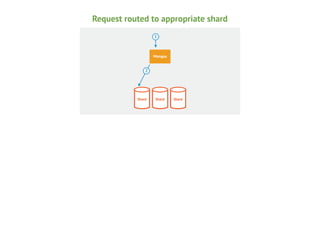
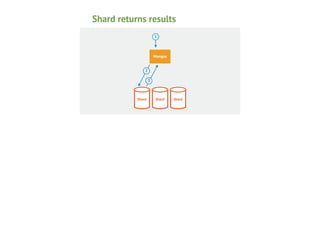
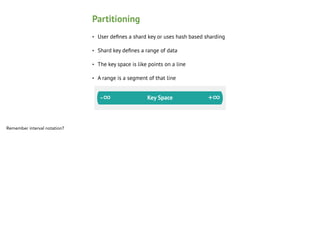
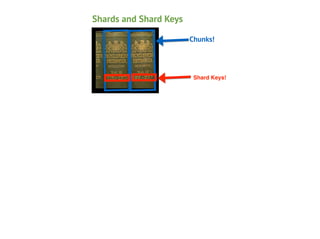
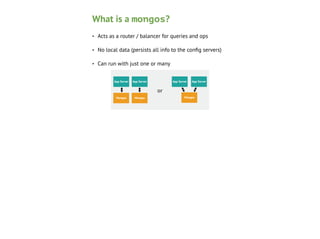
This document provides an overview of MongoDB sharding. It begins with definitions of key terms like shards, chunks, config servers, and mongos. It explains how MongoDB partitions and distributes data across shards. The roles of config servers and mongos routers are outlined. Guidelines for choosing a shard key are presented, emphasizing characteristics like cardinality, write distribution, and query isolation. Best practices for setting up and using MongoDB sharding are also covered.


































![Check that everything is working!
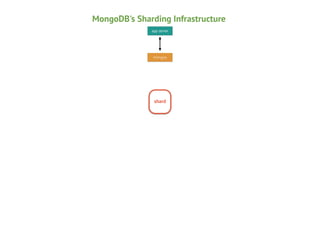
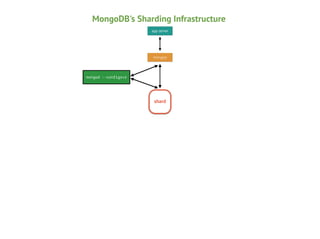
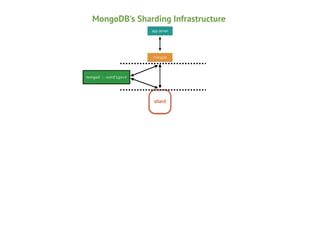
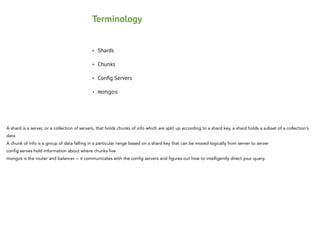
Mongos
Config
Node 1
Secondary
Server
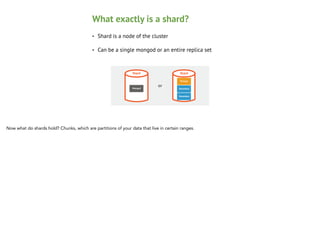
Shard
Mongod
[mongos] admin> db.runCommand({ listshards: 1 })
{
"shards": [
{
"_id": "shard0000",
"host": "cat1.mongodb.com:27018"
}
],
"ok": 1
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/randall-sharding-131207131548-phpapp01/85/Sharding-in-MongoDB-Days-2013-48-320.jpg)