This document discusses station marks and signals used in triangulation surveys. It describes:
1. Station marks are permanent marks buried below the surface to mark survey points. They are usually made of bronze or copper embedded in concrete or rock.
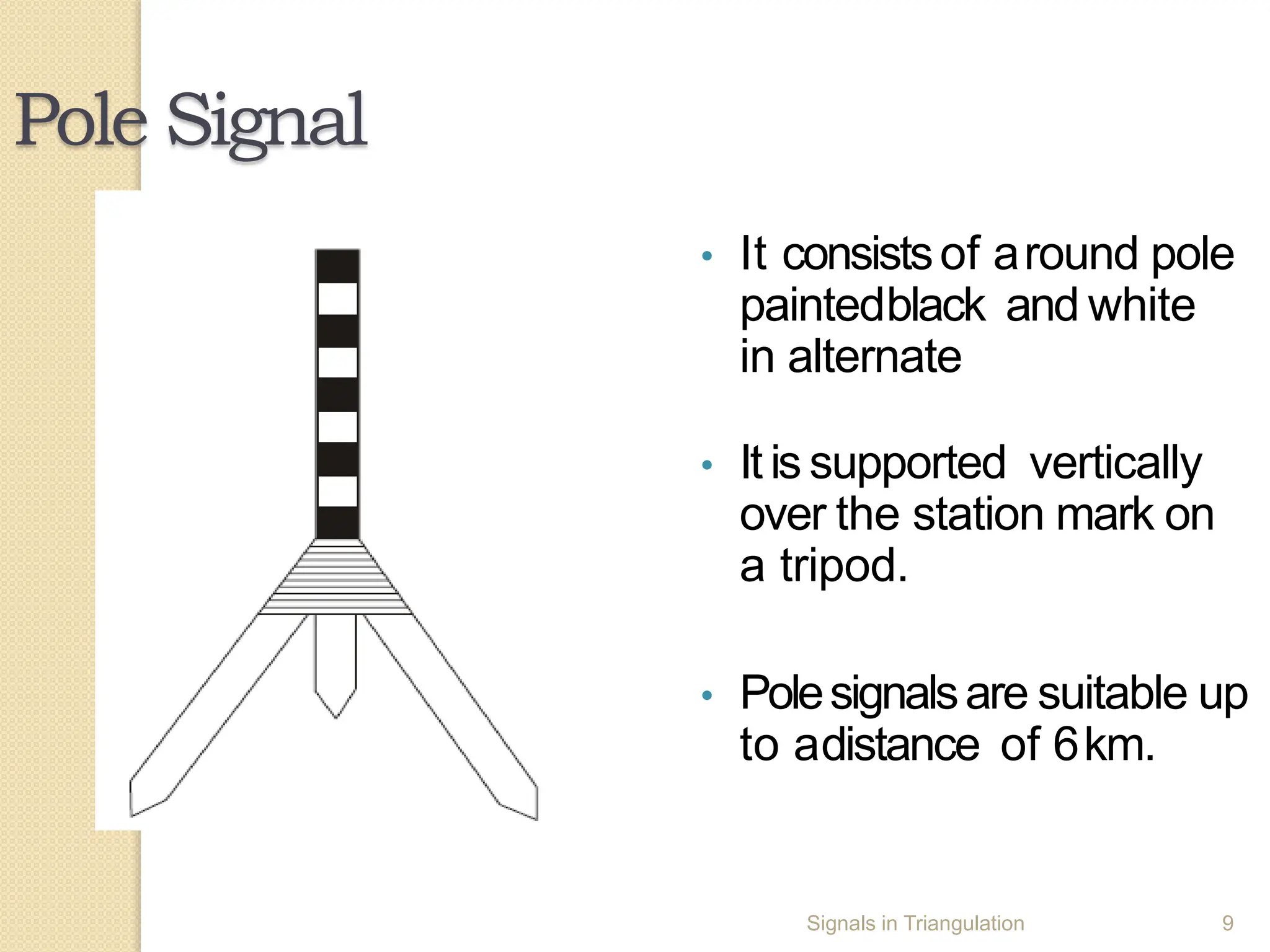
2. Signals are devices erected directly above station marks to define survey points. They can be opaque (pole, target, brush) or luminous (sun, night lamps) depending on lighting conditions.
3. Various types of opaque signals are described including pole signals, target signals, brush signals, stone cairns, and towers. Luminous signals include heliotropes and night lamps using oil or acetylene. Signals must be visible, centered over