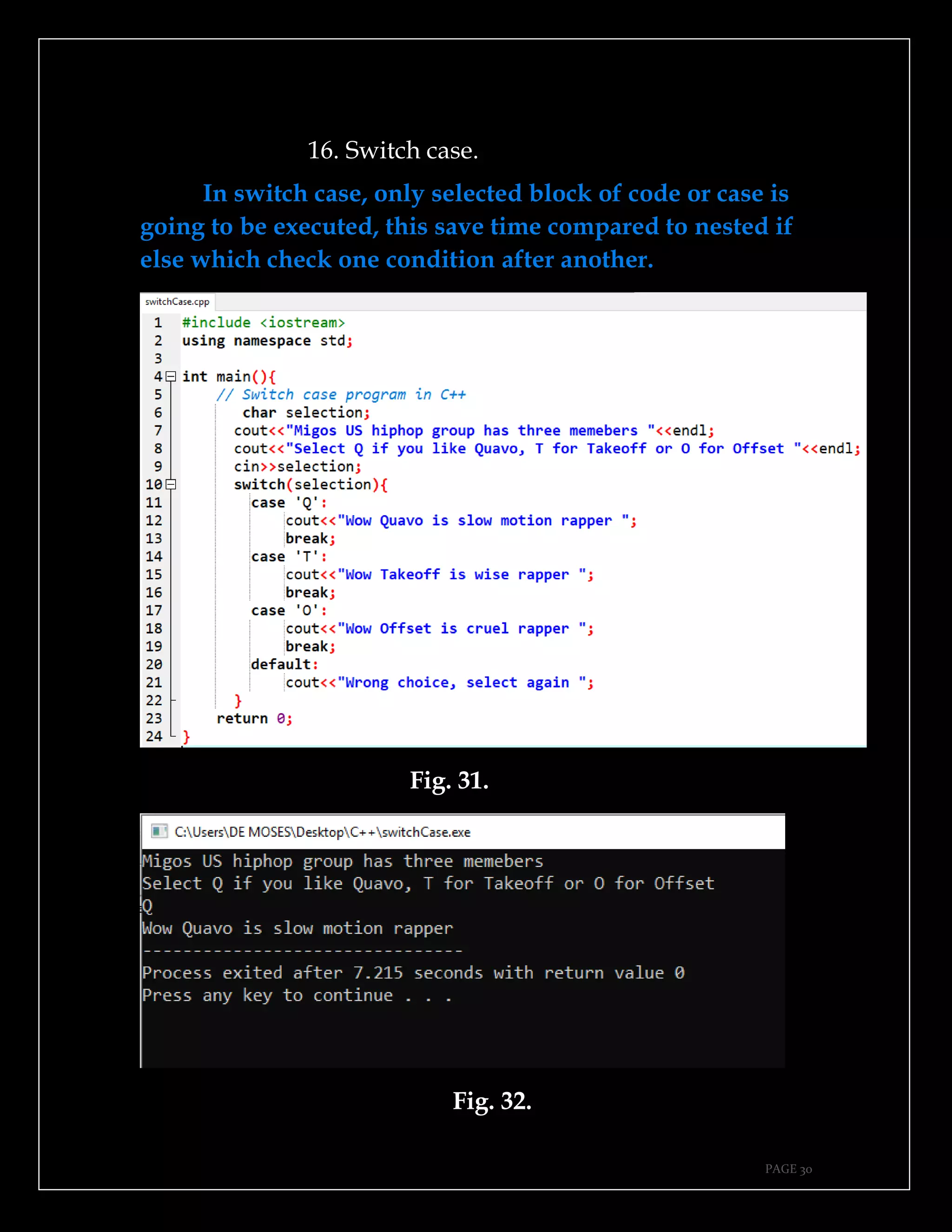
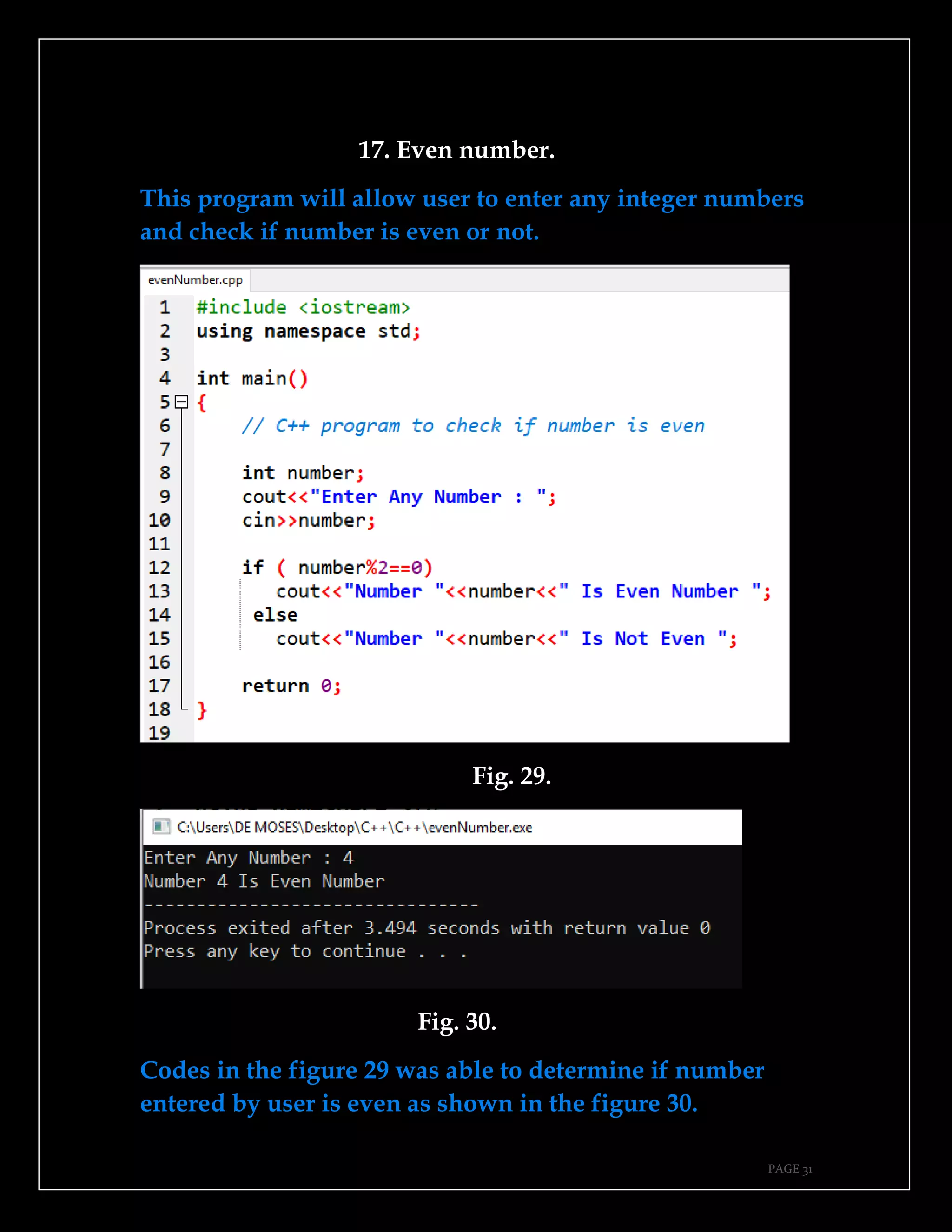
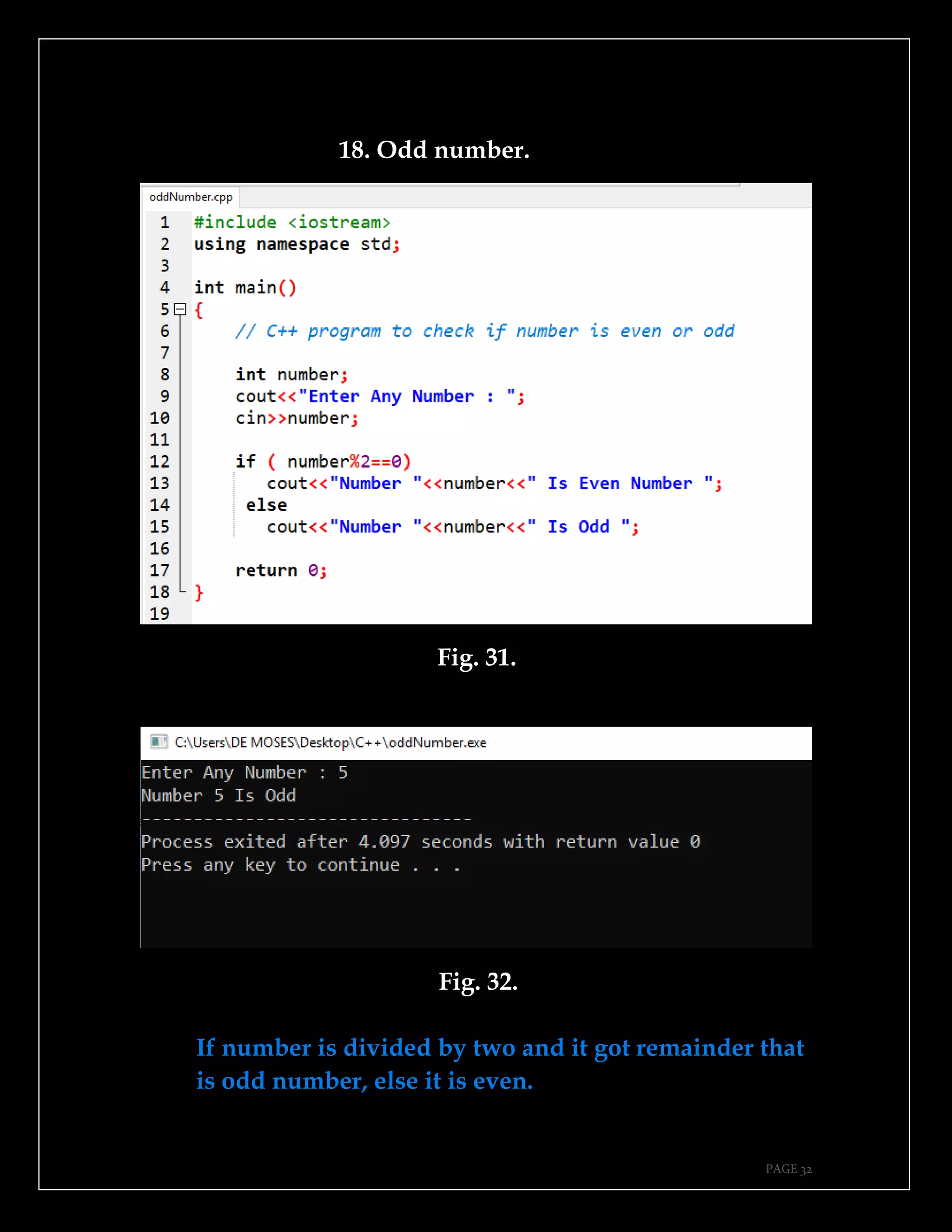
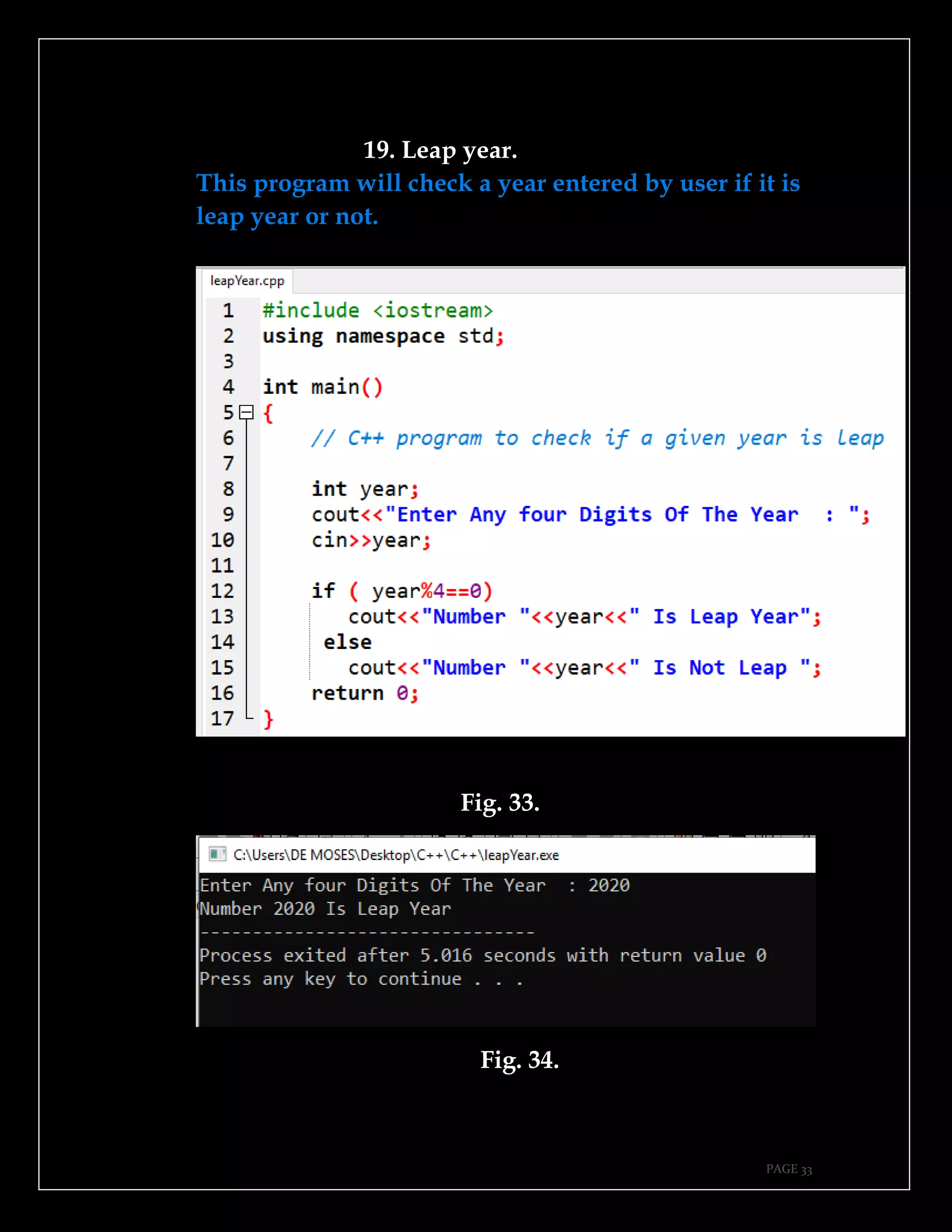
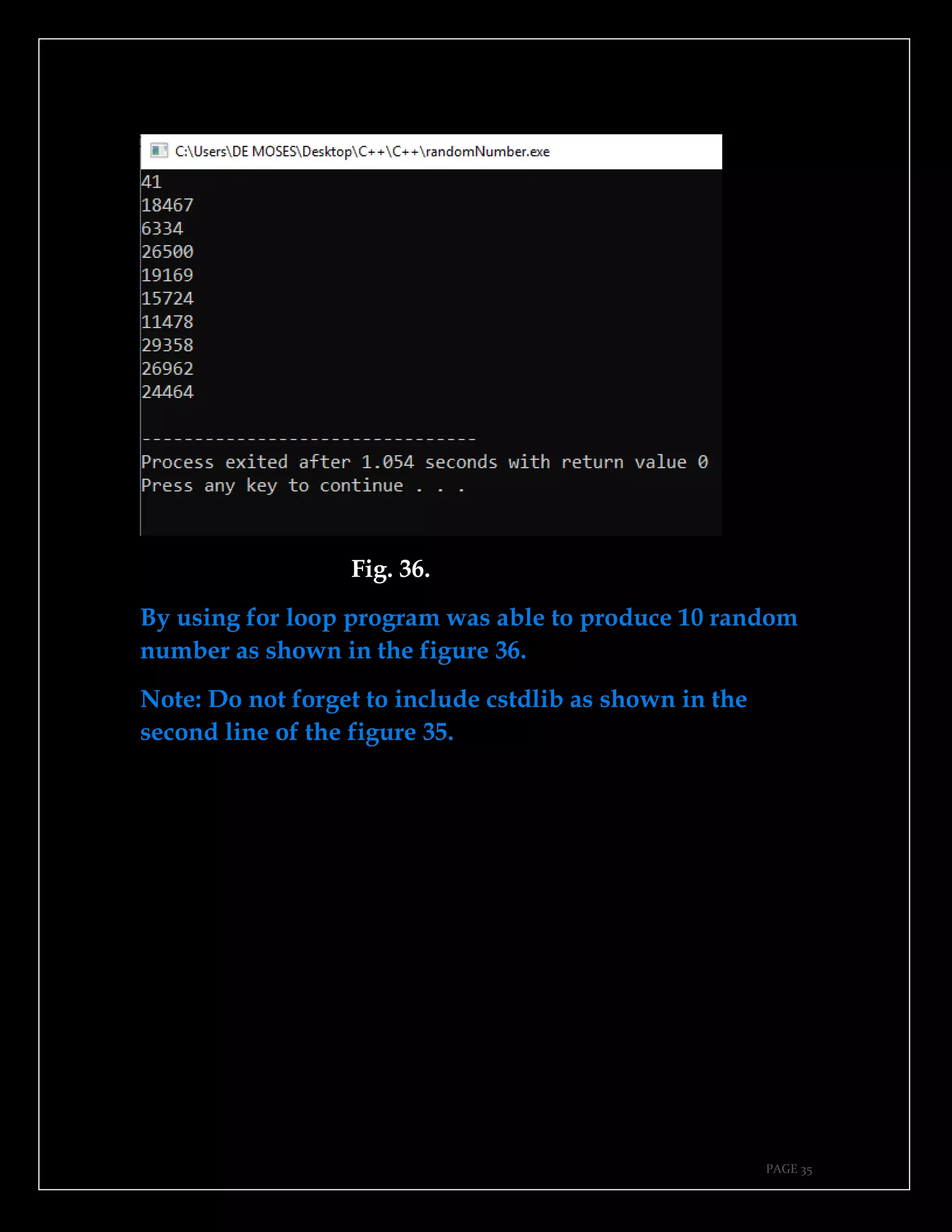
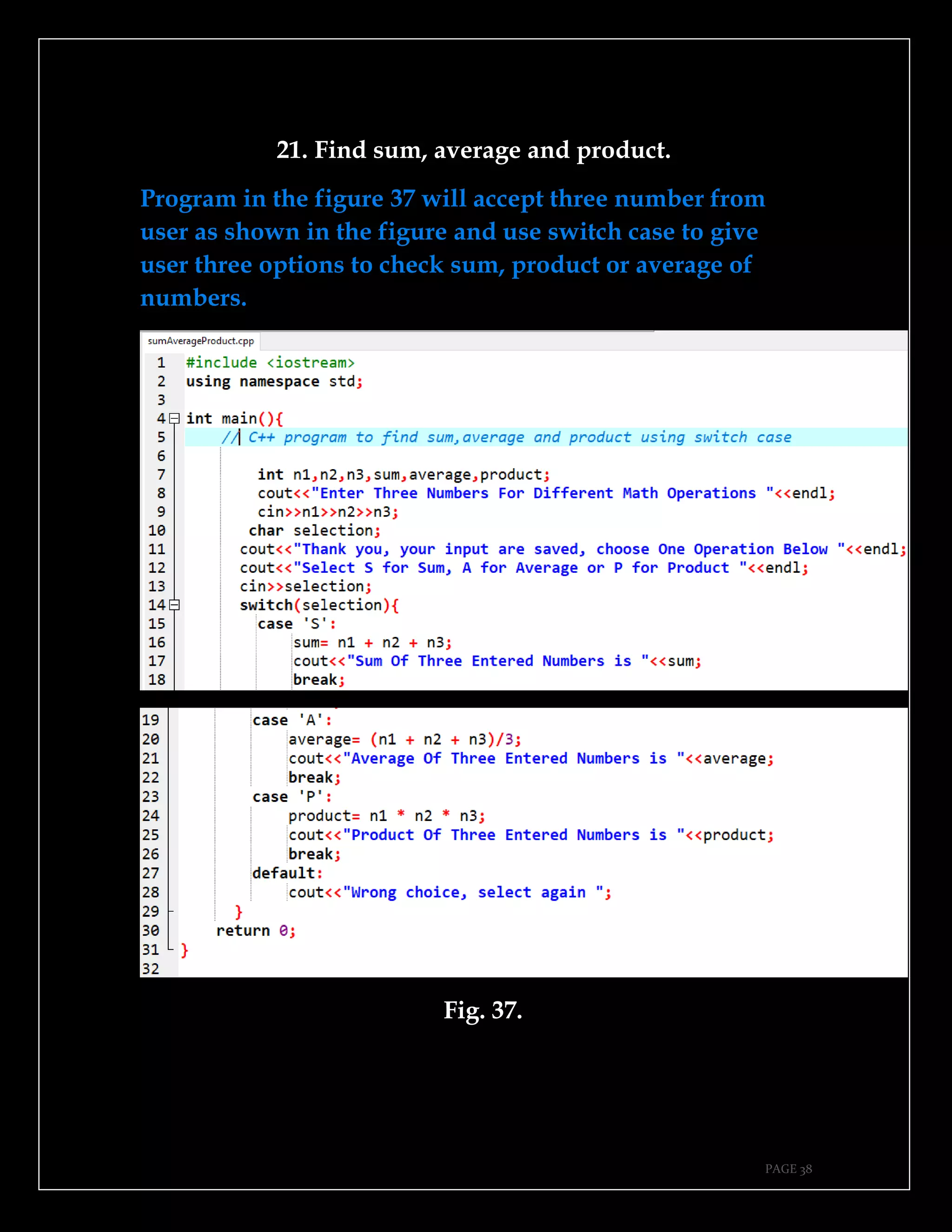
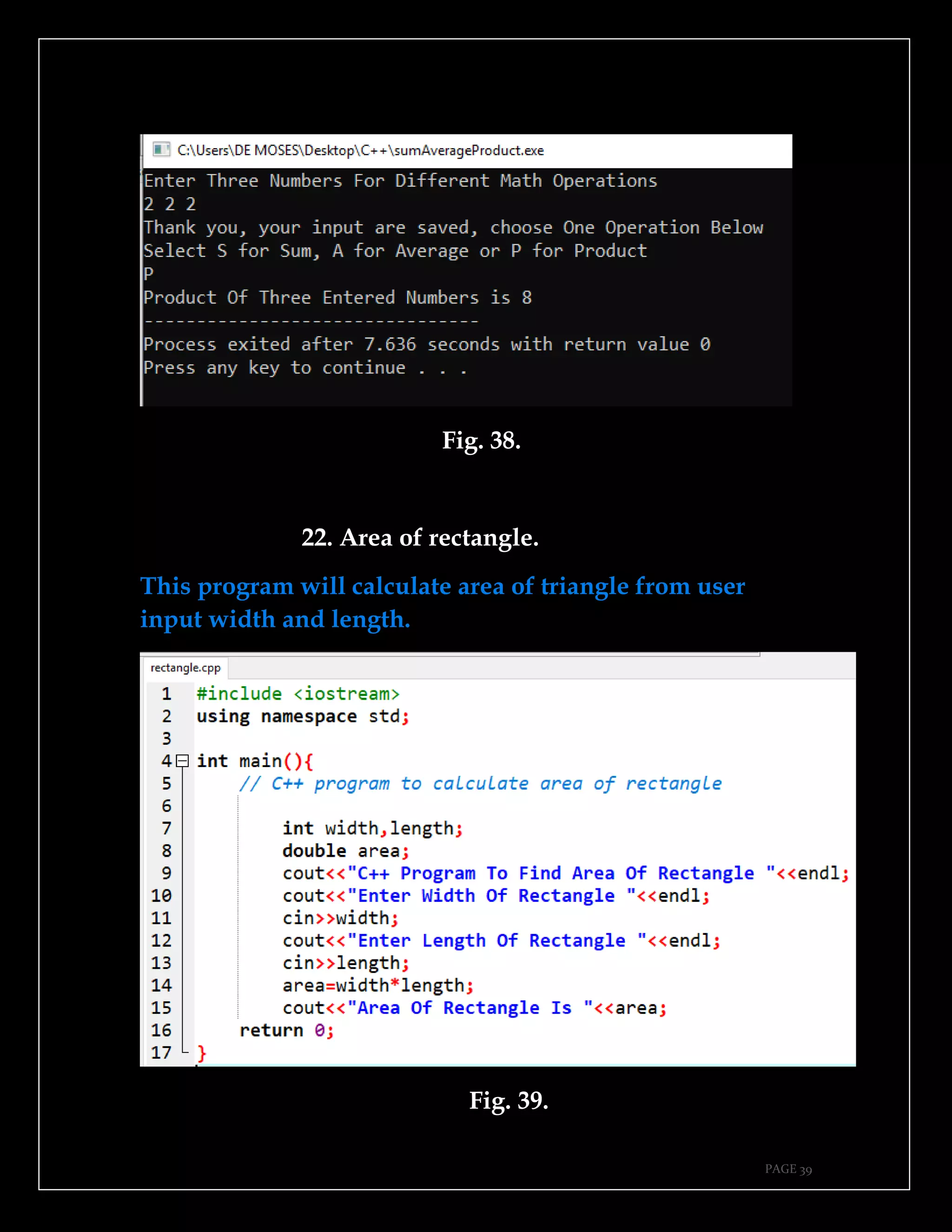
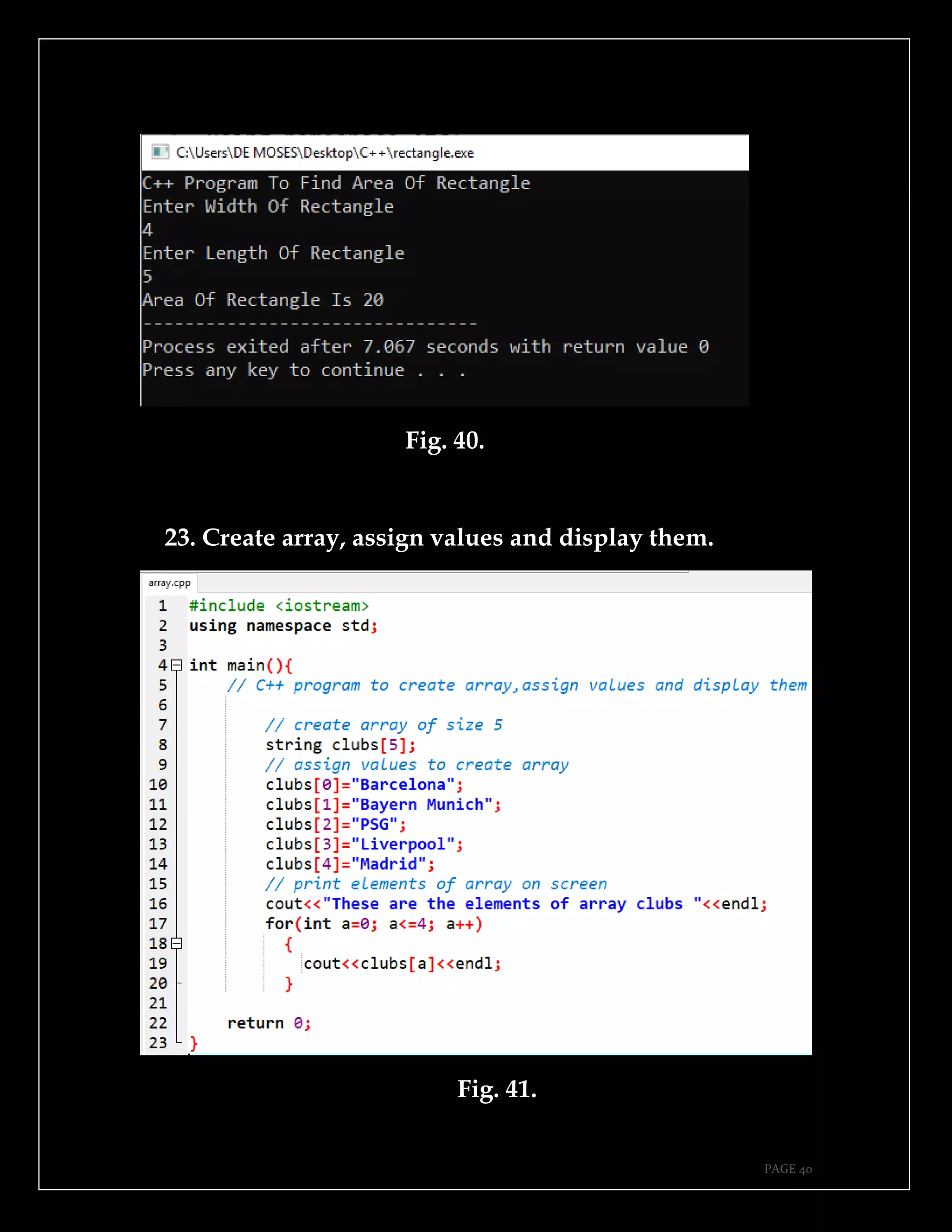
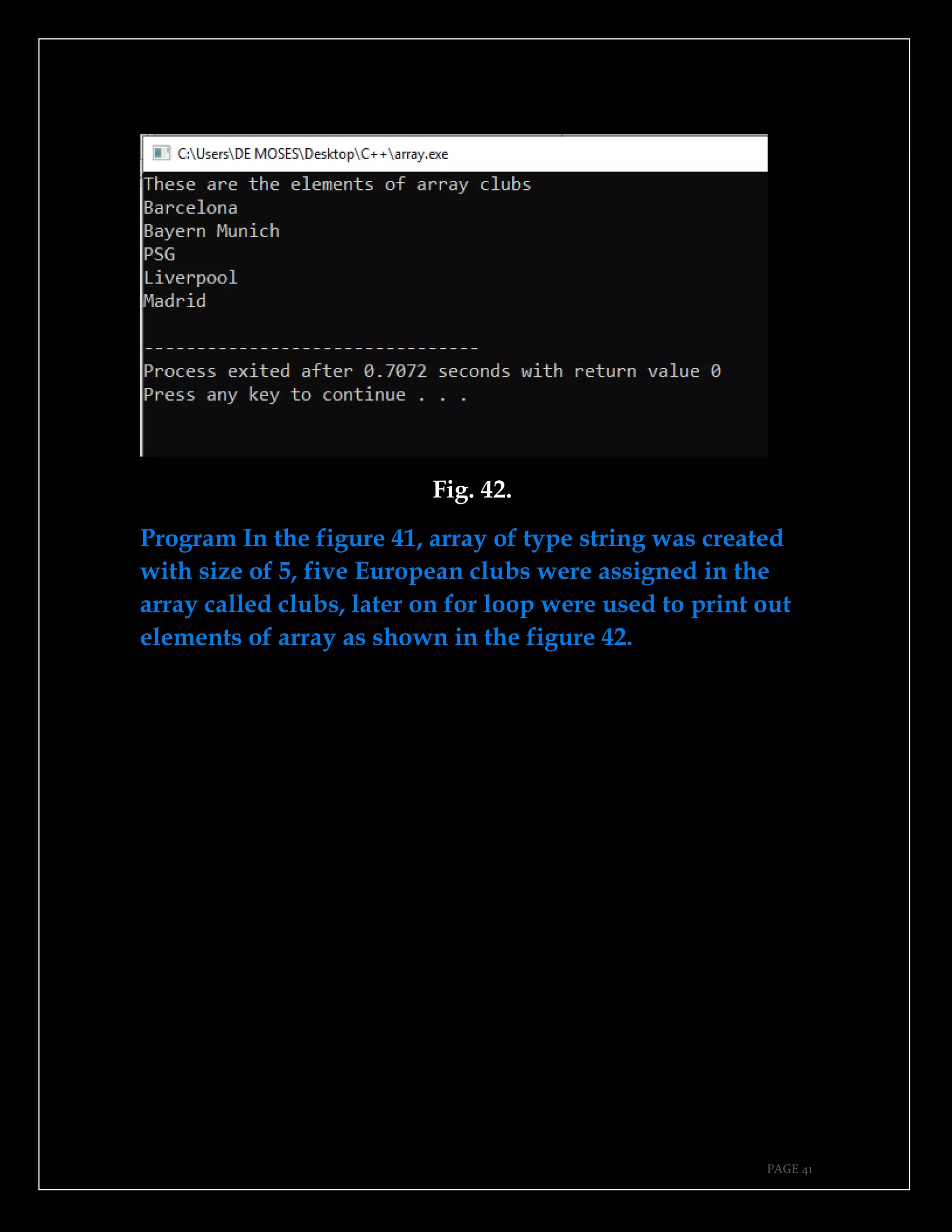
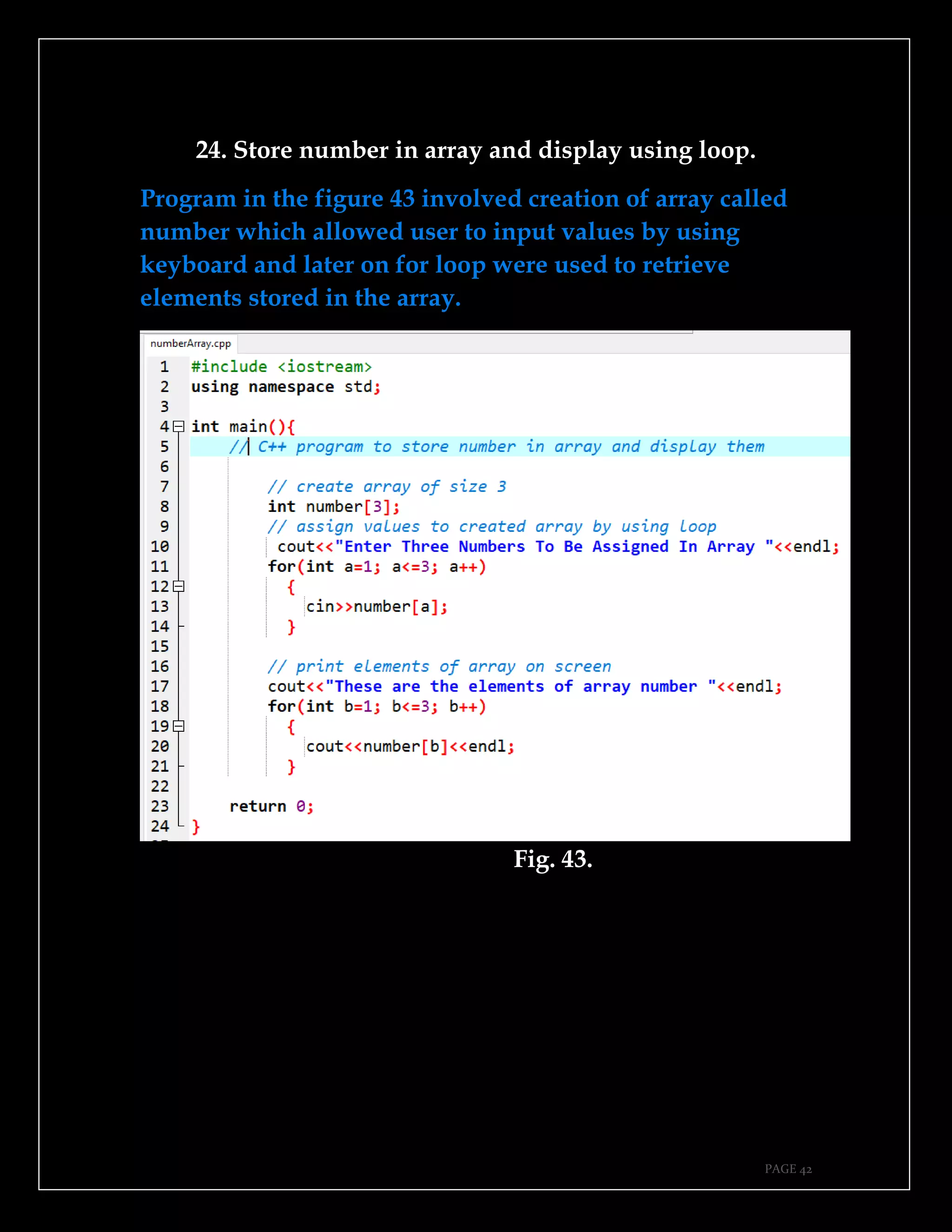
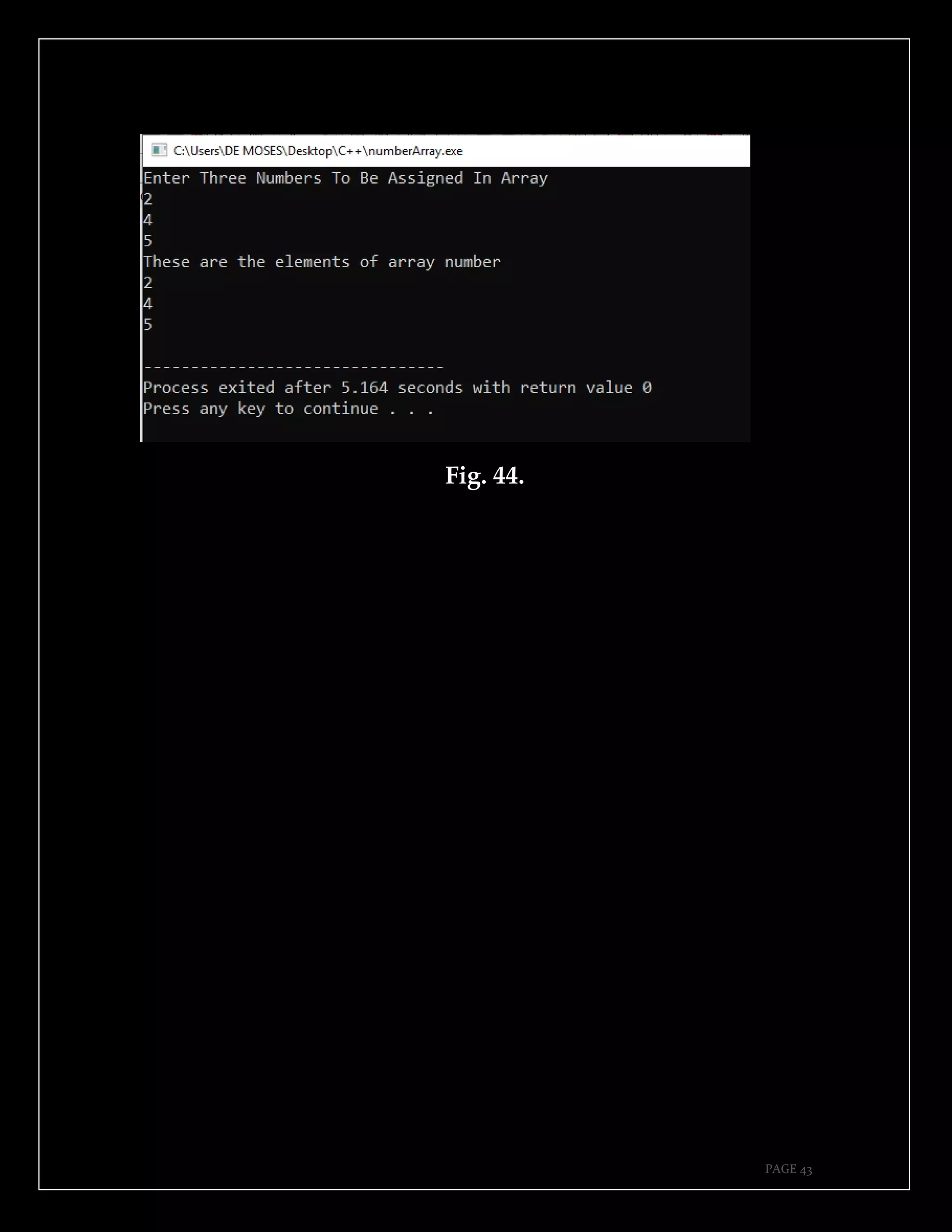
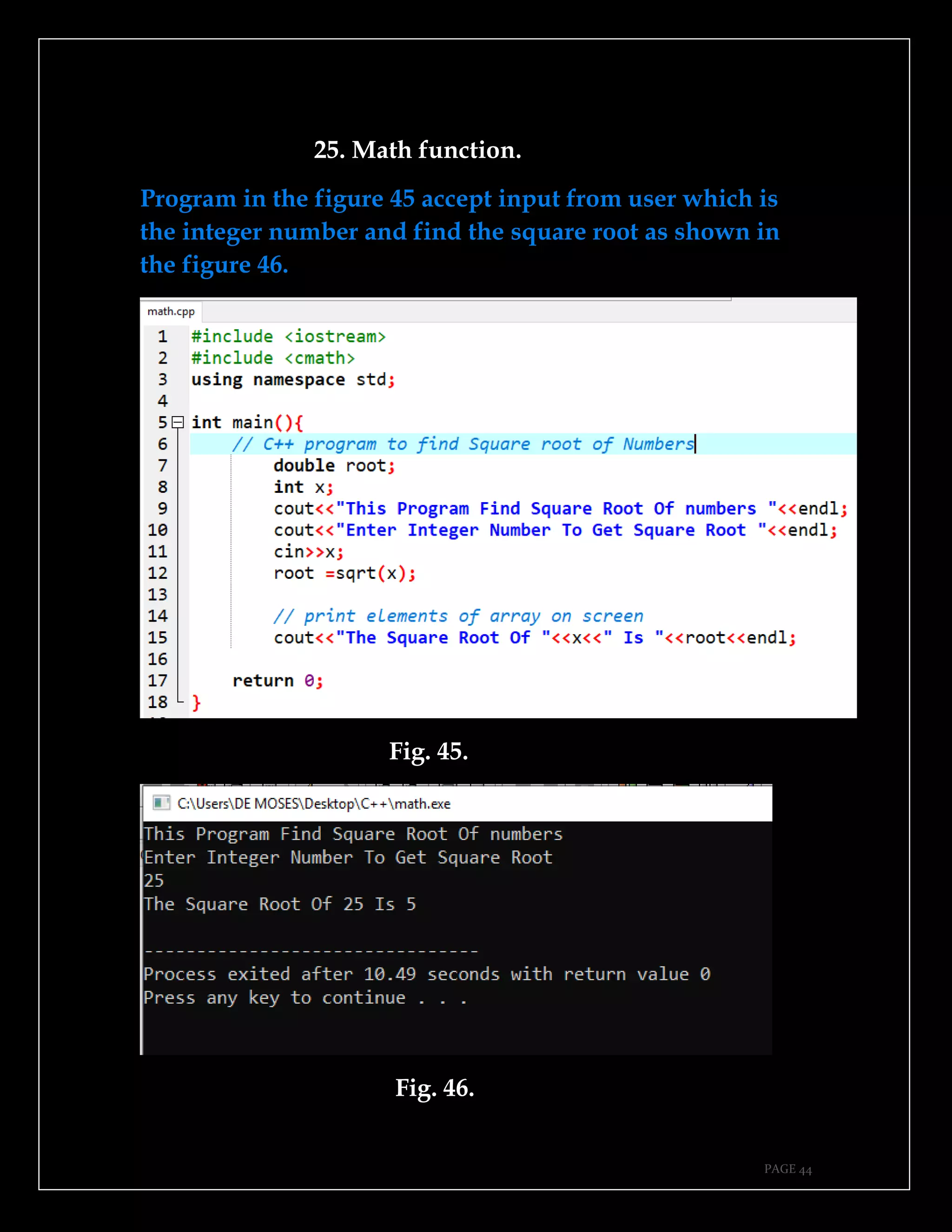
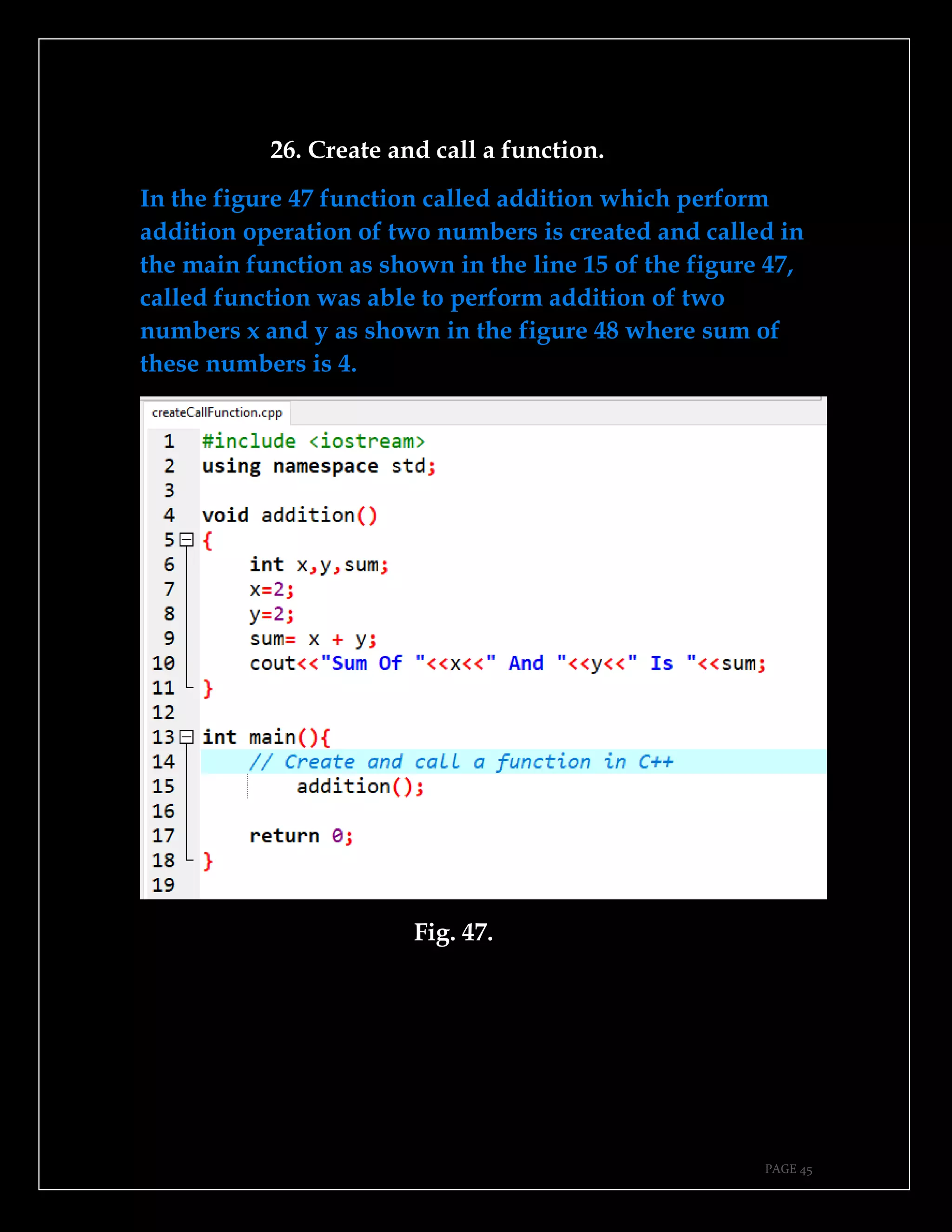
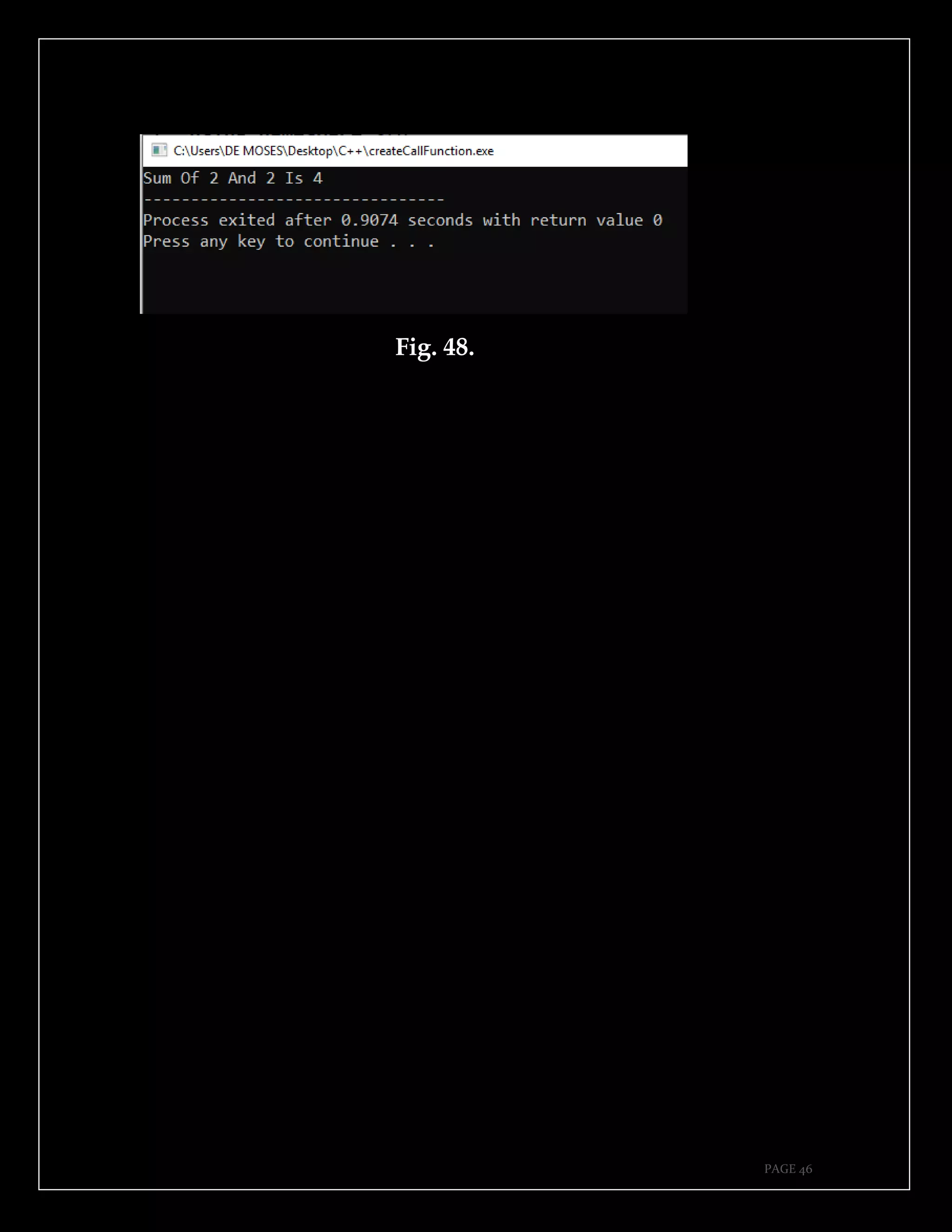
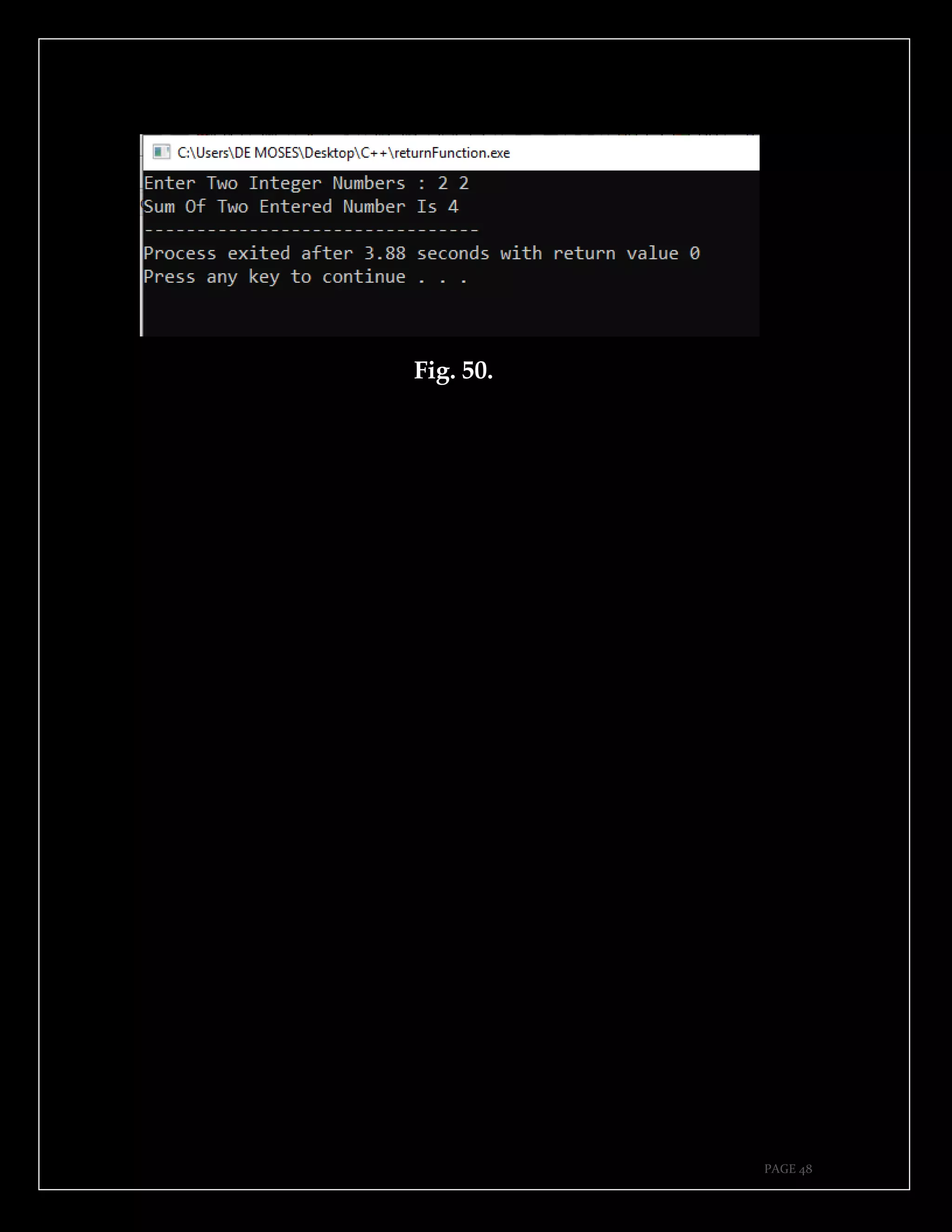
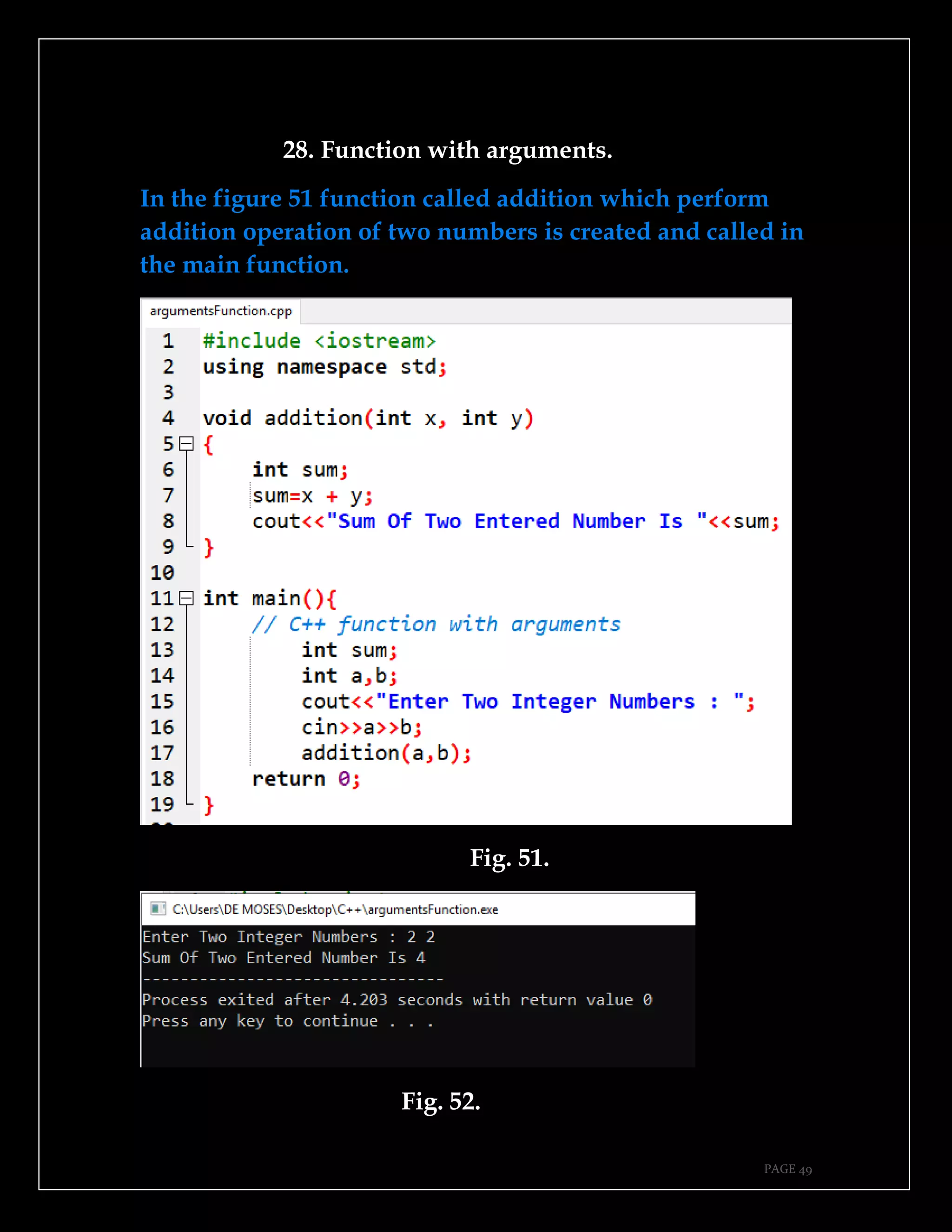
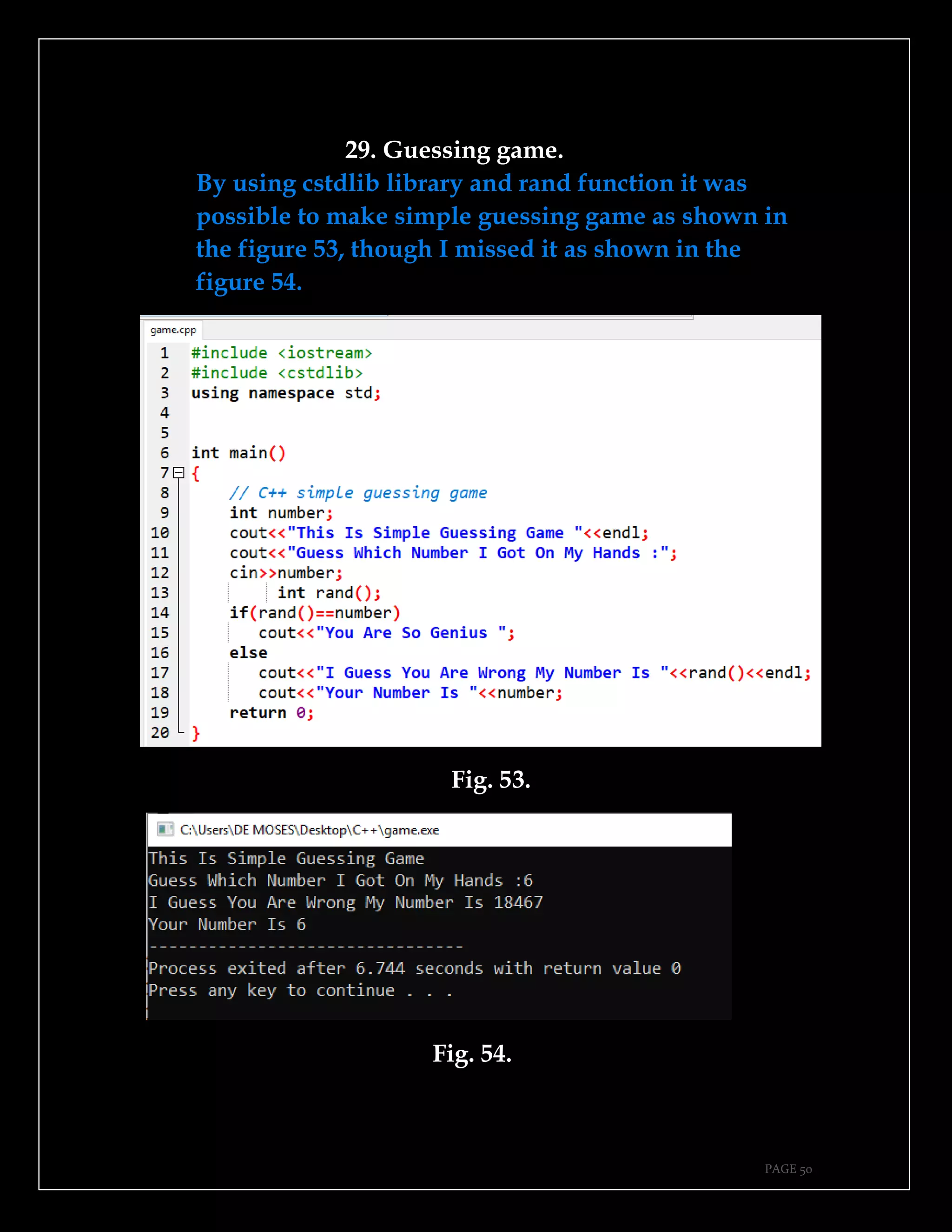
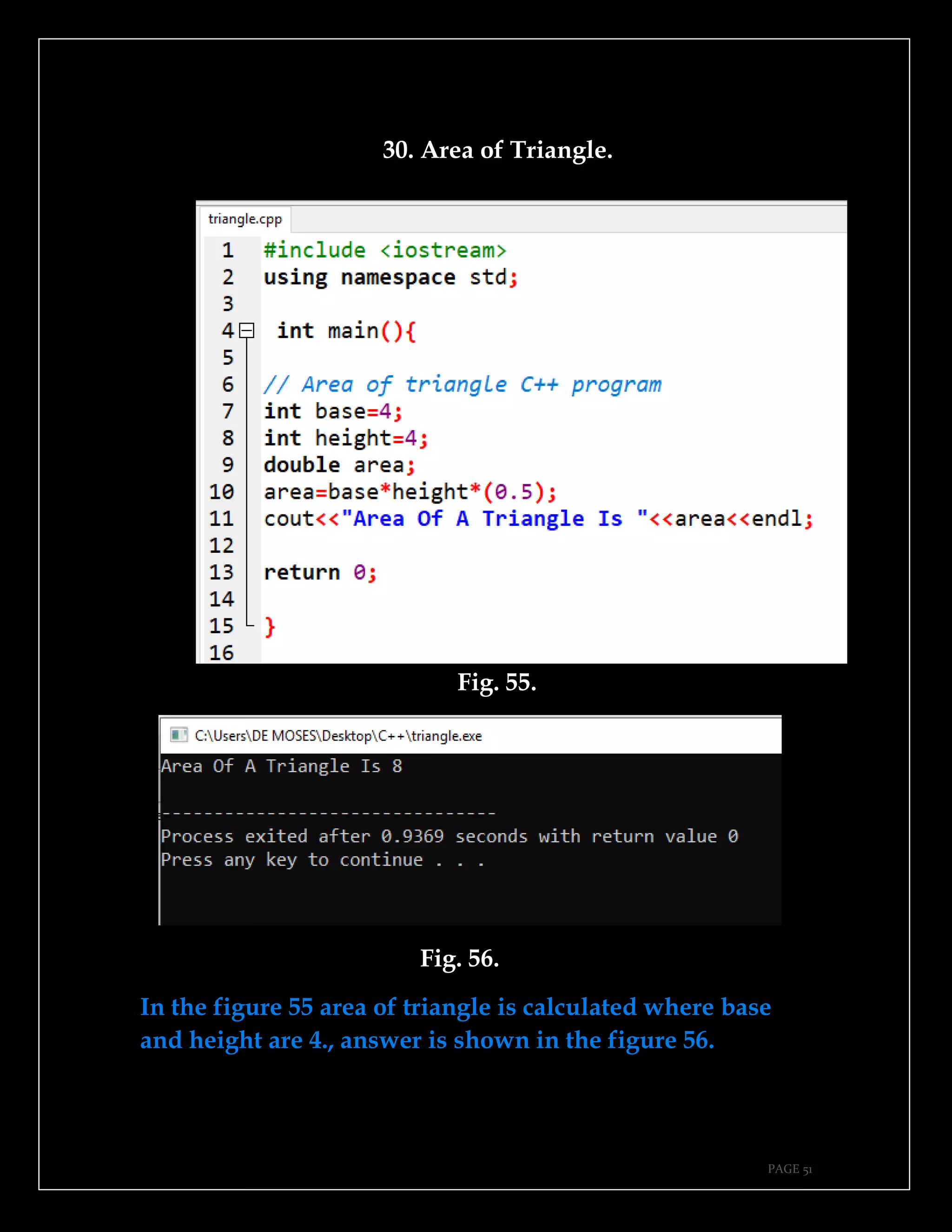
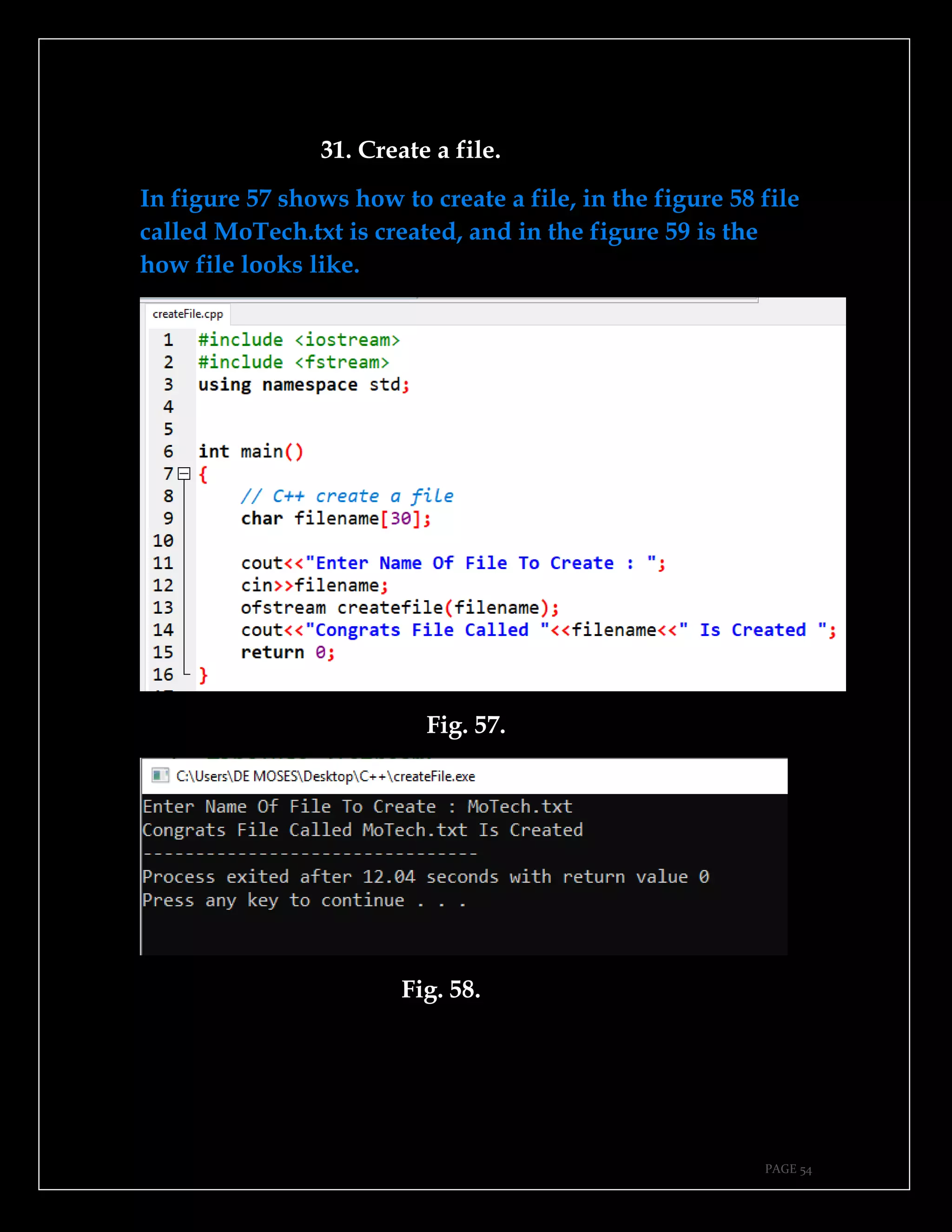
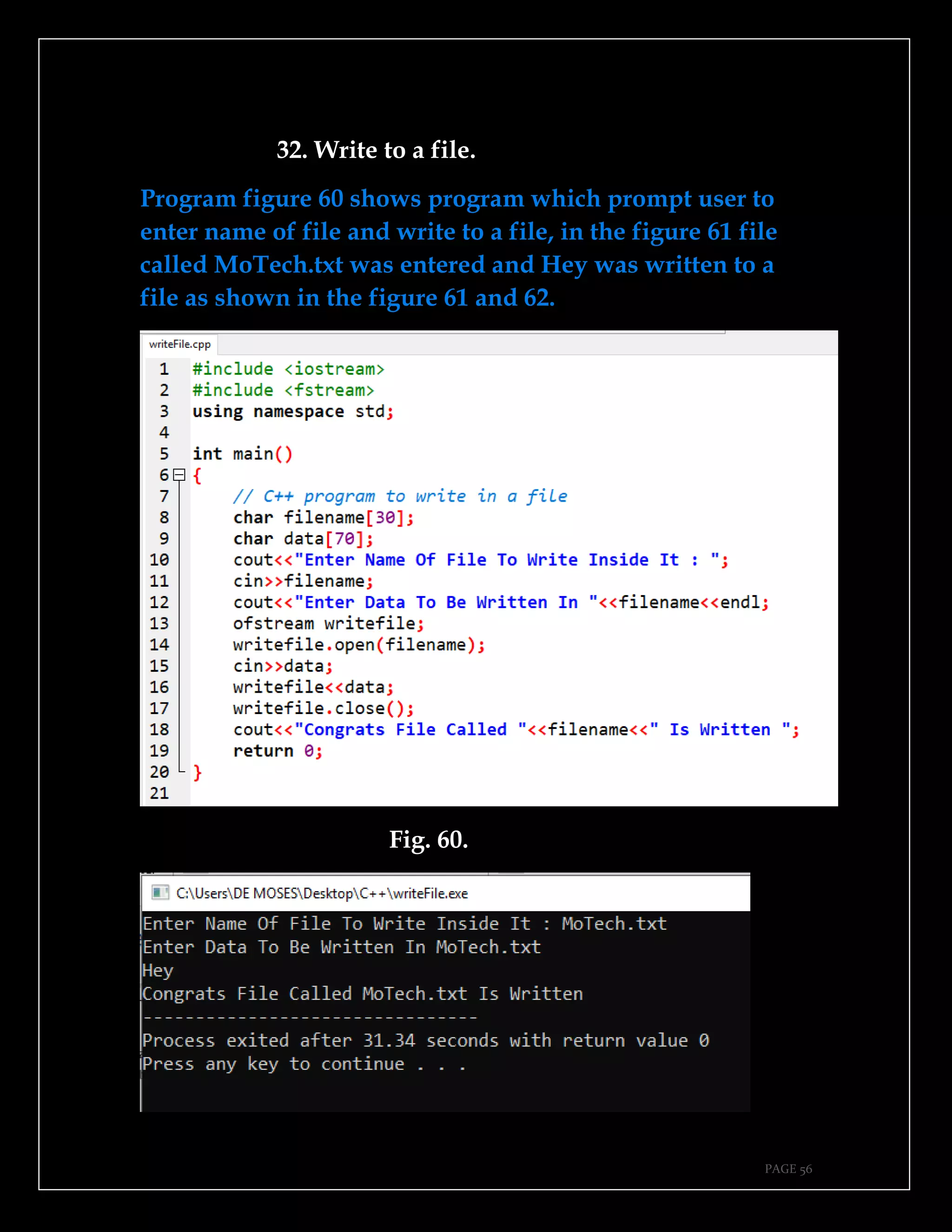
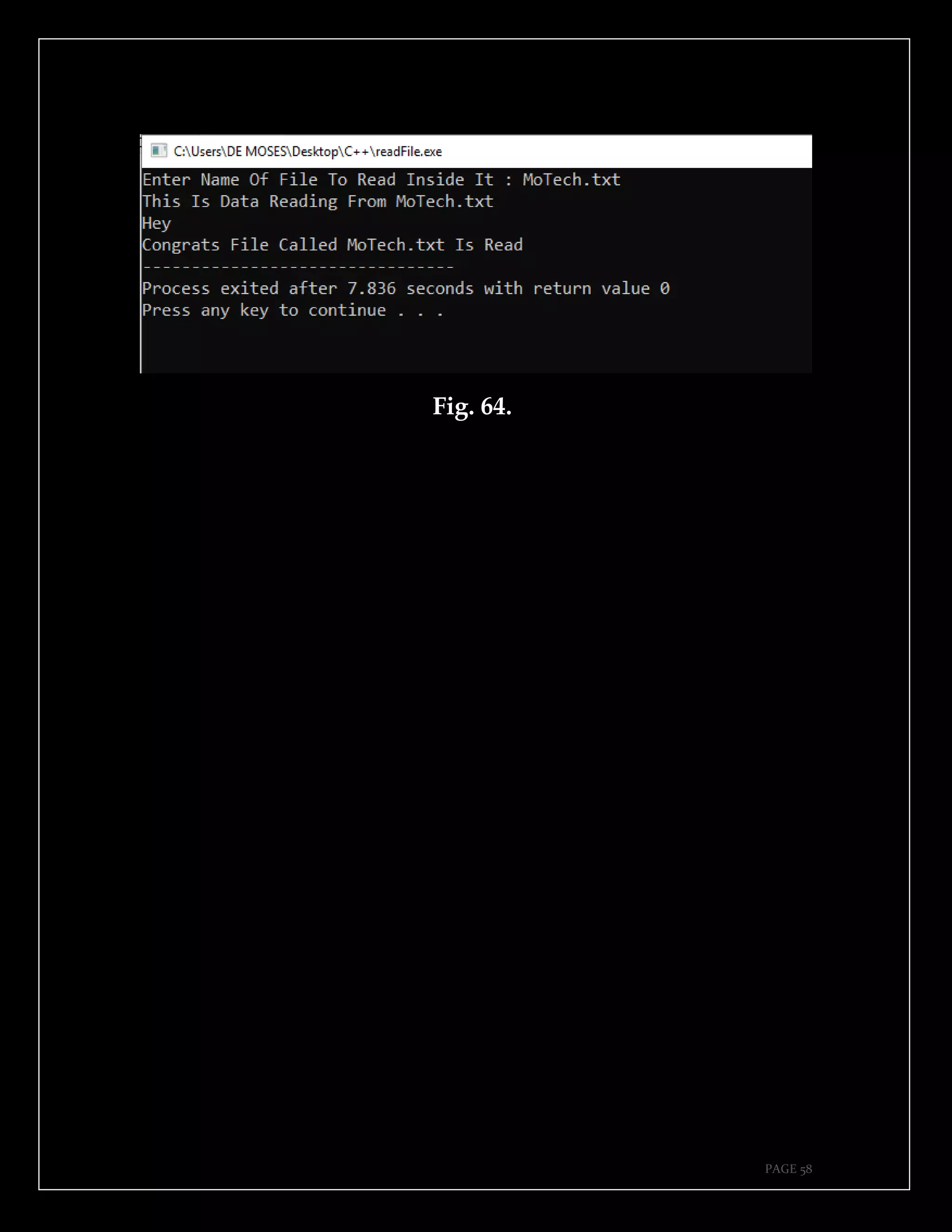
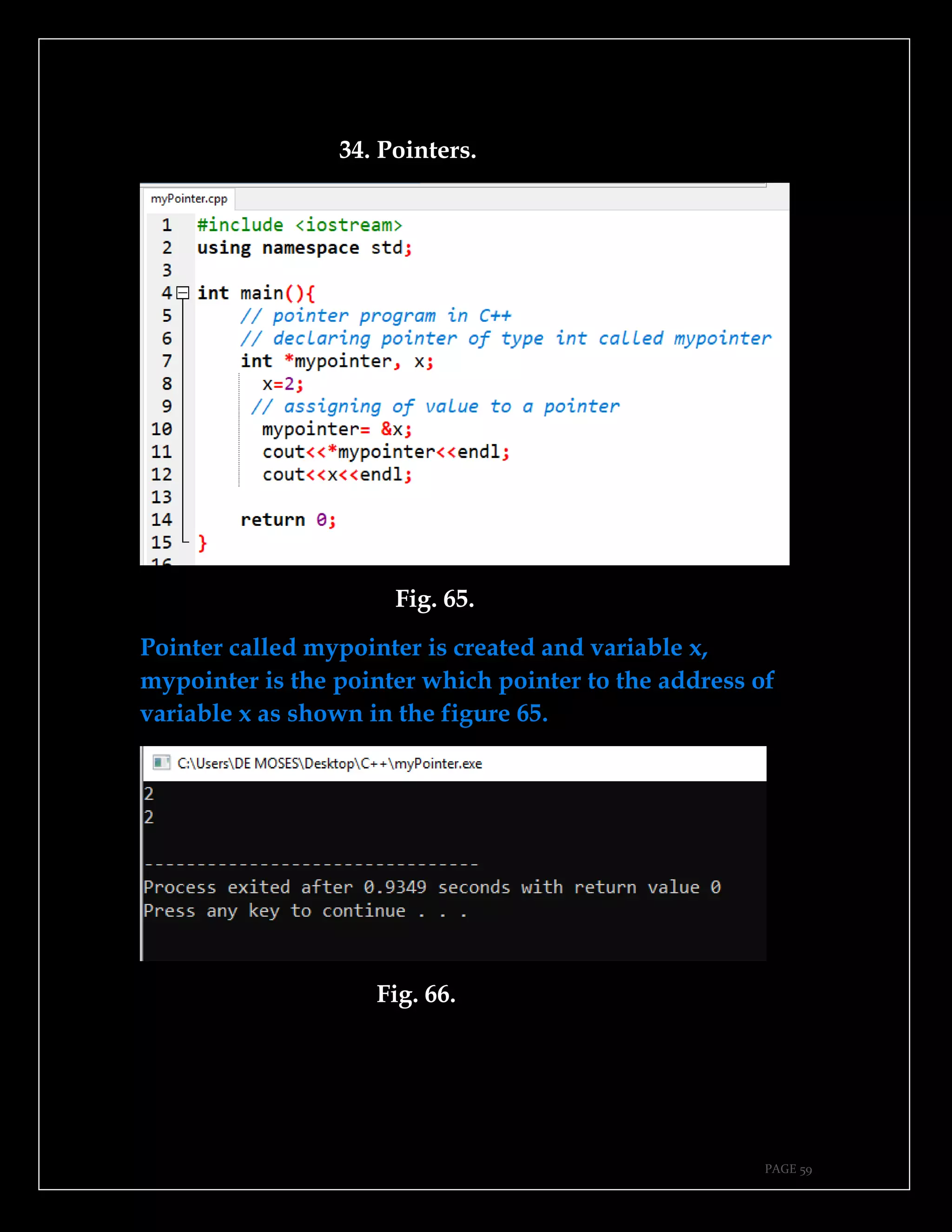
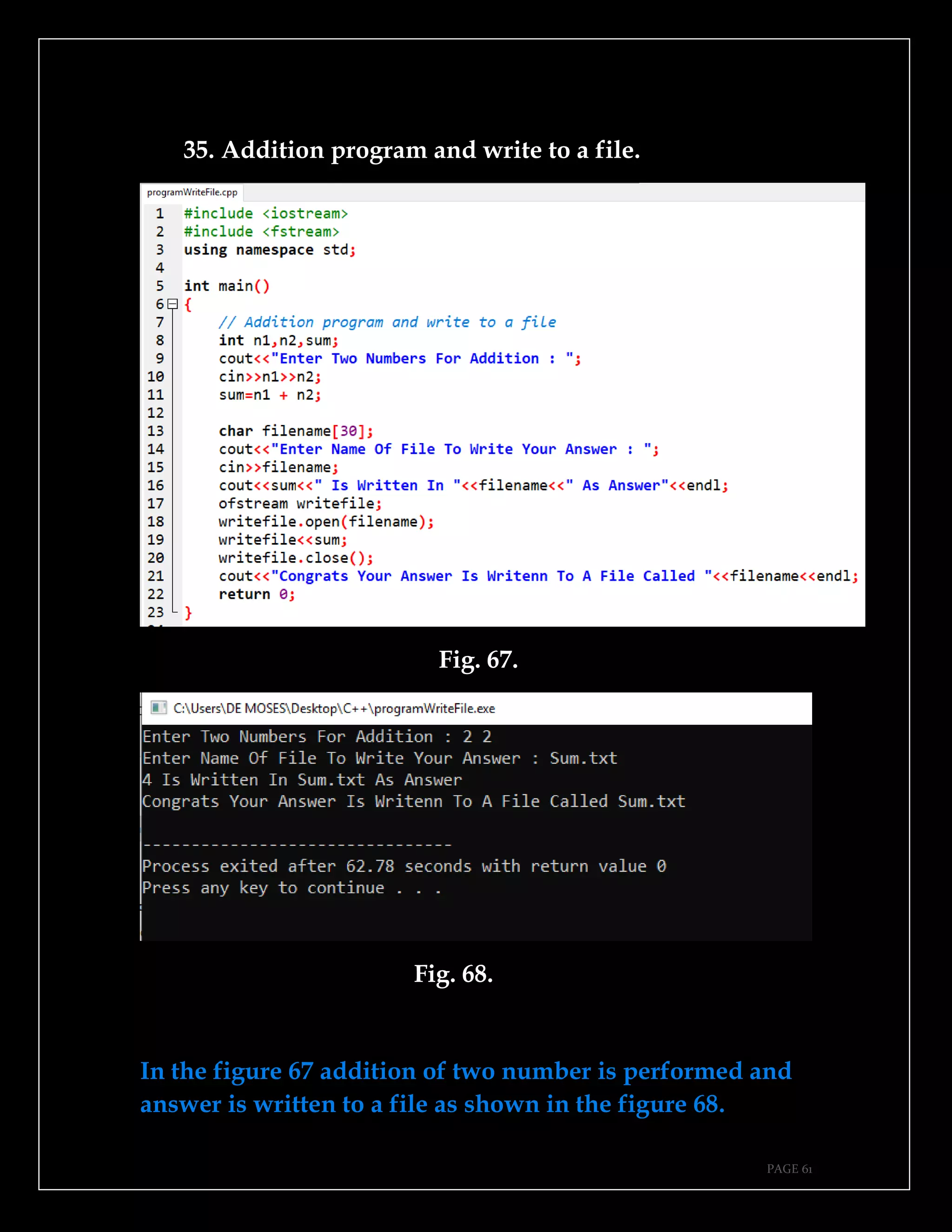
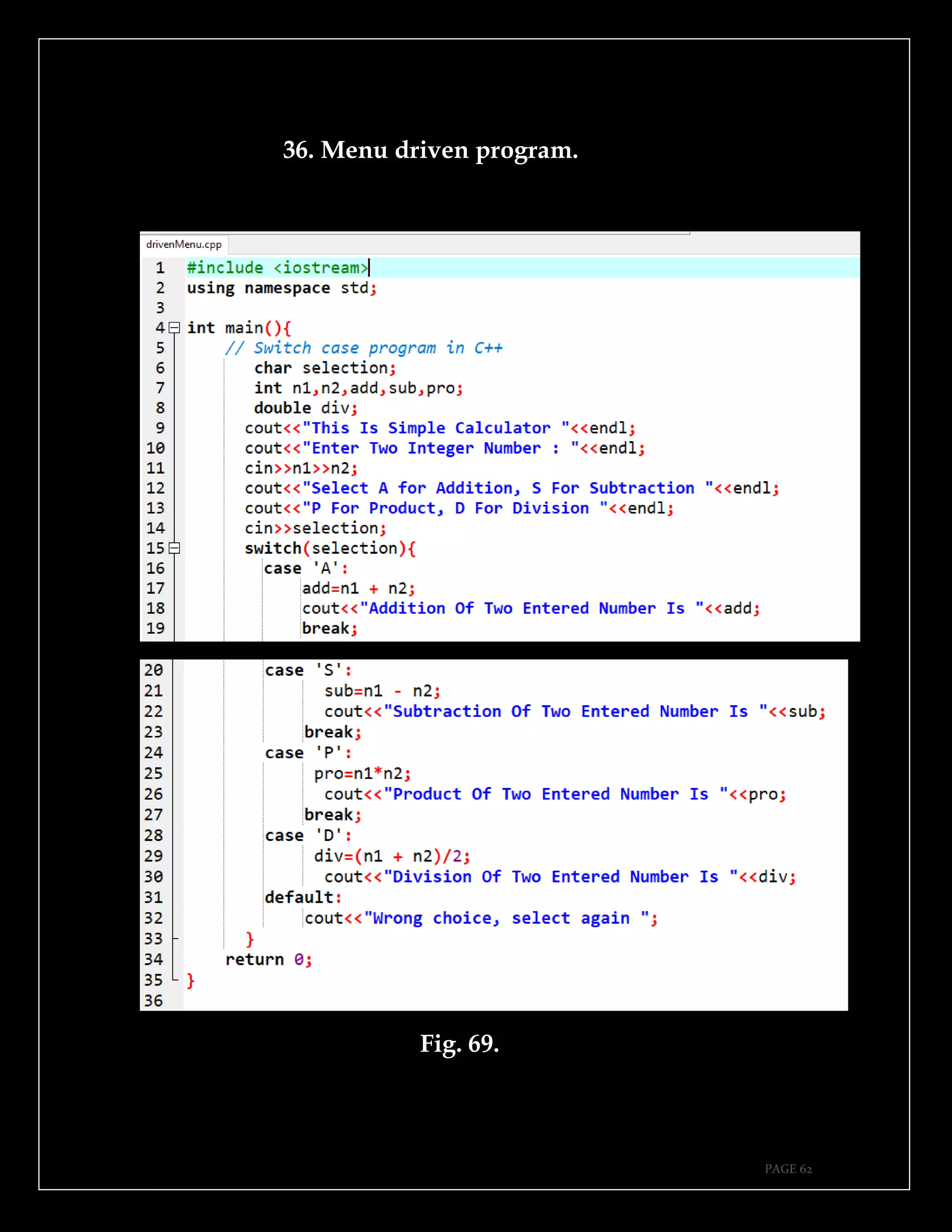
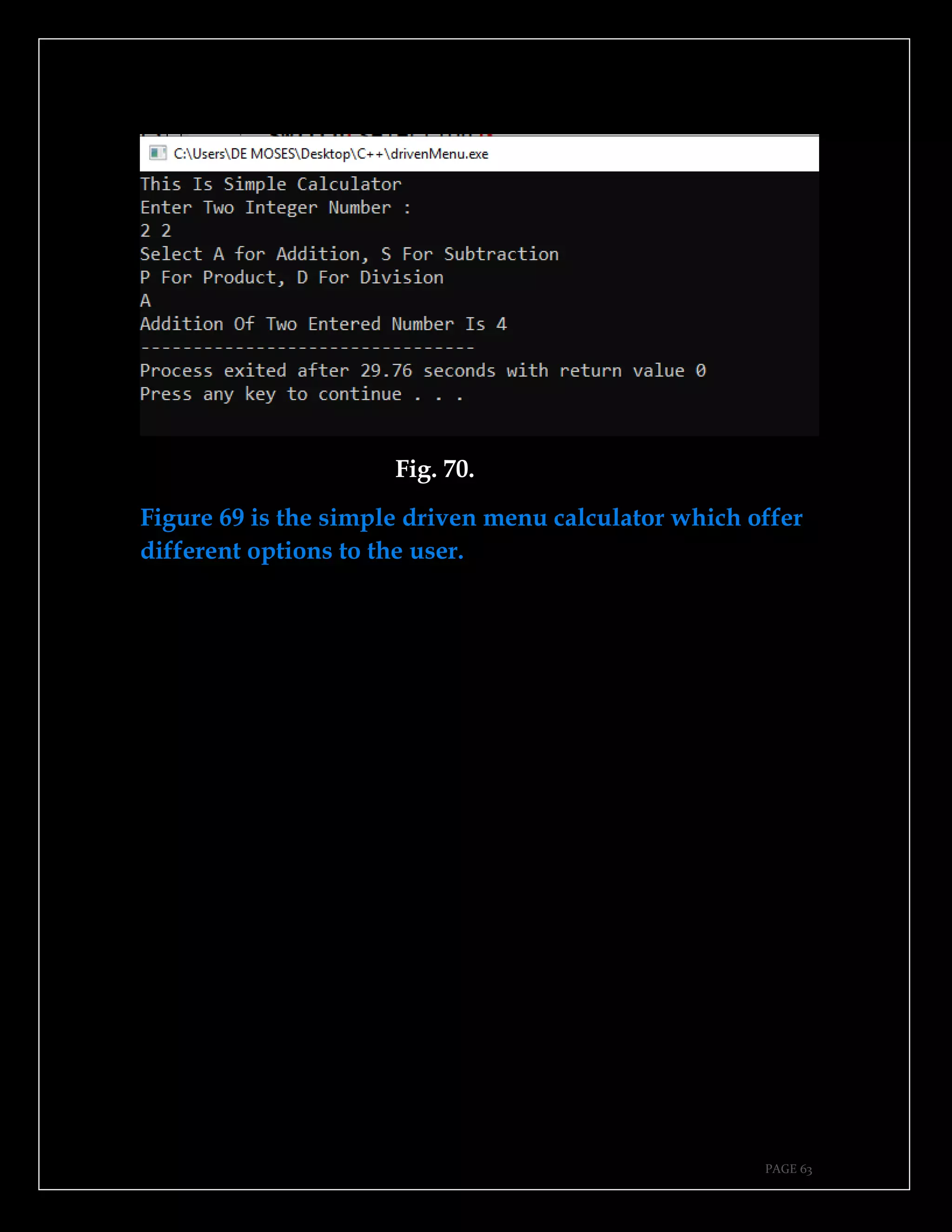
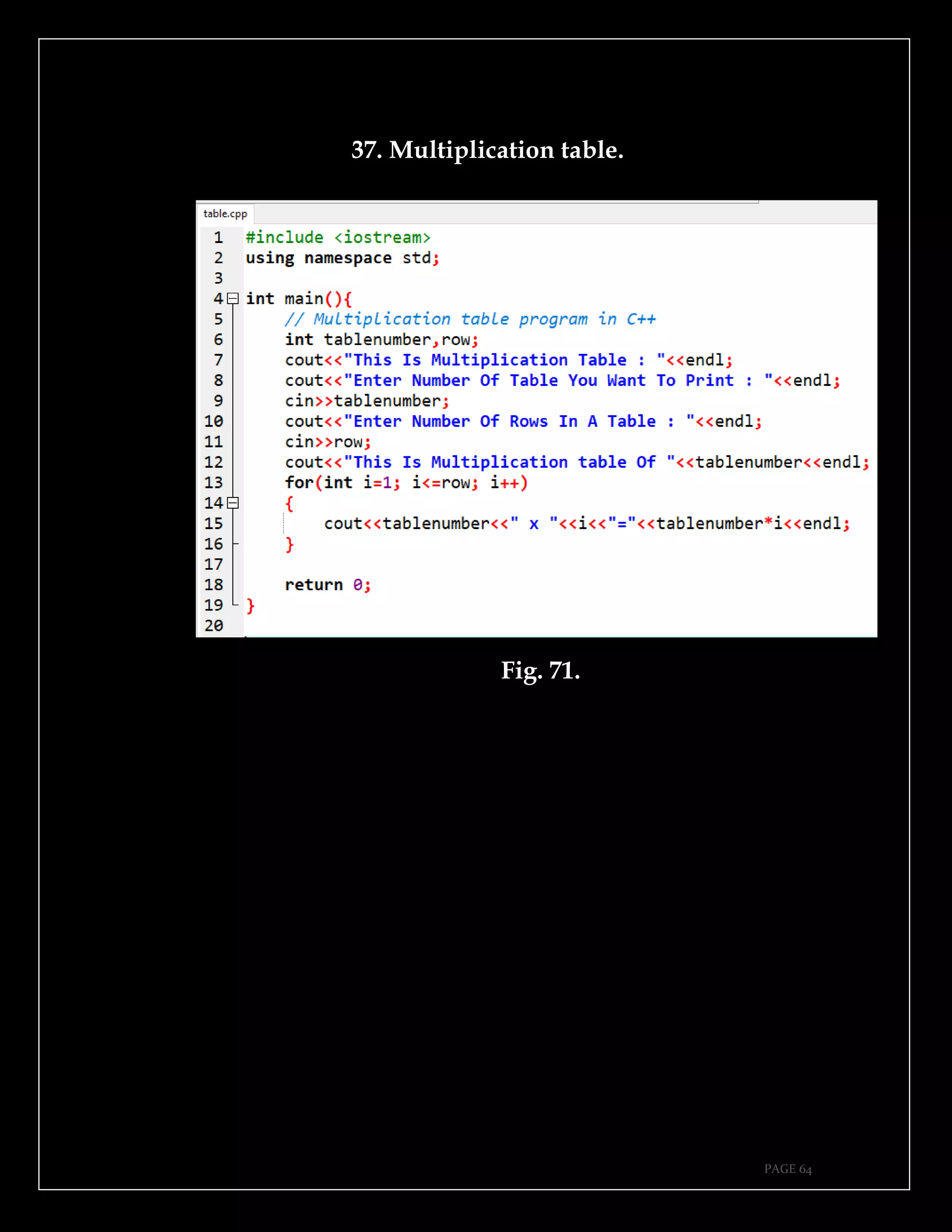
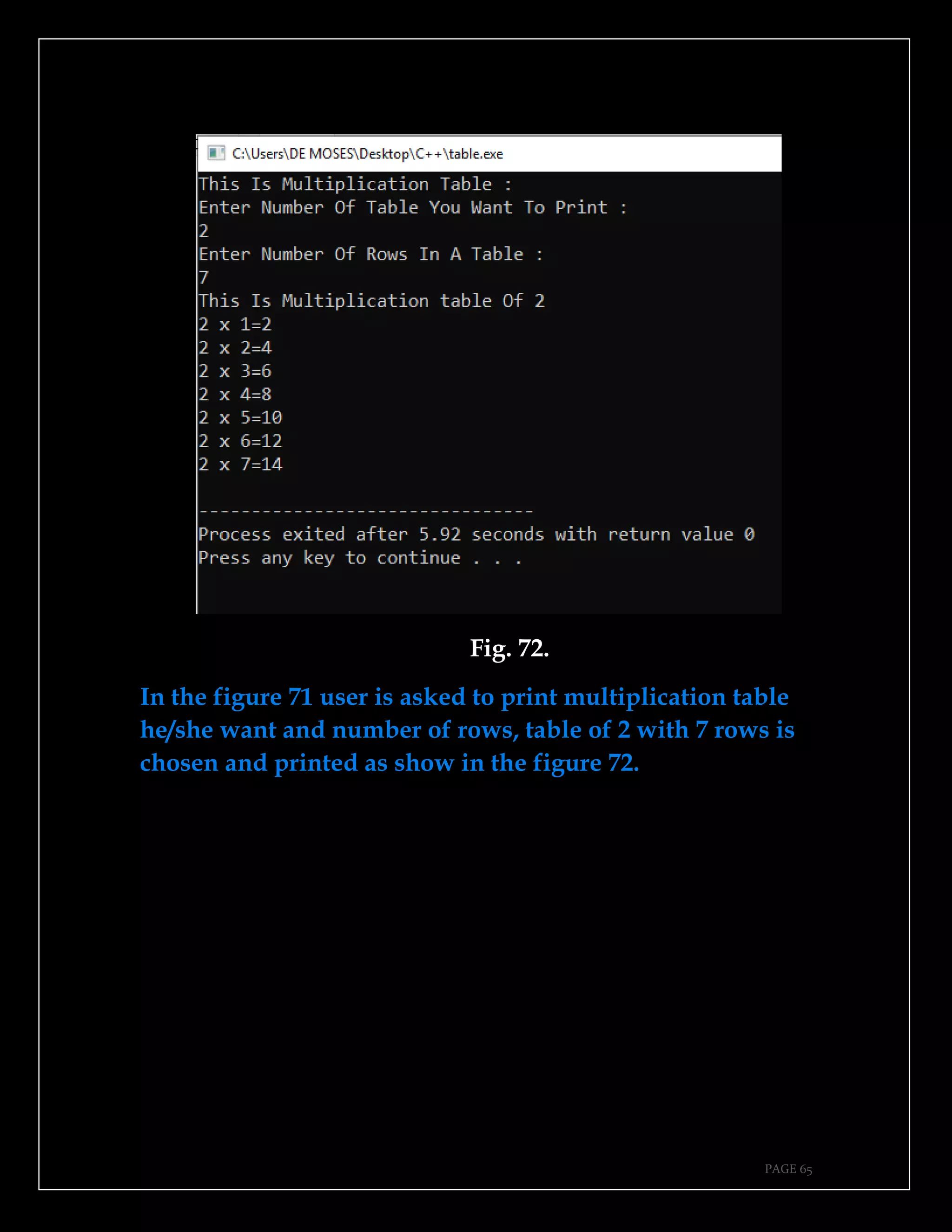
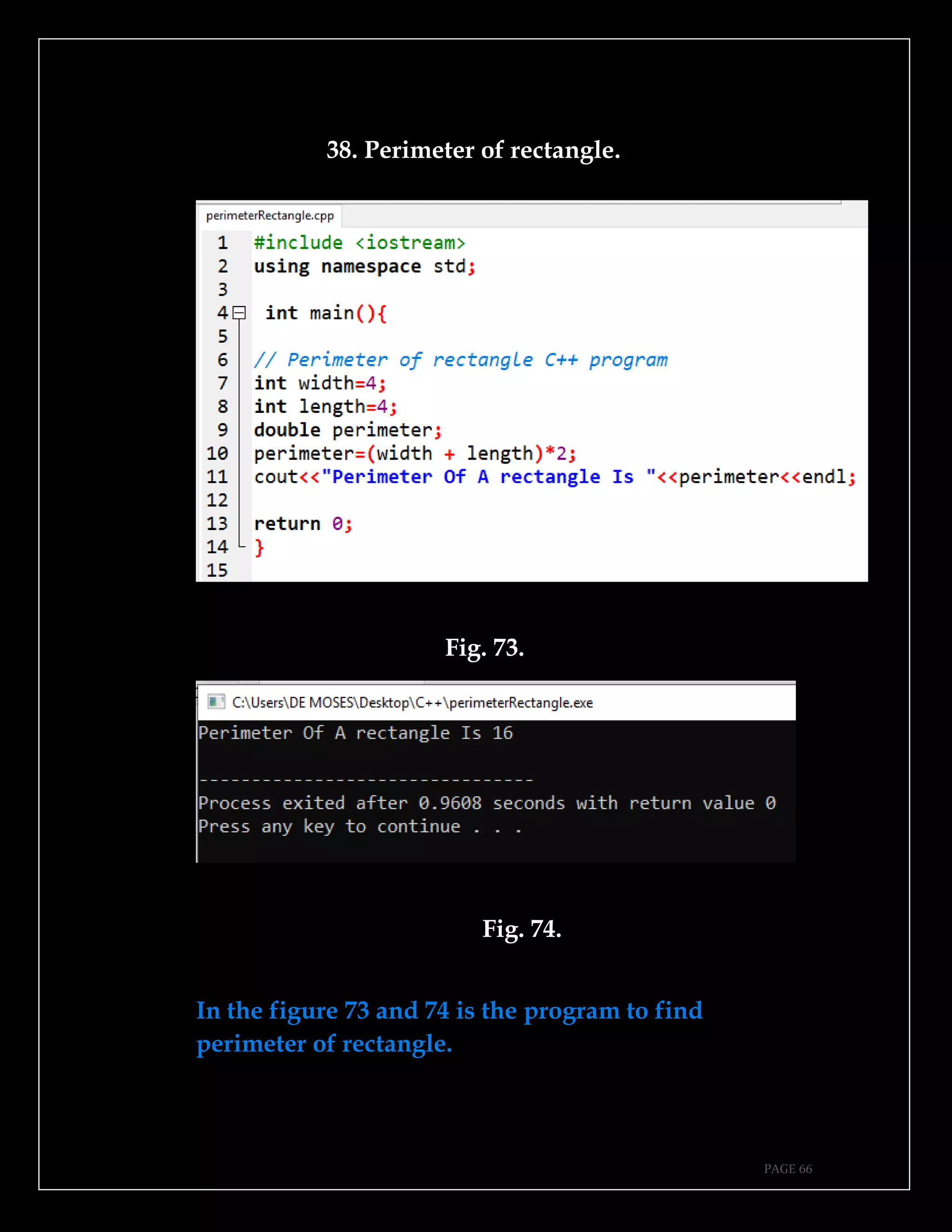
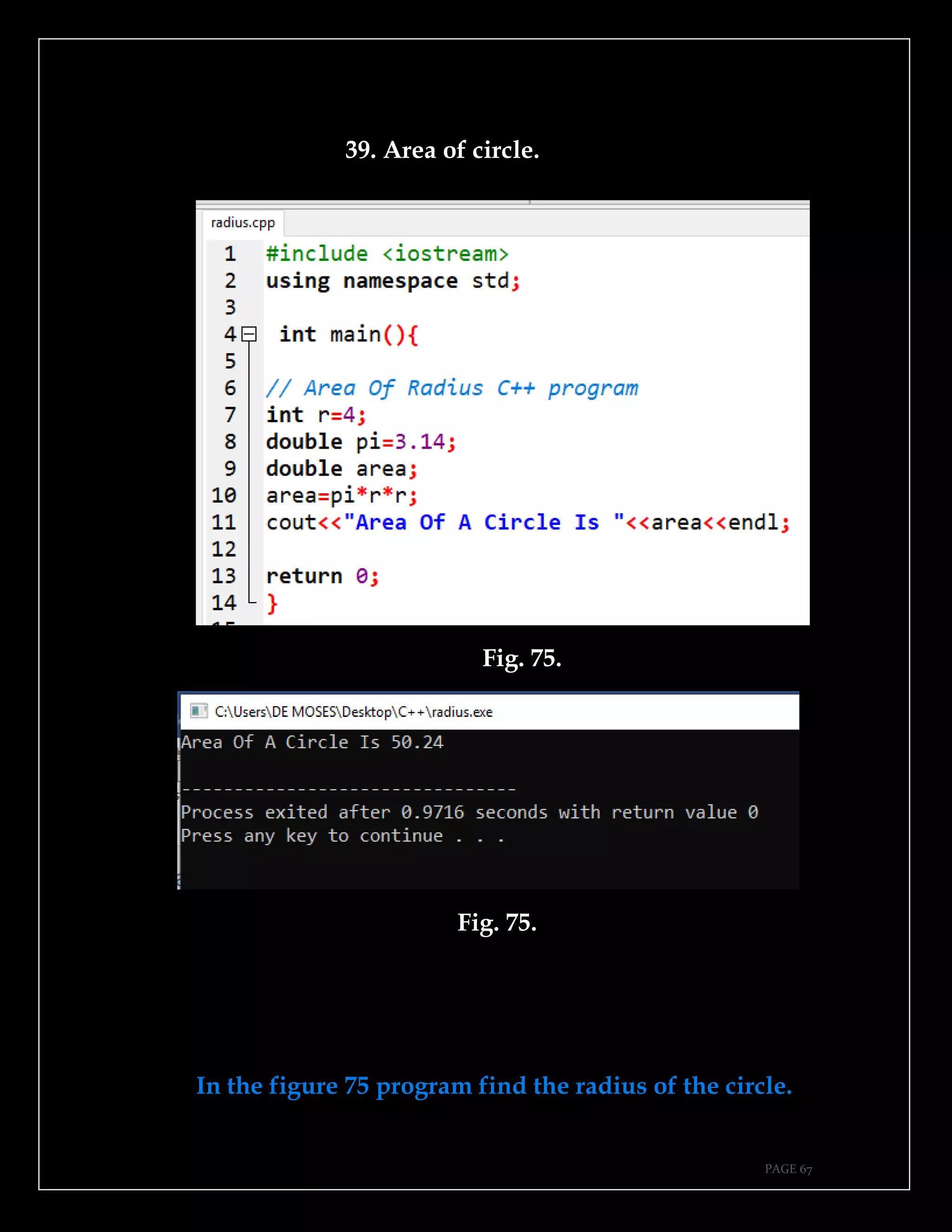
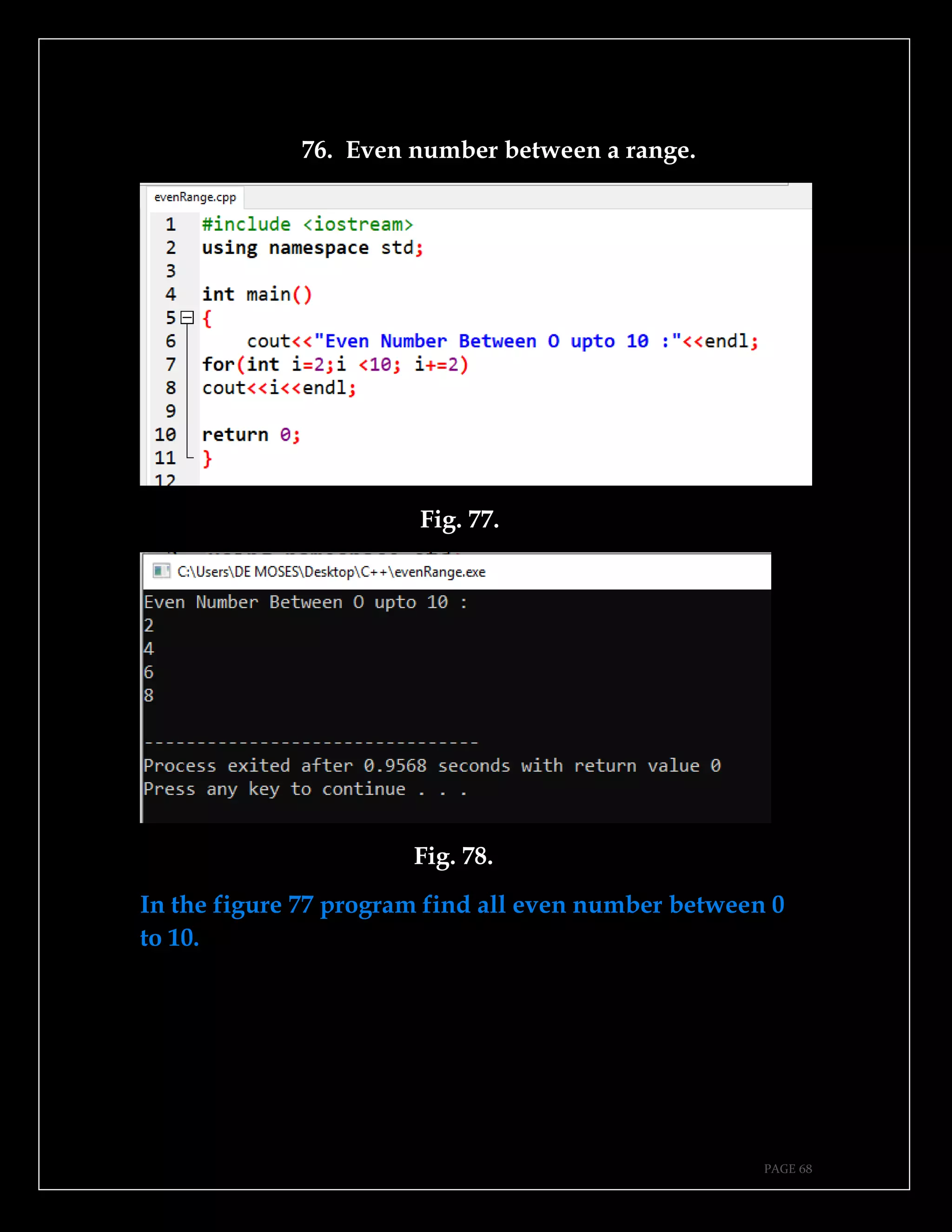
The document is a guide authored by Noel Moses Mwadende, focusing on simplified C++ programming through 40 practical examples. It encourages learning by example and practice, targeting beginners who find C++ challenging. The book is structured into four chapters covering various programming fundamentals such as variable declaration, loops, functions, and file handling.