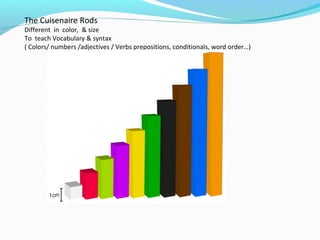
The Silent Way approach emerged in response to the decline of audiolingualism. It is based on cognitive theories of language learning and emphasizes learner independence, discovery learning, and minimal teacher intervention. Key aspects include using colored rods and charts to teach vocabulary and grammar structures visually, the teacher remaining mostly silent, and learners developing self-correction abilities through problem-solving activities with their peers.