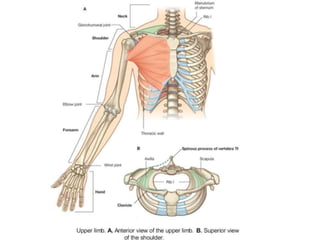
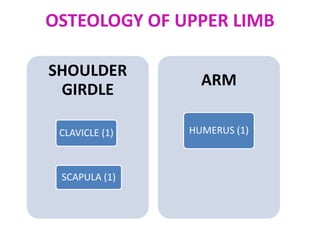
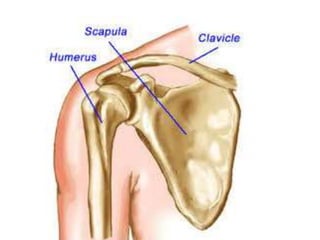
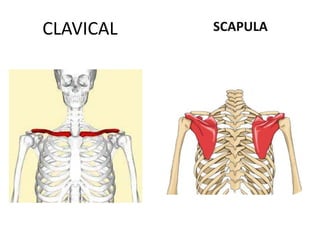
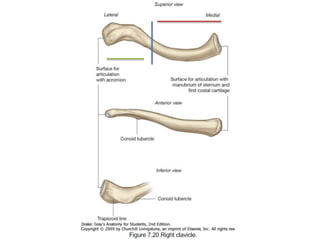
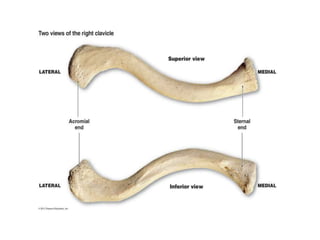
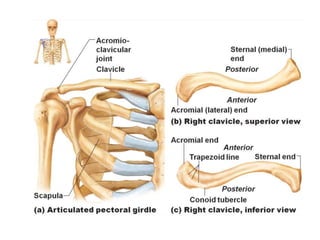
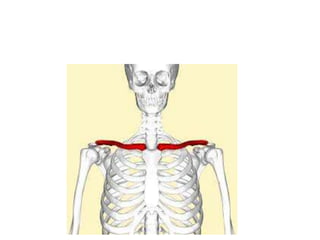
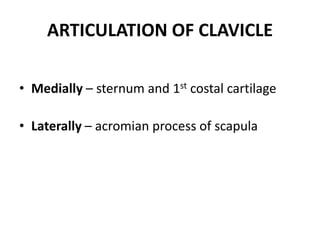
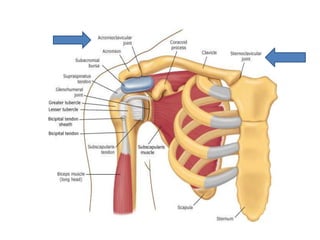
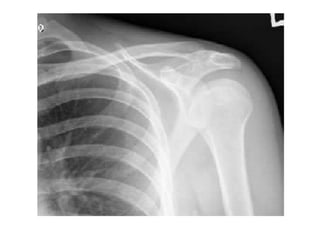
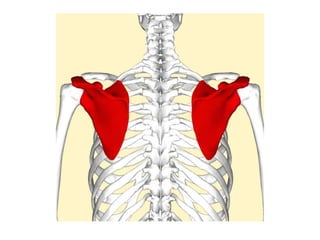
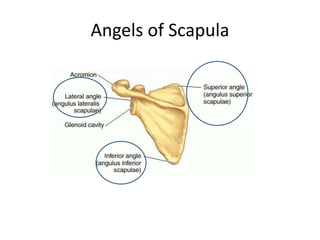
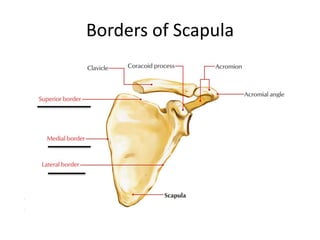
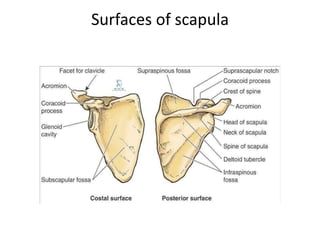
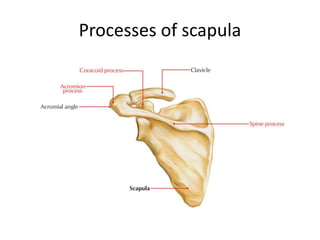
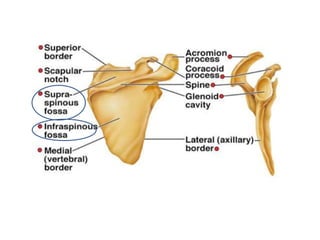
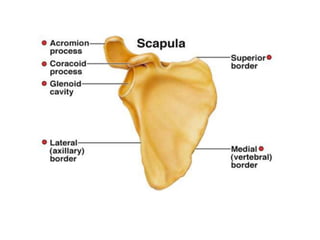
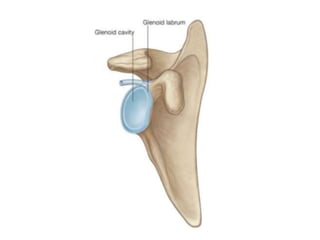
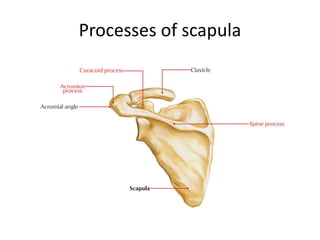
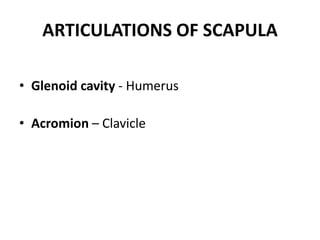
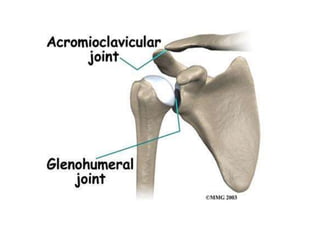
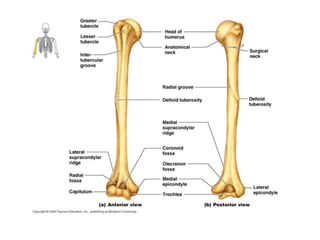
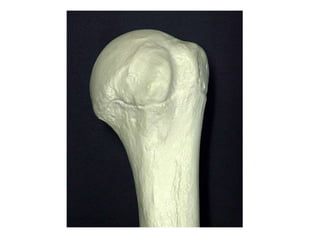
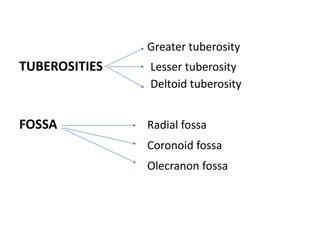
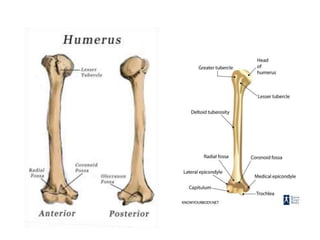
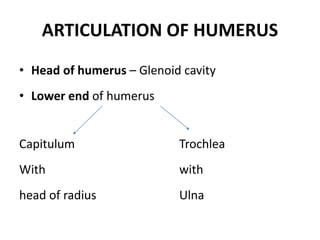
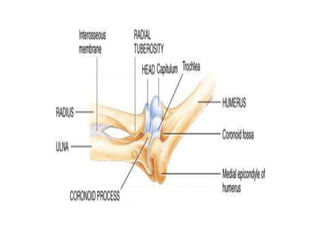
This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the upper limb, including the bones of the shoulder girdle and arm. It discusses the clavicle, scapula, and humerus bones in detail. The clavicle lies horizontally and connects the trunk to the upper limb. The scapula has three angles, three borders, and processes including the glenoid cavity, acromion, coracoid, and spine. The humerus is the long bone of the arm and has a head, neck, shaft and lower end. The document also includes five multiple choice questions to test understanding.