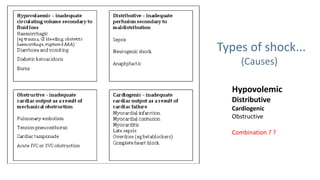
Shock is a pathophysiological state characterized by inadequate oxygen delivery to tissues, leading to organ dysfunction and potentially death. Effective management includes recognizing physiological compromise, identifying causes, resuscitating, and treating underlying issues; early signs and interventions are critical. Types of shock include hypovolemic, distributive, cardiogenic, and obstructive, with treatment strategies varying according to the specific cause and severity.


![Importance of Oxygen delivery
For practical purposes global oxygen delivery can be calculated as:
Cardiac output (HR x SV) x [Hb]g/dl x 10 x 1.34 x Saturation(sO2) ml/l
• ATP is the fuel of body ( energy source in cellular metabolism )
• ATP is produced by glucose metabolism
• Oxygen is needed in this reaction, but limited reaction also possible without oxygen (anerobic)
• Glucose Pyruvate Lactate + CO2
• Limitation of oxygen result in altered cellular activities leading to organ dysfunction
Aerobic >>> Anerobic ( 18 times higher efficacy )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shockmanagement-200904155333/85/Shock-management-3-320.jpg)






![Effect on oxygen delivery Intervention Increase in oxygen delivery
Greatest
Increasing [Hb] from 6g/dl to
9g/dl
50%
Increasing cardiac output by
20% with crystalloid boluses
20%
Increasing oxygen saturation
from 91% to 100% with
supplemental oxygen
10%
Least
Increasing PaO2 from 12kPa to
40kPa with supplemental
oxygen
<1%
Incresing Hb - Blood transfusion – Not more / not less
Increasing Cardiac Output - Crystalloids | Colloids | Inotropes
Increasing oxygen saturation - Supplementary Oxygen | Intubation and Ventilation
GOAL of resuscitation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shockmanagement-200904155333/85/Shock-management-10-320.jpg)

![Role of Inotropes
Exactly which inotrope in which setting is a subject of vigourous ongoing debate
Considered in unresponsive shock for resuscitation
Norepinephrine is considered firstline in Septic shock
Dobutamine increase contractility but vasodilate; worsen the septic or anaphylactic shock if give early.
Useful in cardiogenic shock
Intubation & Ventilation
Early intubation and ventilation may needed
Oxygen consumption can be dramatically reduced by taking over the work of breathing
Need to consider intubation once fluid resuscitation exceeds 40-60 ml/kg in children due to risk of
pulmonary edema
Role of Low dose steroids ??
Initial enthusiasm for low dose steroids in sepsis is now waning
[ exception in adrenal insufficiency (Addisonian crisis) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shockmanagement-200904155333/85/Shock-management-13-320.jpg)
