This document provides an overview of human resource management (HRM). It discusses the history and evolution of HRM from personnel management. Key points include:
- HRM has evolved from a focus on administrative personnel functions to a more strategic approach integrated with organizational goals.
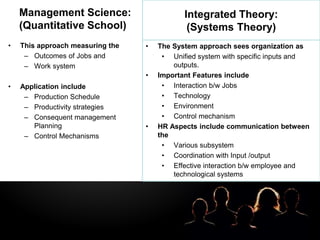
- Theories like scientific management, behavioral science and systems theory influenced the development of HRM concepts.
- HRM development stages include welfare/administrative, personnel management incorporating training/staffing, and the modern strategic HRM approach.
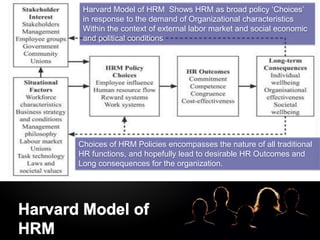
- HRM models like Harvard model emphasize strategic choices in response to organizational needs within the external context.
- The roles of HRM involve meeting current and future labor needs through workforce planning,