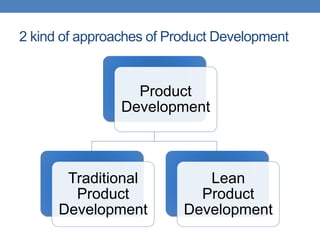
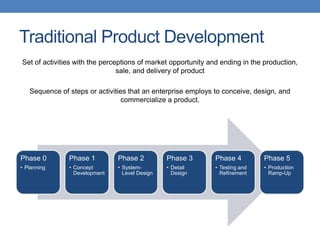
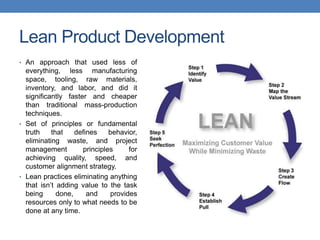
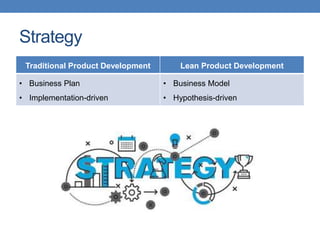
The document outlines two approaches to product development: traditional and lean. Traditional product development follows a linear process from planning to production, while lean product development focuses on efficiency by minimizing resources and eliminating waste. It contrasts strategies, engineering practices, organizational structures, financial reporting, and approaches to failure and speed in both methodologies.