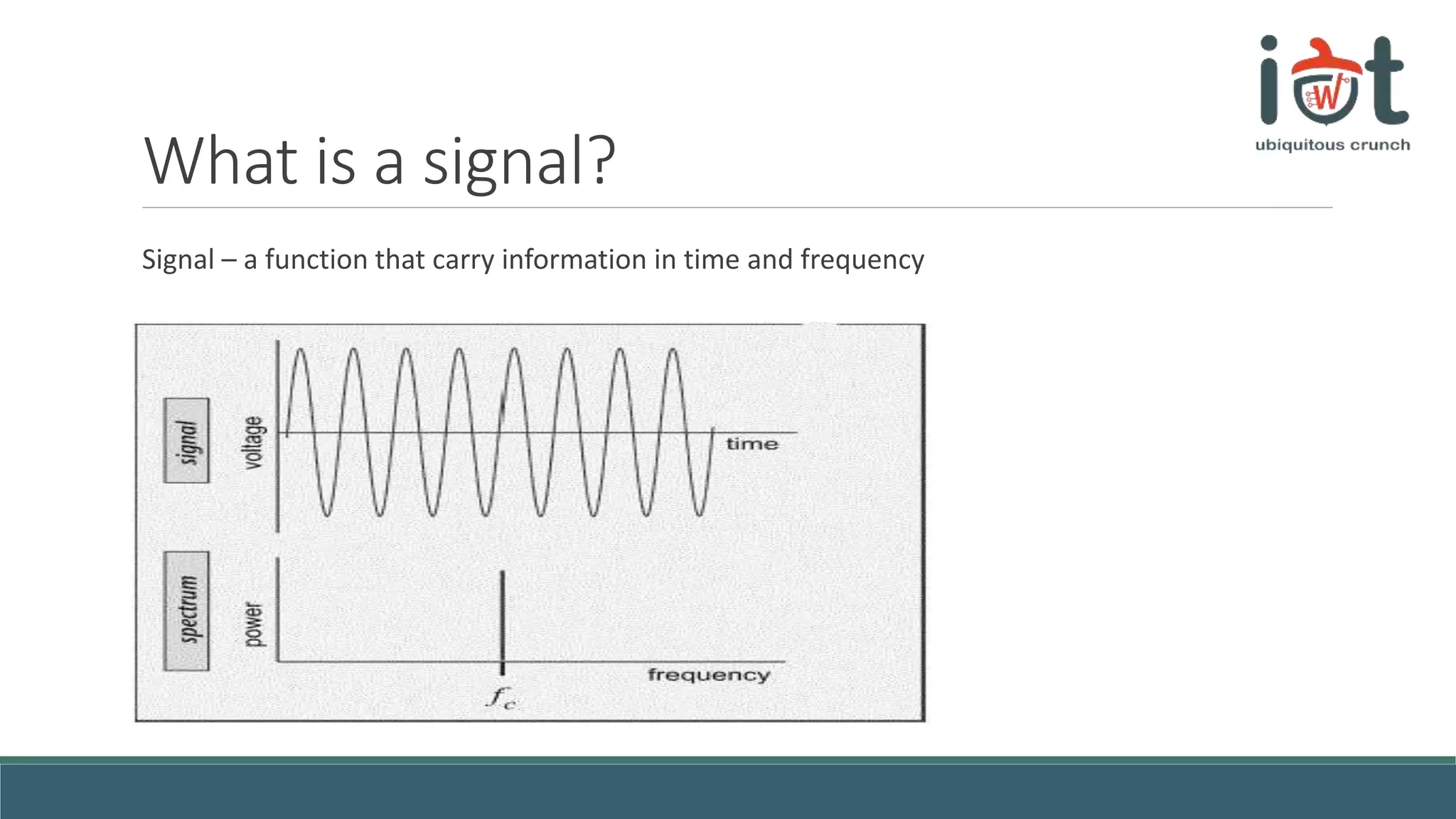
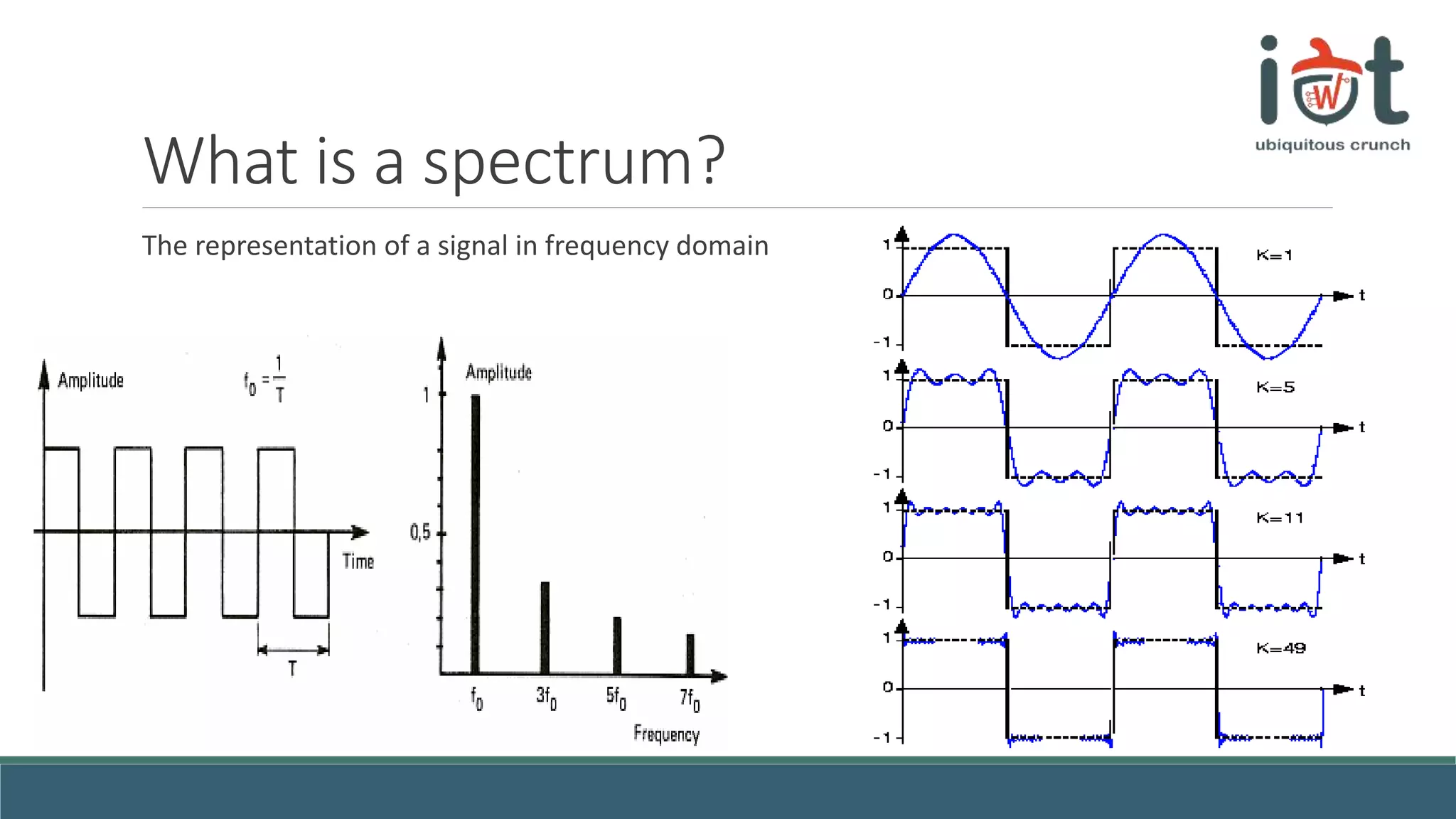
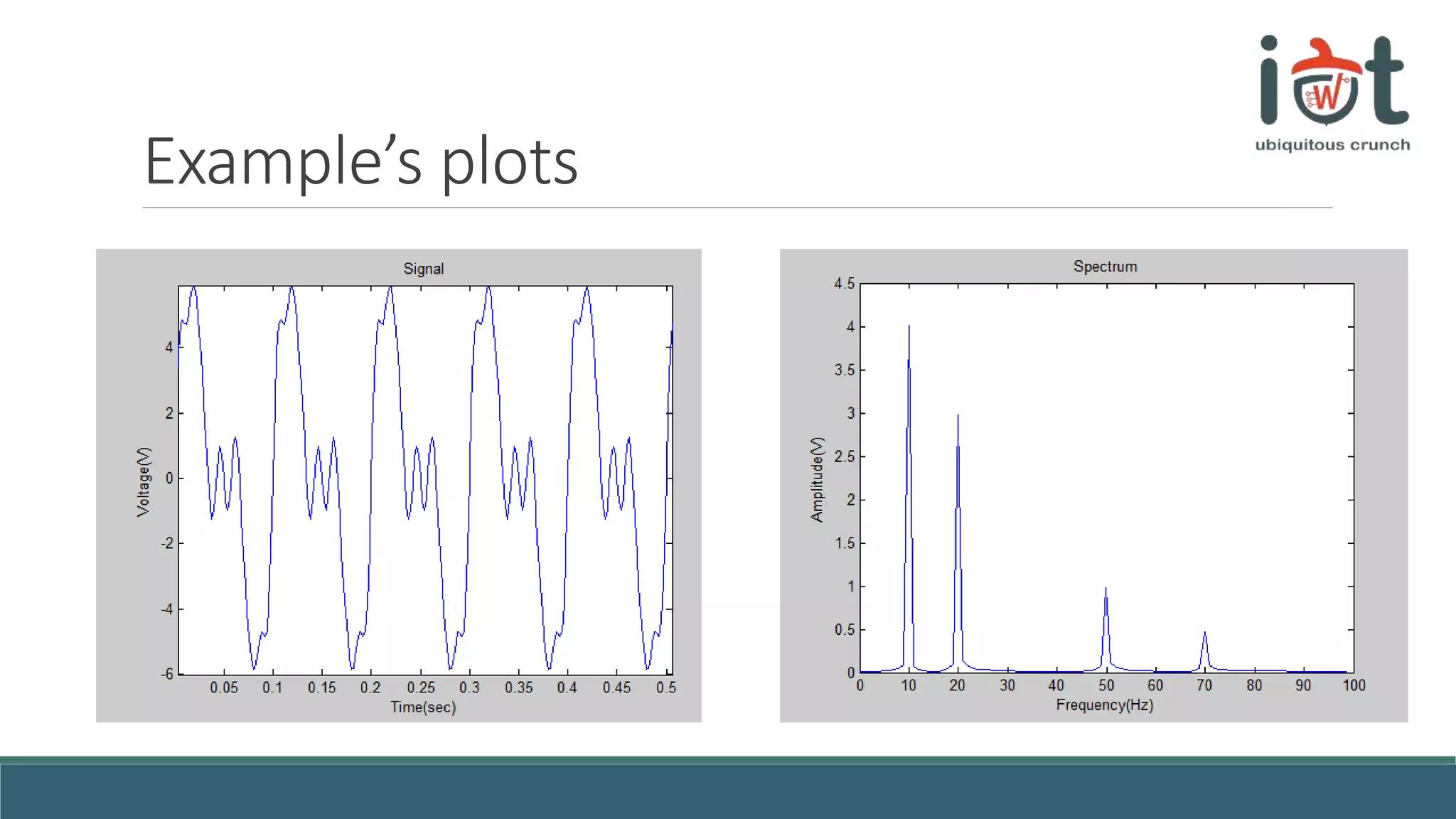
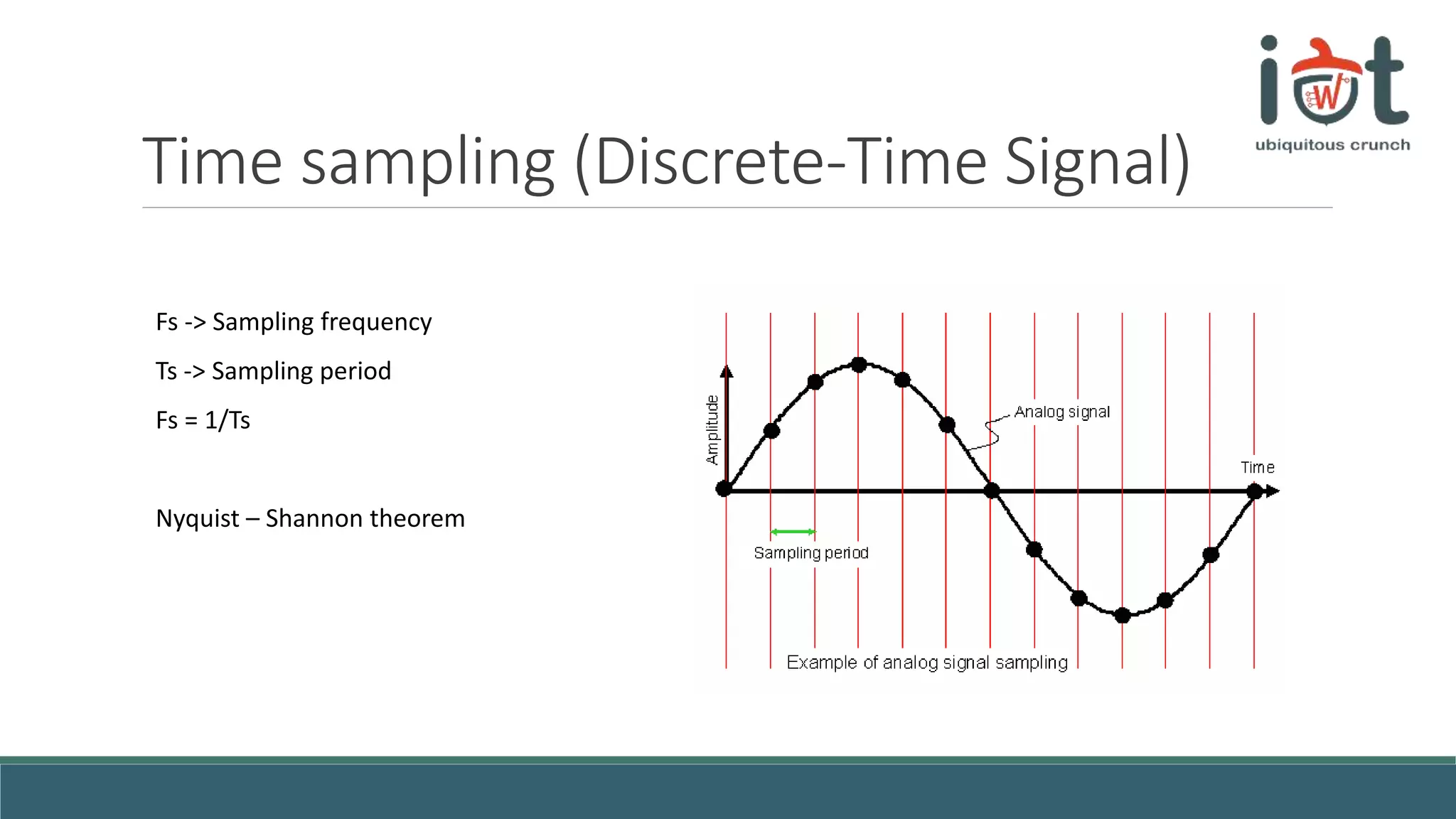
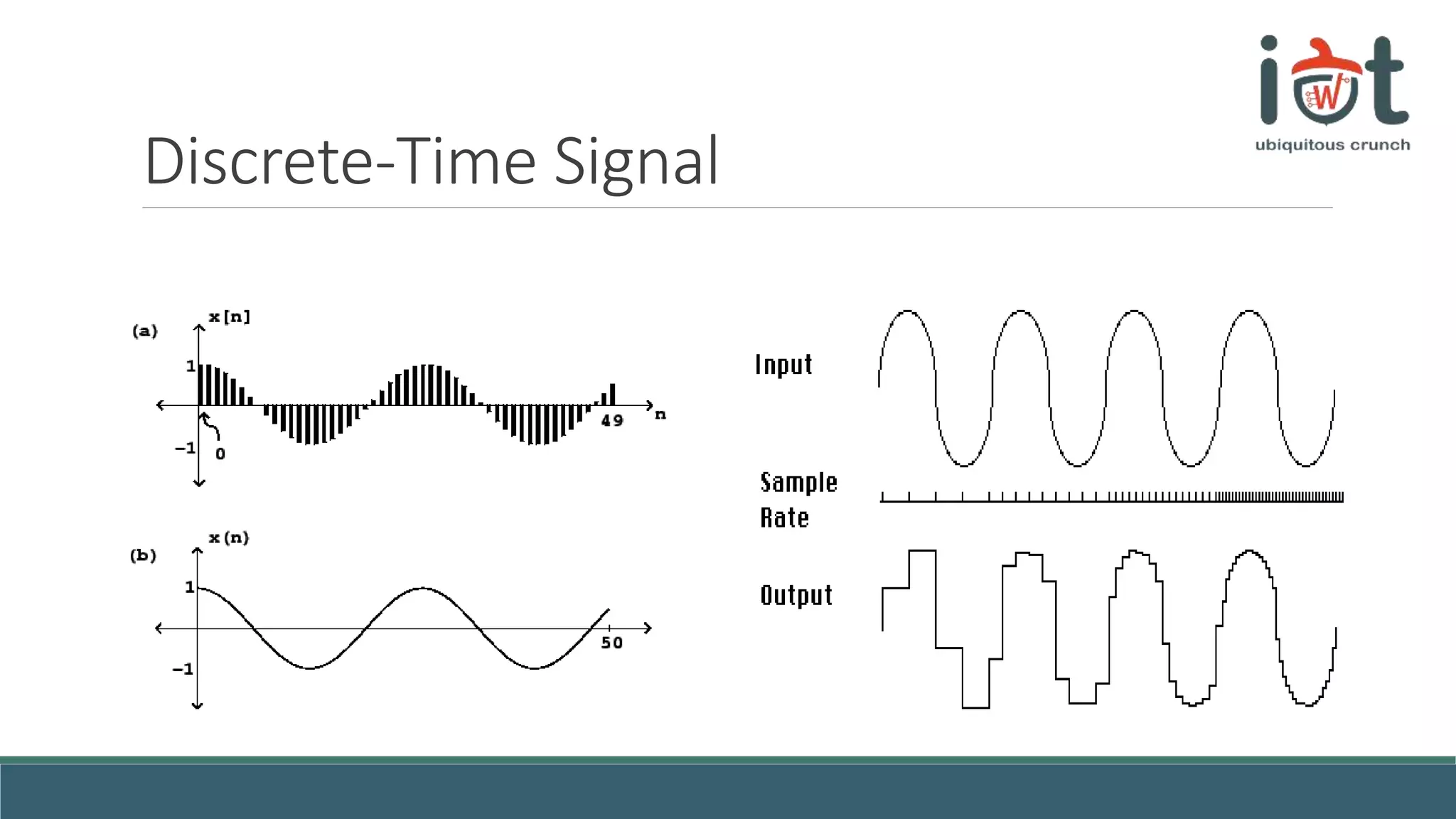
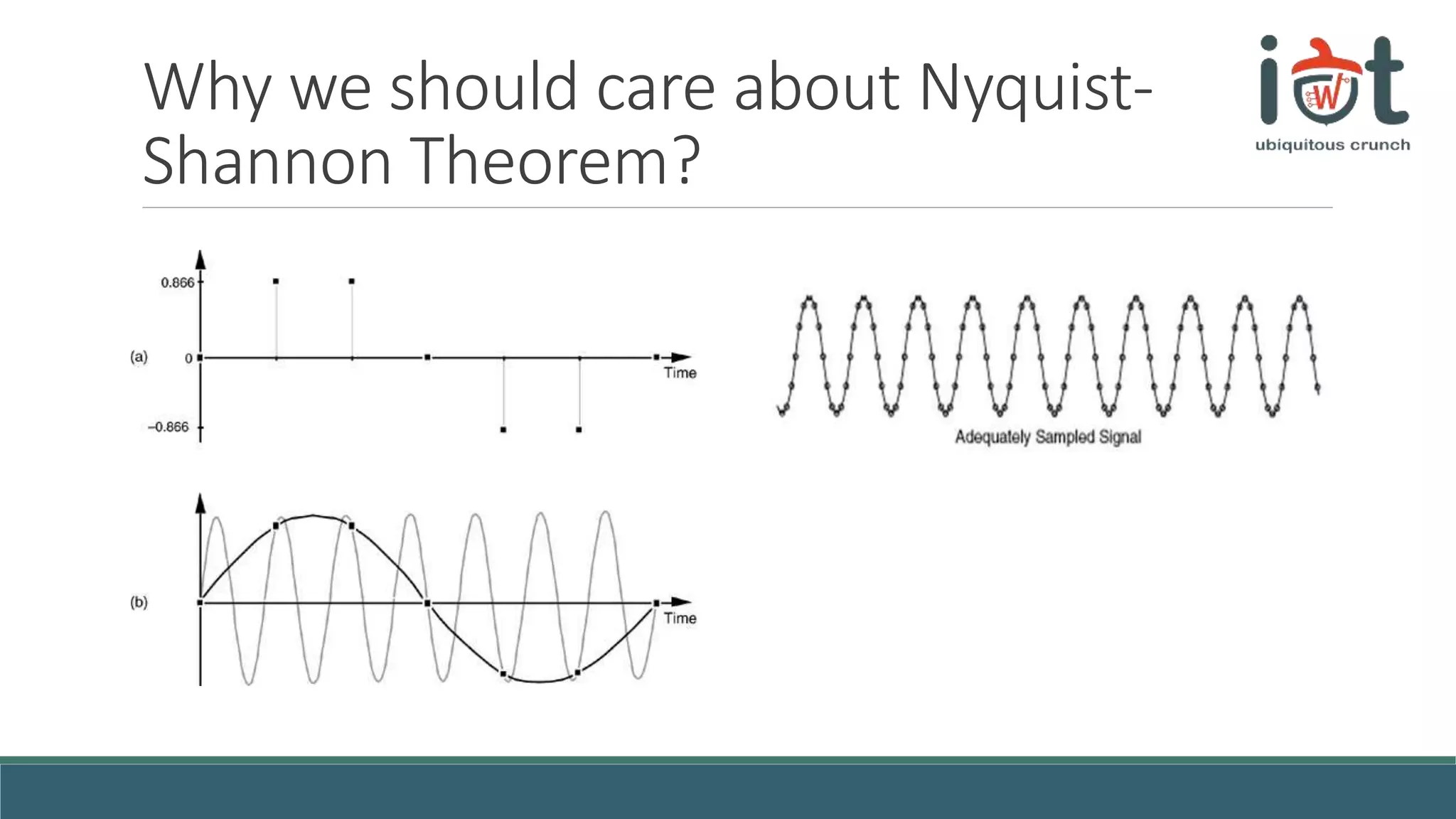
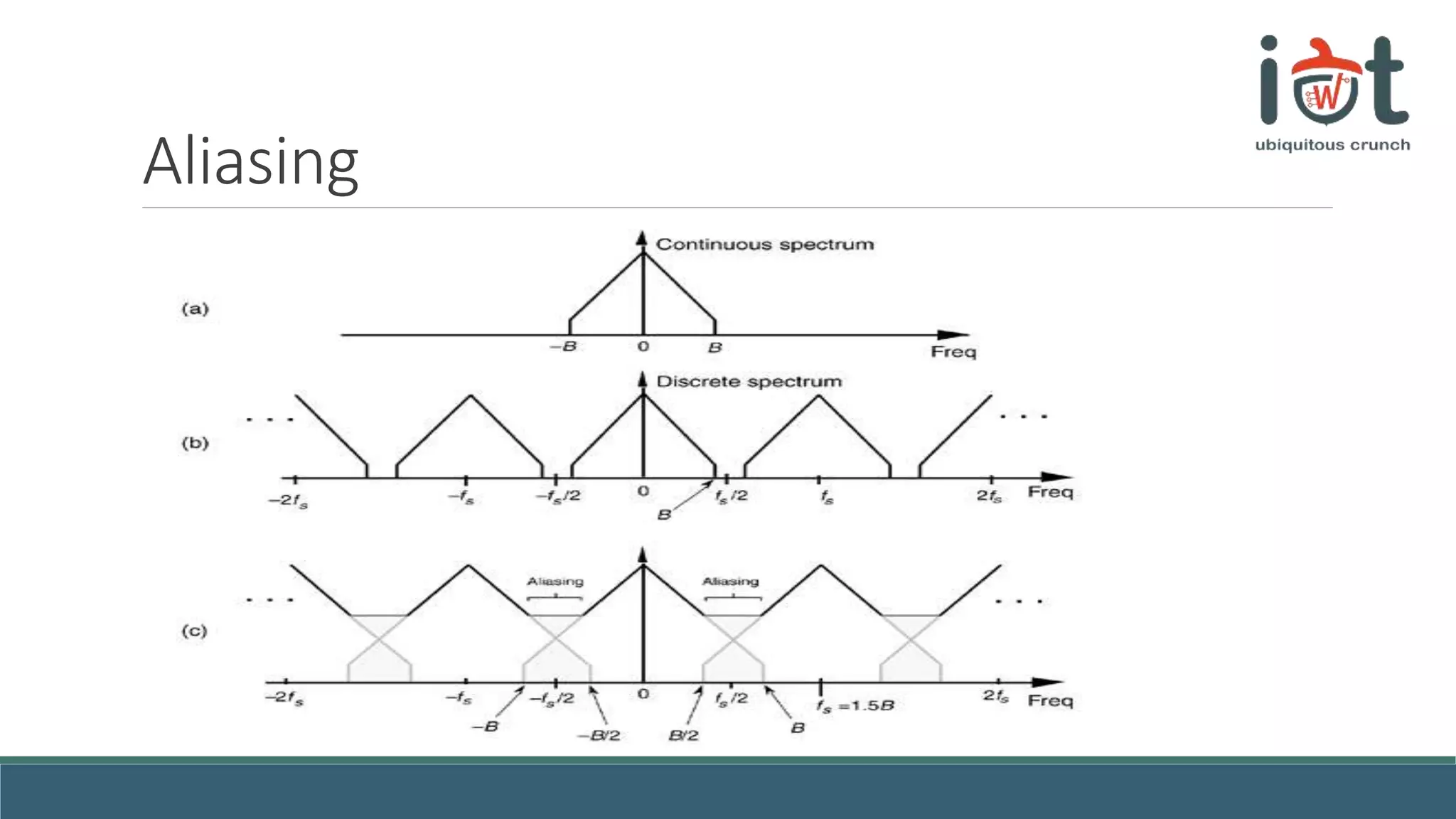
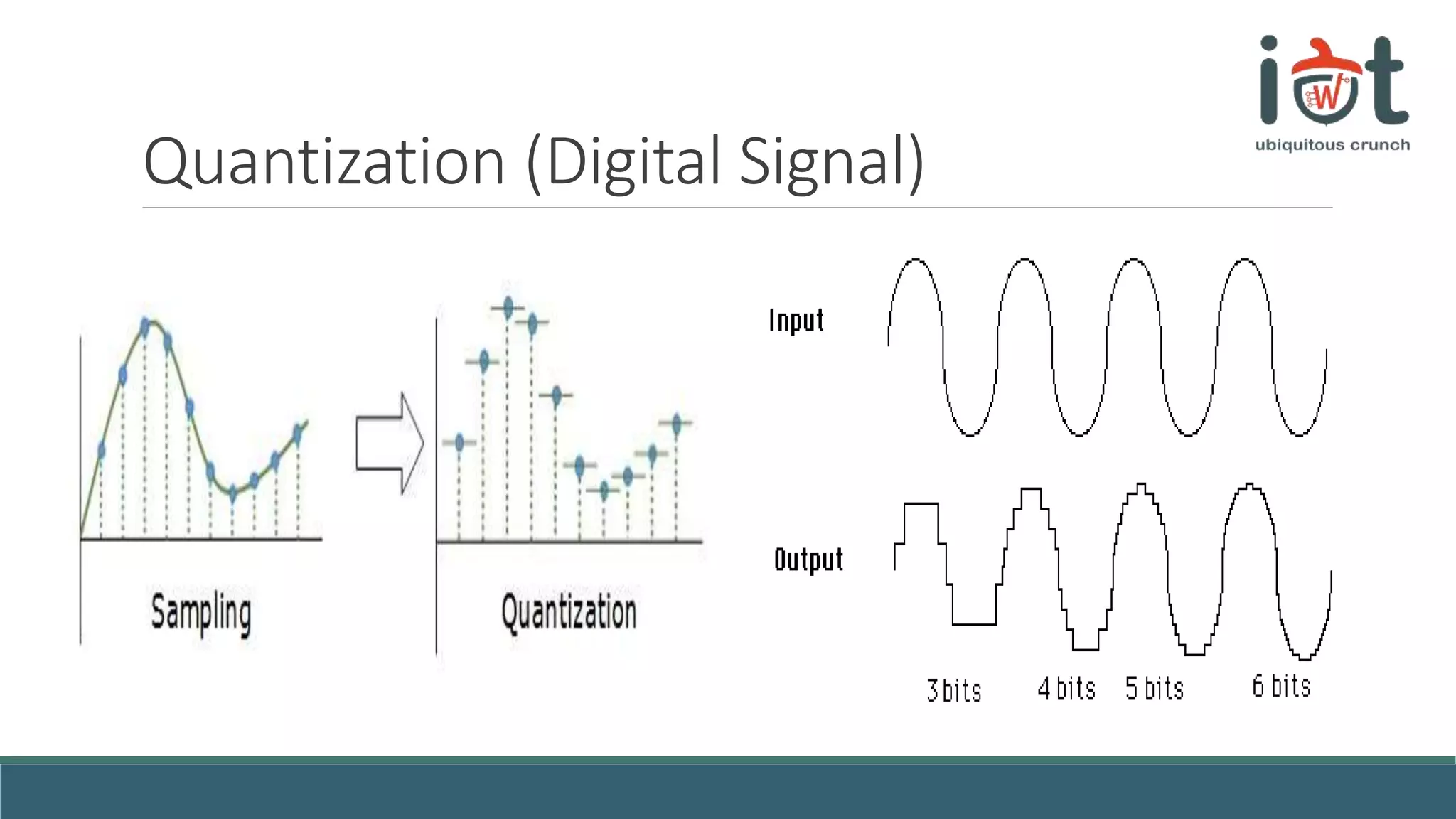
This document provides an overview of signals and systems concepts for a summer school on real-time applications. It defines what signals and spectra are, discusses analog versus digital signals, time sampling and quantization, system properties, and considerations for real-time systems including constraints, specifications, hardware components, and trade-offs between factors like time, energy, performance and more. Examples are provided on representing signals in the time and frequency domains.