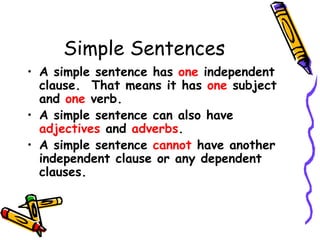
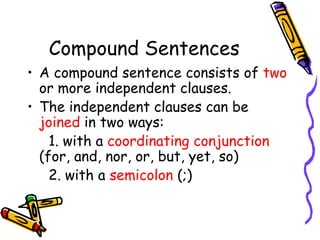
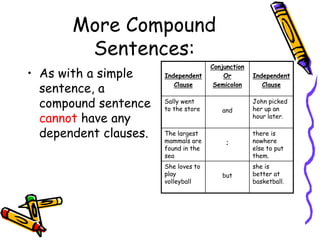
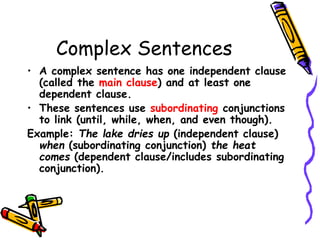
This document provides an overview of sentences and sentence structures in English. It defines what constitutes a sentence and identifies the key elements of a subject and predicate. It describes the four basic types of sentences: simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex. It also covers sentence functions, common sentence errors like fragments and run-ons, and ways to correct run-on sentences.