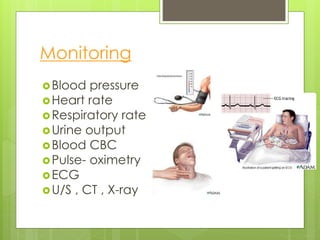
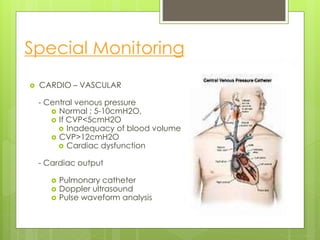
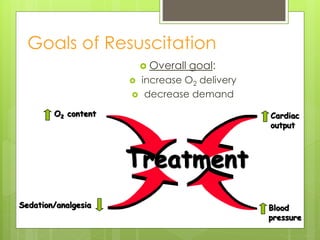
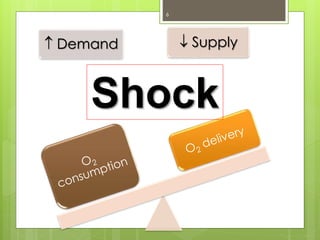
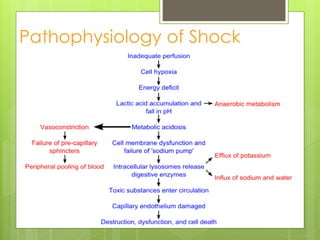
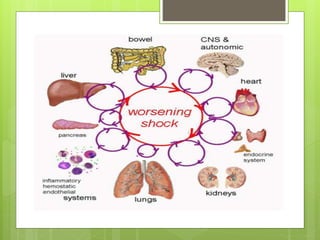
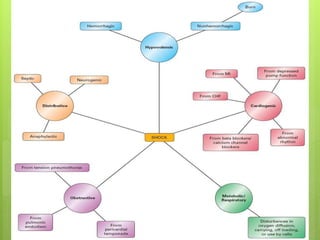
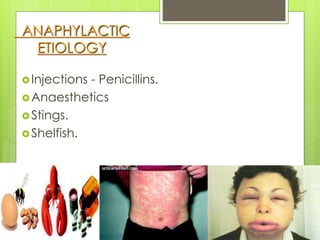
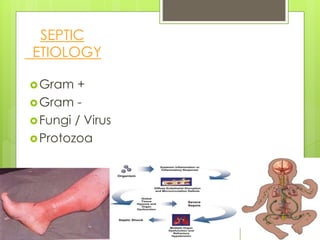
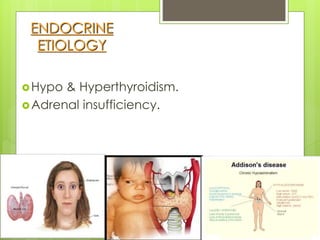
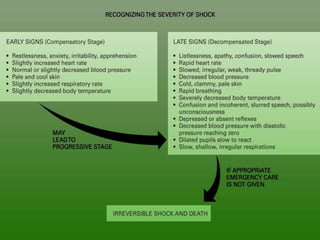
Shock is a condition where circulation fails to meet the metabolic needs of tissues due to inadequate oxygen delivery. There are several types of shock based on etiology, including hypovolemic from blood/fluid loss, cardiogenic from heart failure, obstructive from pulmonary embolism, and septic from infection. Signs of shock range from mild with pale skin to severe with unconsciousness. Treatment focuses on restoring tissue perfusion through fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and inotropes while also treating the underlying cause. The goals of resuscitation are to increase oxygen delivery and decrease oxygen demand through stabilization of vital signs and tissue perfusion markers.
![SHOCK
[ Pathophysiology,Types & Mgt ]
Prof. Utham Murali. M.S; M.B.A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock-types-141009102815-conversion-gate011-230406021816-1cb30507/85/shock-types-141009102815-conversion-gate01-1-pdf-1-320.jpg)









![SHOCK
[ Management ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock-types-141009102815-conversion-gate011-230406021816-1cb30507/85/shock-types-141009102815-conversion-gate01-1-pdf-25-320.jpg)