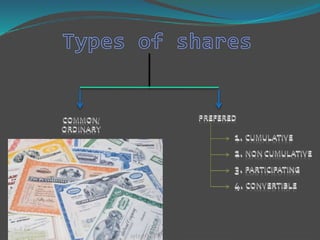
There are two main types of shares - common shares and preferred shares. Common shares give shareholders partial ownership, voting rights, and dividend income from company profits. Preferred shares give ownership but no voting rights, and priority over common shares for recovery of money if the company winds up. Preferred shares may also accumulate unpaid dividends or convert to common shares depending on their specific features. Shares are divided into different classes to provide varying dividend and voting rights to shareholders.