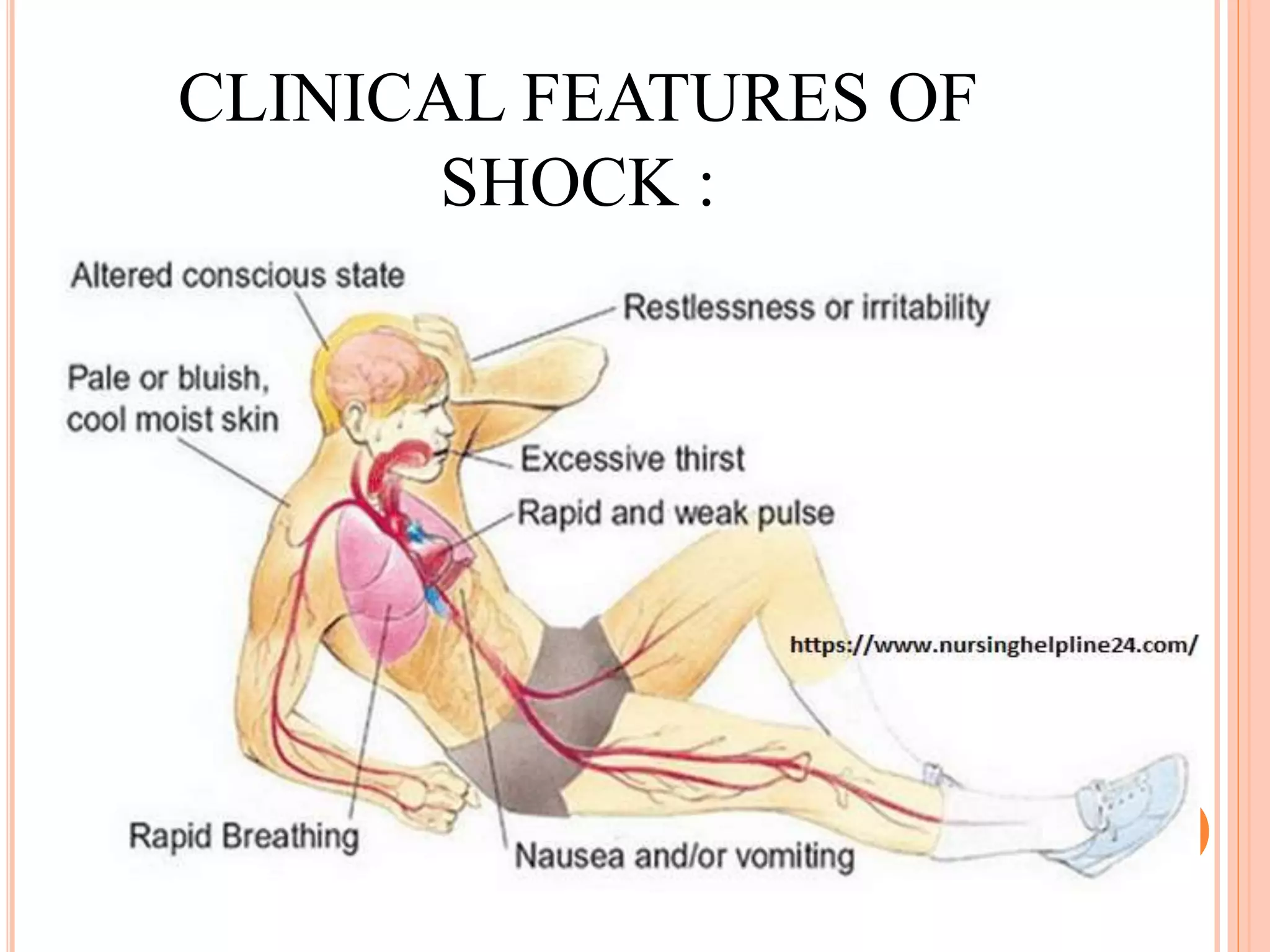
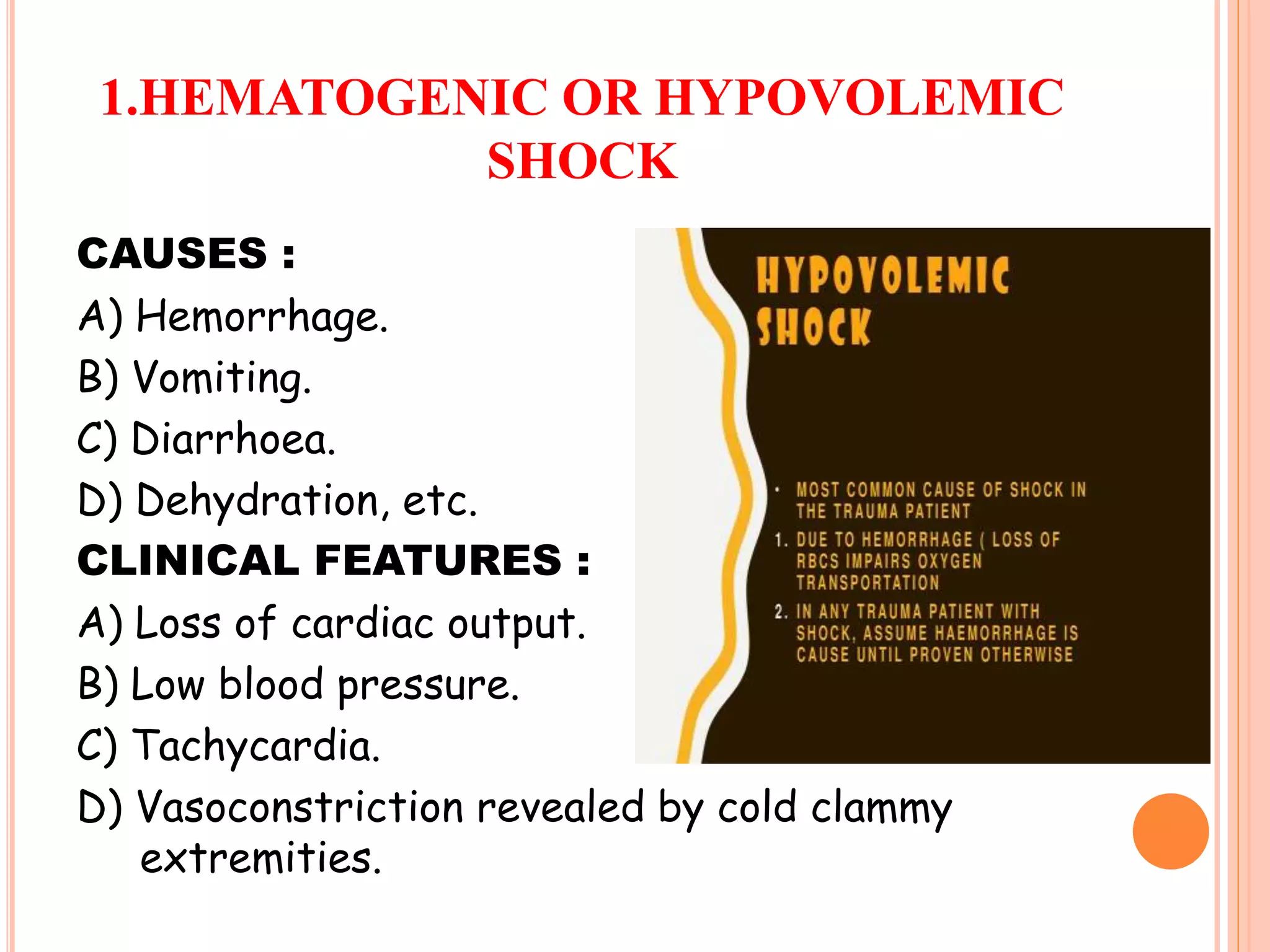
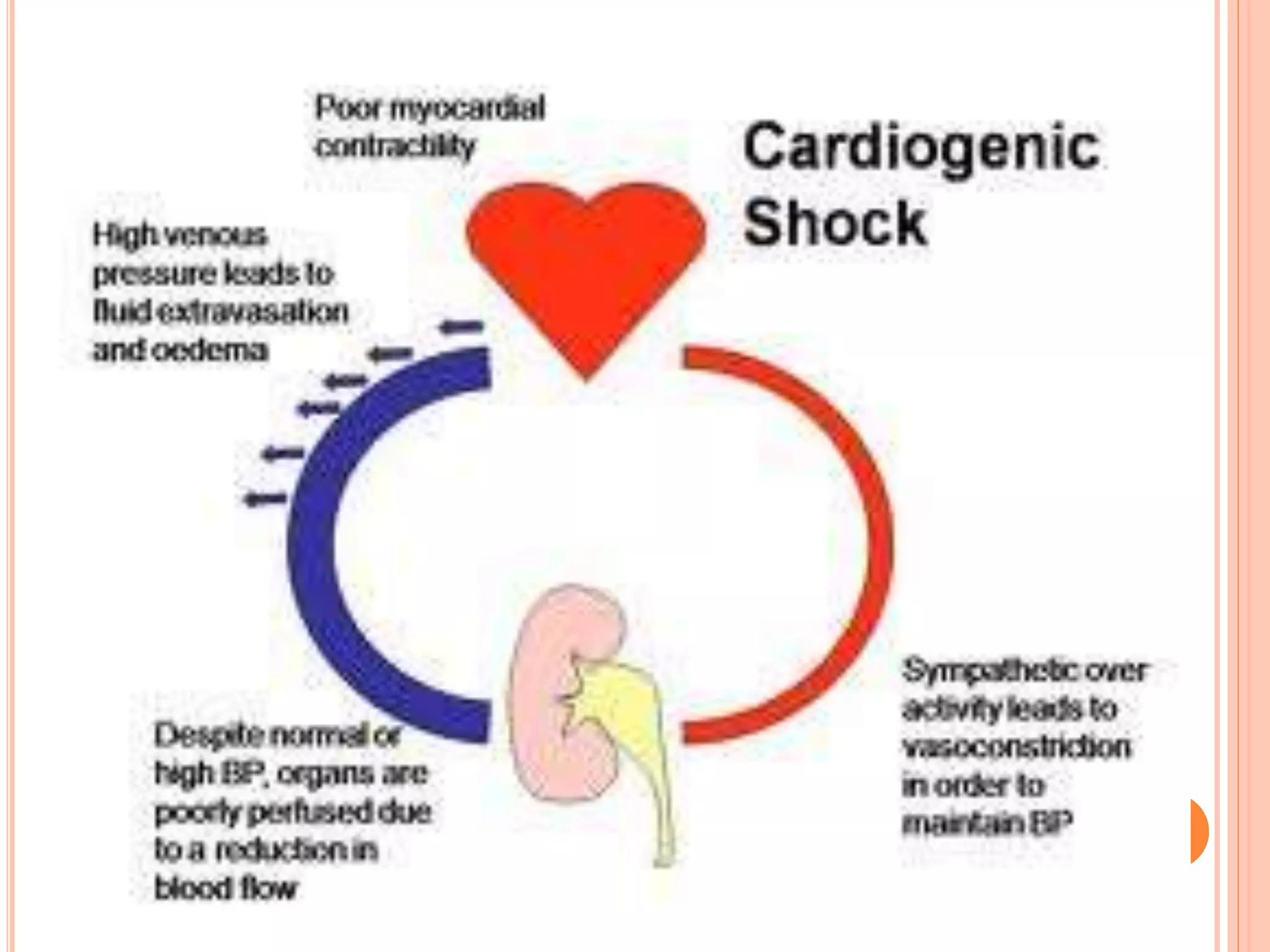
Shock is defined as a state of acute energy failure due to inadequate glucose and oxygen delivery or mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to an inability to meet tissue metabolic needs and remove waste products. There are several types of shock, including hypovolemic, traumatic, neurogenic, cardiogenic, septic, and anaphylactic shock, each with specific causes and clinical features. Common clinical signs include low blood pressure, tachycardia, vasoconstriction, and varying degrees of consciousness loss.